The WINDOW clause defines named windows for window functions and aggregate functions used as window functions.
Purpose
Window functions are used to compute an aggregate or cumulative value, based on a group of objects. The objects are not grouped into a single output object — each object remains separate in the query output.
All window functions must have a window definition. This divides the query result set into one or more partitions, and determines the order of objects in those partitions. Within each partition, a movable window frame is defined for every input object. The window frame determines the objects to be used by the window function.
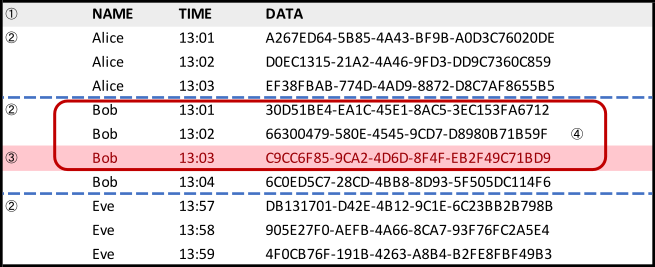
➀ The query result set.
➁ Window partitions — partitioned by name, ordered by time.
➂ The current object.
➃ The window frame — between unbounded preceding and current object.
SQL++ has a dedicated set of window functions. Each window function call includes an OVER clause, which introduces the window specification. Some window functions take additional window options, which are specified by further clauses before the OVER clause.
In Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition, aggregate functions can also be used as window functions when they are used with an OVER clause.
In Couchbase Server 7.0 and later, window functions (and aggregate functions used as window functions) may specify their own inline window definitions, or they may refer to a named window defined by the WINDOW clause elsewhere in the query. By defining a named window with the WINDOW clause, you can reuse the window definition across several functions in the query, potentially making the query easier to write and maintain.
Prerequisites
For you to select data from keyspace or expression, you must have the query_select privilege on that keyspace.
For more details about user roles, see
Authorization.
Syntax
This page gives the syntax of the WINDOW clause. Refer to Aggregate Functions or Window Functions for the details of window function calls.
window-clause ::= 'WINDOW' window-declaration ( ',' window-declaration )*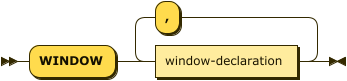
Window Declaration
window-declaration ::= window-name 'AS' '(' window-definition ')'
| window-name | |
| window-definition |
The window declaration assigns a name to the window definition.
Window Definition
window-definition ::= window-ref? window-partition-clause? window-order-clause?
window-frame-clause?
| window-ref | |
| window-partition-clause | |
| window-order-clause | |
| window-frame-clause |
The window definition specifies the partitioning, ordering, and framing for window functions.
Window Reference
window-ref ::= identifier
The window reference enables you to reuse the definition of an existing named window, and extend that definition if necessary. For example, you may refer to an existing named window which specifies partitioning and ordering options, and extend that window definition with additional framing options.
The referenced named window must be within the scope of the current window definition. Furthermore, when one named window refers to another existing named window, the referenced named window must be declared earlier in the current query block.
The following syntax restrictions apply when using a window reference:
-
The current window definition may not include a window partition clause.
-
The current window definition may only include a window order clause if the referenced named window does not specify a window order clause.
-
The referenced named window may not specify a window frame clause.
Window Partition Clause
window-partition-clause ::= 'PARTITION' 'BY' expr ( ',' expr )*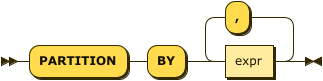
The window partition clause groups the query results into partitions using one or more expressions.
This clause may be used with any window function, or any aggregate functions used as a window function.
This clause is optional. If omitted, all the query results are grouped into single partition.
Window Order Clause
window-order-clause ::= 'ORDER' 'BY' ordering-term ( ',' ordering-term )*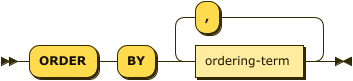
The window order clause determines how objects are ordered within each partition. The window function works on objects in the order specified by this clause.
This clause may be used with any window function, or any aggregate functions used as a window function.
This clause is optional for some functions, and required for others. See the Aggregate Functions page or Window Functions page for details of the syntax of individual functions.
If this clause is omitted, all objects are considered peers, i.e. their order is tied. When objects in the window partition are tied, each window function behaves differently.
