The EXECUTE FUNCTION statement enables you to execute a user-defined function.
Purpose
The EXECUTE FUNCTION statement enables you to execute a user-defined function.
It is useful for testing user-defined functions outside the context of a query.
It also enables you to execute functions which have side effects, such as performing mutations, which is not possible when calling a user-defined function in an expression.
You cannot use the EXECUTE FUNCTION statement to execute a built-in SQL++ function.
If you do this, error 10101: Function not found is generated.
Prerequisites
| To execute … | You must have … |
|---|---|
Global inline functions |
Execute Global Functions role. |
Scoped inline functions |
Execute Scope Functions role, with permissions on the specified bucket and scope. |
Global external functions |
Execute Global External Functions role. |
Scoped external functions |
Execute Scope External Functions role, with permissions on the specified bucket and scope. |
For more details about user roles, see Authorization.
Syntax
execute-function ::= 'EXECUTE' 'FUNCTION' function '(' ( expr ( ',' expr )* )? ')'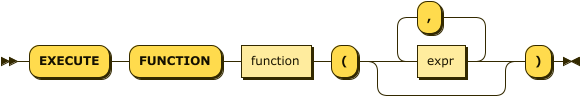
| function | |
| expr |
Function Name
function ::= ( namespace ':' ( bucket '.' scope '.' )? )? identifier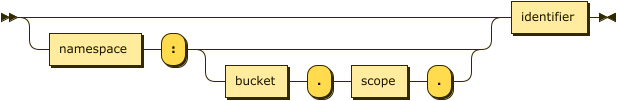
The name of the function.
This is usually an unqualified identifier, such as func1 or `func-1`.
In this case, the path to the function is determined by the current query context.
To execute a global function in a particular namespace, the function name must be a qualified identifier with a namespace, such as default:func1.
Similarly, to execute a scoped function in a particular scope, the function name must be a qualified identifier with the full path to a scope, such as default:`travel-sample`.inventory.func1.
Refer to Global Functions and Scoped Functions for more information.
| The name of a user-defined function is case-sensitive, unlike that of a built-in function. You must execute the user-defined function using the same case that was used when it was created. |
Arguments
[Optional] Comma-separated expressions specify arguments for the function. If the function was created with named parameters, you must supply all the arguments that were specified when the function was created. If the function was created without named parameters, you cannot supply an argument. If the function is variadic, you can supply as many arguments as needed, or none.
Return Value
The function returns one value, of any valid SQL++ type. The result (and the data type of the result) depend on the expression or code that were used to define the function.
If you supply the wrong number of arguments, or arguments with the wrong data type, the possible results differ, depending on whether the function is variadic, or requires a definite number of arguments.
If the function requires a definite number of arguments:
-
If you do not supply enough arguments, the function generates error
10104: Incorrect number of arguments. -
If you supply too many arguments, the function generates error
10104: Incorrect number of arguments. -
If any of the arguments have the wrong data type, the function may return unexpected results, depending on the function expression or code.
If the function is variadic:
-
If you do not supply enough arguments, the function may return unexpected results, depending on the function expression or code.
-
If you supply too many arguments, the extra parameters are ignored.
-
If any of the arguments have the wrong data type, the function may return unexpected results, depending on the function expression or code.
Examples
For examples, refer to CREATE FUNCTION.
Related Links
-
To create user-defined functions, refer to CREATE FUNCTION.
-
To manage user-defined functions in the Query Workbench, see User-Defined Functions UI.
-
To manage external libraries and external functions, see Query Functions REST API.
-
To see the execution plan for a user-defined function, see EXPLAIN FUNCTION.
-
To include a user-defined function in an expression, see User-Defined Functions.
-
To monitor user-defined functions, see Monitor Functions.
-
To drop a user-defined function, see DROP FUNCTION.