MVVM Architecture
The Model-View-ViewModel pattern
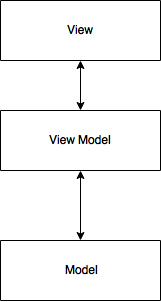
In our app, we follow the MVVM pattern, which decouples the retrieval of data, view logic, and presentation into three distinct areas.
Model
The model provides and stores the internal data.
In our travel app, for simplicity, we use standard data types of Dictionary and Array to represent the data.
In a real application, one would use a custom object to represent the model.
The app implements the following models - Booking which represents a flight reservation - Flight which represents airline details - Airport which represents airport name - Hotel which represents hotel details
In addition, the CouchbaseSession class is used to keep state through multiple pages.
View
In the Travel app, the ContentPage class represents the "view" in MVVM.
It handles user input and forwards requests to the VIew Model.
It updates the UI based on response from the View Model.
The app implements the following Views - LoginPage which represents the login UI - BookmarkedHotelsPage which represents the UI that lists bookmarked hotels - FlightBookingsPage which represents the flight reservations UI - HotelsListPage which represents the UI that lists hotels - HotelDetailsPage which represents the UI that lists hotel details
View Model
The View Model acts as the intermediary between the View and the Model. It is responsible for interacting with the model and updating it’s state to indicate how the view should present itself. There is one view model per view and is named according to the view
-
LoginViewModel
-
BookmarkedHotelsViewModel
-
FlightBookingsViewModel
-
HotelsListViewModel
-
HotelDetailsViewModel