-
The ROW_NUMBER() function returns a distinct number for each object. If objects are tied, the results may be unpredictable.
-
The RANK(), DENSE_RANK(), PERCENT_RANK(), and CUME_DIST() functions return the same result for each object.
-
For other functions, if the window frame is defined by
ROWS, the results may be unpredictable. If the window frame is defined byRANGEorGROUPS, the results are same for each object.
This clause may have multiple ordering terms. To reduce the number of ties, add additional ordering terms.
|
This clause does not guarantee the overall order of the query results. To guarantee the order of the final results, use the query ORDER BY clause. |
Ordering Term
ordering-term ::= expr ( 'ASC' | 'DESC' )? ( 'NULLS' ( 'FIRST' | 'LAST' ) )?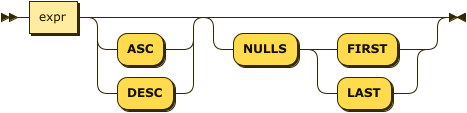
The ordering term specifies an ordering expression, collation, and nulls ordering.
This clause has the same syntax and semantics as the ordering term for queries. Refer to ORDER BY clause for details.
Window Frame Clause
window-frame-clause ::= ( 'ROWS' | 'RANGE' | 'GROUPS' ) window-frame-extent
window-frame-exclusion?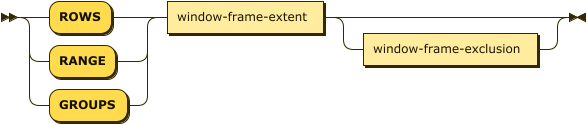
| window-frame-extent | |
| window-frame-exclusion |
The window frame clause defines the window frame.
This clause can be used with all Aggregate Functions and some Window Functions — see the descriptions of individual functions for more details.
This clause is allowed only when the window order clause is present.
This clause is optional.
-
If this clause is omitted and there is no window order clause, the window frame is the entire partition.
-
If this clause is omitted but there is a window order clause, the window frame becomes all objects in the partition preceding the current object and its peers — the same as
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW.
The window frame can be defined in the following ways:
ROWS-
Counts the exact number of objects within the frame. If window ordering doesn’t result in unique ordering, the function may produce unpredictable results. You can add a unique expression or more window ordering expressions to produce unique ordering.
RANGE-
Looks for a value offset within the frame. The function produces deterministic results.
GROUPS-
Counts all groups of tied rows within the frame. The function produces deterministic results.
|
If this clause uses If the ordering term expression does not evaluate to a number, the window frame will be empty, which means the window function will return its default value: in most cases this is NULL, except for COUNT() or COUNTN(), whose default value is 0. This restriction does not apply when the window frame uses |
|
The If you want to use |
Window Frame Extent
window-frame-extent ::= 'UNBOUNDED' 'PRECEDING' | valexpr 'PRECEDING' | 'CURRENT' 'ROW' |
'BETWEEN' ( 'UNBOUNDED' 'PRECEDING' | 'CURRENT' 'ROW' |
valexpr ( 'PRECEDING' | 'FOLLOWING' ) )
'AND' ( 'UNBOUNDED' 'FOLLOWING' | 'CURRENT' 'ROW' |
valexpr ( 'PRECEDING' | 'FOLLOWING' ) )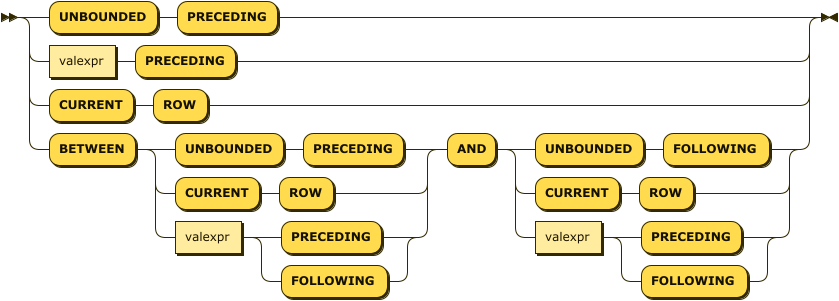
| valexpr |
The |
The window frame extent clause specifies the start point and end point of the window frame.
