Multi-Collection Behavior
Couchbase’s FTS service is the only service that can create indexes that span collections.
Multi-Collection Index: A user can search multi-collection indexes in the same way as that of a bucket-based index. Since a multi-collection index contains data from multiple source collections, it is helpful to know the source collection of every document hit in the search result.
-
Users can see the source collection names in the fields section of each document hit under the key _$c. See the image below for an example.
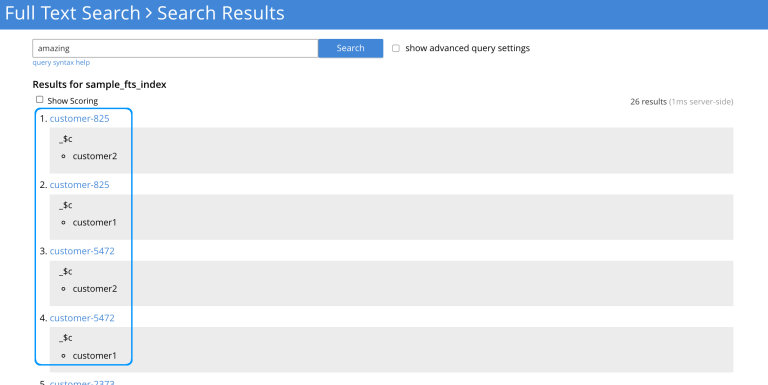
-
Users can also narrow their full-text search requests to only specific Collection(s) within the multi-Collection index. This focus speeds up searches on a large index.
Below is a sample Collection search request for Collections "airport".
Example
curl -XPOST -H “Content-Type:application/json” - u
<username>:<password> http://localhost:8094/api/index/demoindex/query -d
‘{
“explain”: true,
“fields”:[
“*”
],
“highlight”:{},
“query”:{
“query”:”france”
},
“size”:10,
“from”:50,
“collections”:[“airport”]
}’-
At search time, there is no validation to determine whether or not a collection with a given name exists. As a result, users won’t receive any validation errors for the incorrect collection names within the search request. See the below example:
Example
An incorrect collection name “XYZ” is used.
curl -XPOST -H “Content-Type:application/json” - u
<username>:<password> http://localhost:8094/api/index/demoindex/query -d
‘{
“query”:{
“query”:”france”
},
“size”:10,
“from”:50,
“collections”:[“XYZ”]
}’Result:
Result:
{
"status": {
"total": 1,
"failed": 0,
"successful": 1
},
"request": {
"query": {
"query": "france"
},
"size": 10,
"from": 50,
"highlight": null,
"fields": null,
"facets": null,
"explain": false,
"sort": [
"-_score"
],
"includeLocations": false,
"search_after": null,
"search_before": null
},
"hits": [
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21844",
"score": 0.8255329922213157,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21652",
"score": 0.8236828315727989,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_1364",
"score": 0.8232253432142588,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21721",
"score": 0.8225069701742189,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21674",
"score": 0.8218917130827247,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_35854",
"score": 0.8218917094653351,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21847",
"score": 0.8212458150010249,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21849",
"score": 0.8201164200350234,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_21846",
"score": 0.8197896824791812,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
},
{
"index": "demoindex_6dbcc808a8278714_4c1c5584",
"id": "hotel_20421",
"score": 0.8191068922164917,
"sort": [
"_score"
],
"fields": {
"_$c": "hotel"
}
}
],
"total_hits": 141,
"max_score": 1.0743017811485551,
"took": 999962,
"facets": null
}Impact of using Role-Based Access Control
The Couchbase Full Admin can administer Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) roles for full-text search indexes at a Bucket, Scope, or Collection(s) level.
FTS provides two primary roles for managing the access control:
A user must have at least search reader permissions at the source Bucket or Scope or Collection level to access the FTS index.
| With multi-collection indexes, the user must have search reader roles for all source collections in order to access a multi-collection index. |