The expression before AND is the start point and expression after AND is the end point.
If BETWEEN is omitted, you can only specify the start point; the end point becomes CURRENT ROW.
The window frame end point can’t be before the start point. If this clause violates this restriction explicitly, an error will result. If it violates this restriction implicitly, the window frame will be empty, which means the window function will return its default value: in most cases this is NULL, except for COUNT() or COUNTN(), whose default value is 0.
Window frame extents that result in an explicit violation are:
-
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN CURRENT ROW AND valexpr PRECEDING -
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN valexpr FOLLOWING AND valexpr PRECEDING -
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN valexpr FOLLOWING AND CURRENT ROW
Window frame extents that result in an implicit violation are:
-
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND valexpr PRECEDING— ifvalexpris too high, some objects may generate an empty window frame. -
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN valexpr PRECEDING AND valexpr PRECEDING— if the secondvalexpris greater than or equal to the firstvalexpr, all result sets will generate an empty window frame. -
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN valexpr FOLLOWING AND valexpr FOLLOWING— if the firstvalexpris greater than or equal to the secondvalexpr, all result sets will generate an empty window frame. -
( ROWS | RANGE | GROUPS ) BETWEEN valexpr FOLLOWING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING— ifvalexpris too high, some objects may generate an empty window frame. -
If the window frame exclusion clause is present, any window frame specification may result in empty window frame.
Window Frame Exclusion
window-frame-exclusion ::= 'EXCLUDE' ( 'CURRENT' 'ROW' | 'GROUP' | 'TIES' | 'NO' 'OTHERS' )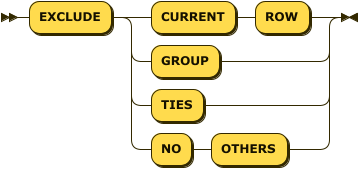
The window frame exclusion clause enables you to exclude specified objects from the window frame.
This clause can be used with all aggregate functions and some window functions — see the descriptions of individual functions for more details.
This clause is allowed only when the window frame clause is present.
This clause is optional.
If this clause is omitted, the default is no exclusion — the same as EXCLUDE NO OTHERS.
EXCLUDE CURRENT ROW-
If the current object is still part of the window frame, it is removed from the window frame.
EXCLUDE GROUP-
The current object and any peers of the current object are removed from the window frame.
EXCLUDE TIES-
Any peers of the current object, but not the current object itself, are removed from the window frame.
EXCLUDE NO OTHERS-
No additional objects are removed from the window frame.
If the current object is already removed from the window frame, then it remains removed from the window frame.
Usage
If present, the WINDOW clause must be included after the GROUP BY, LETTING, and HAVING clauses, and before the ORDER BY clause.
When the WINDOW clause is present, SQL++ rewrites the query by replacing window names with inline window definitions. If a window is declared by the WINDOW clause, but not actually used by any window function or aggregate function in the query, that window definition is ignored and not used for determining the query plan.
Examples
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
For each airline, show each route operated by that airline, including the length of the route, the length of the next-longest route, and the length of the next-shortest route.
SELECT r.airline, r.id, r.distance,
LEAD(r.distance, 1, "No next distance") OVER win AS `next-distance`,
LAG(r.distance, 1, "No previous distance") OVER win AS `previous-distance`
FROM route AS r
WINDOW win AS (
PARTITION BY r.airline
ORDER BY r.distance NULLS LAST
) (1)
LIMIT 7;| 1 | The two window functions in this example share the same window definition, so it makes sense to use a named window. |
[
{
"airline": "2L",
"distance": 770.9691328580009,
"id": 125,
"next-distance": 770.969132858001,
"previous-distance": "No previous distance"
},
{
"airline": "2L",
"distance": 770.969132858001,
"id": 117,
"next-distance": 922.7579695456559,
"previous-distance": 770.9691328580009
},
{
"airline": "2L",
"distance": 922.7579695456559,
"id": 118,
"next-distance": 922.7579695456559,
"previous-distance": 770.969132858001
},
{
"airline": "2L",
"distance": 922.7579695456559,
"id": 126,
"next-distance": "No next distance",
"previous-distance": 922.7579695456559
},
{
"airline": "3F",
"distance": 23.957943869396804,
"id": 274,
"next-distance": 23.957943869396804,
"previous-distance": "No previous distance"
},
{
"airline": "3F",
"distance": 23.957943869396804,
"id": 276,
"next-distance": 26.397914084363418,
"previous-distance": 23.957943869396804
},
{
"airline": "3F",
"distance": 26.397914084363418,
"id": 282,
"next-distance": 26.397914084363418,
"previous-distance": 23.957943869396804
}
]For each destination airport, number all routes in order of distance, and calculate the distance of each route as a fraction of the total distance of all routes.
Compare this example with the examples for RATIO_TO_REPORT() and ROW_NUMBER().
SELECT d.id, d.destinationairport,
RATIO_TO_REPORT(d.distance) OVER win1 AS `distance-ratio`,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER win2 AS `row`
FROM route AS d
WINDOW win1 AS (PARTITION BY d.destinationairport), (1)
win2 AS (win1 ORDER BY d.distance NULLS LAST) (2)
LIMIT 7;| 1 | The two window functions in this example share similar window definitions, so it makes sense to use named windows. |
| 2 | The window named win2 reuses the specification of the existing window win1, and extends the specification with a window order clause.
Note that the definition of win2 must come after the definition of win1. |
[
{
"destinationairport": "AAE",
"distance-ratio": 0.16690466642630636,
"id": 10201,
"row": 1
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAE",
"distance-ratio": 0.22082544177013463,
"id": 10190,
"row": 2
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAE",
"distance-ratio": 0.3033841055547952,
"id": 10240,
"row": 3
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAE",
"distance-ratio": 0.3088857862487639,
"id": 10136,
"row": 4
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAL",
"distance-ratio": 0.07236336293503035,
"id": 14392,
"row": 1
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAL",
"distance-ratio": 0.25521719160354467,
"id": 14867,
"row": 2
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAL",
"distance-ratio": 0.6724194454614251,
"id": 22505,
"row": 3
}
]For each airport, show each route starting at that airport, including the distance of the route, the distance of the shortest route from that airport, and the distance of the longest route from that airport.
Compare this example with the examples for FIRST_VALUE() and LAST_VALUE().
SELECT r.sourceairport, r.destinationairport, r.distance,
FIRST_VALUE(r.distance) OVER win AS `shortest_distance`, (1)
LAST_VALUE(r.distance) OVER (
win ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING (2)
) AS `longest_distance`
FROM route AS r
WINDOW win AS (
PARTITION BY r.sourceairport
ORDER BY r.distance
)
LIMIT 7;| 1 | The two window functions in this example share similar window definitions, so it makes sense to use a named window. |
| 2 | The inline window definition reuses the specification of the existing window win, and extends the specification with a window frame clause.
Note that the inline window definition comes before the definition of win. |
[
{
"destinationairport": "MRS",
"distance": 767.6526005881392,
"longest_distance": 1420.6731433915318,
"shortest_distance": 767.6526005881392,
"sourceairport": "AAE"
},
{
"destinationairport": "LYS",
"distance": 1015.6529968903878,
"longest_distance": 1420.6731433915318,
"shortest_distance": 767.6526005881392,
"sourceairport": "AAE"
},
{
"destinationairport": "ORY",
"distance": 1395.3690007167947,
"longest_distance": 1420.6731433915318,
"shortest_distance": 767.6526005881392,
"sourceairport": "AAE"
},
{
"destinationairport": "CDG",
"distance": 1420.6731433915318,
"longest_distance": 1420.6731433915318,
"shortest_distance": 767.6526005881392,
"sourceairport": "AAE"
},
{
"destinationairport": "AAR",
"distance": 99.89861063028253,
"longest_distance": 928.284226131001,
"shortest_distance": 99.89861063028253,
"sourceairport": "AAL"
},
{
"destinationairport": "OSL",
"distance": 352.33081791745275,
"longest_distance": 928.284226131001,
"shortest_distance": 99.89861063028253,
"sourceairport": "AAL"
},
{
"destinationairport": "LGW",
"distance": 928.284226131001,
"longest_distance": 928.284226131001,
"shortest_distance": 99.89861063028253,
"sourceairport": "AAL"
}
]