Comparison Operators
- reference
Comparison operators enable you to compare expressions.
The following tables describe each comparison operator and its return values.
Relational Operators
relational-expr ::= expr '=' expr |
expr '==' expr |
expr '!=' expr |
expr '<>' expr |
expr '>' expr |
expr '>=' expr |
expr '<' expr |
expr '<=' expr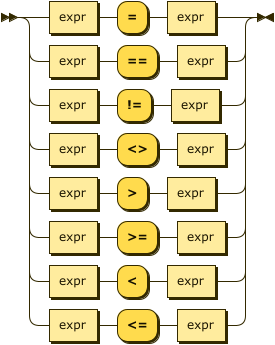
| Operator | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|
= |
Equal to. Functionally equivalent to == for compatibility with other languages. |
TRUE or FALSE |
== |
Equal to. Functionally equivalent to = for compatibility with other languages. |
TRUE or FALSE |
!= |
Not equal to. Functionally equivalent to <> for compatibility with other languages. |
TRUE or FALSE |
<> |
Not equal to. Functionally equivalent to != for compatibility with other languages. |
TRUE or FALSE |
> |
Greater than. |
TRUE or FALSE |
>= |
Greater than or equal to. |
TRUE or FALSE |
< |
Less than. |
TRUE or FALSE |
<= |
Less than or equal to. |
TRUE or FALSE |
BETWEEN
between-expr ::= expr 'NOT'? 'BETWEEN' start-expr 'AND' end-expr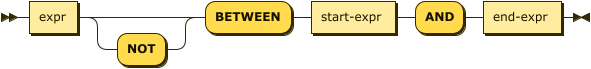
| Operator | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|
BETWEEN |
Search criteria for a query where the value is between two values, including the end values specified in the range. Values can be numbers, text, or dates. |
TRUE or FALSE |
NOT BETWEEN |
Search criteria for a query where the value is outside the range of two values, including the end values specified in the range. Values can be numbers, text, or dates. |
TRUE or FALSE |
LIKE
like-expr ::= expr 'NOT'? 'LIKE' expr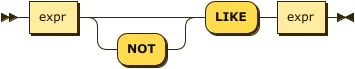
| Operator | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|
LIKE |
Matches a string against a pattern. Returns TRUE if they match. The pattern can include regular characters and the following wildcards:
To match a literal wildcard character, use an escape character.
The default escape character is the backslash ( To define a custom escape character, use the To match the escape character itself, escape it with another escape character (for example, An empty pattern matches only an empty string.
To match any string, including an empty string, use |
TRUE or FALSE |
NOT LIKE |
Inverse of LIKE. Returns TRUE if the string does not match the given pattern. |
TRUE or FALSE |
Examples
SELECT "hello world" LIKE "h_llo%" AS match_1,
"hello world" NOT LIKE "h_llo%" AS match_2,
"hello world" LIKE "h%world" AS match_3,
"hello world" LIKE "h%z%" AS match_4,
"hello% world" LIKE "hello#% world" ESCAPE "#" AS match_5;[
{
"match_1": true,
"match_2": false,
"match_3": true,
"match_4": false,
"match_5": true
}
]IS
The IS family of operators lets you specify conditions based on the existence (or absence) of attributes in a data set.
is-expr ::= expr 'IS' 'NOT'? 'NULL' |
expr 'IS' 'NOT'? 'MISSING' |
expr 'IS' 'NOT'? 'VALUED' |
expr 'IS' 'NOT'? 'UNKNOWN'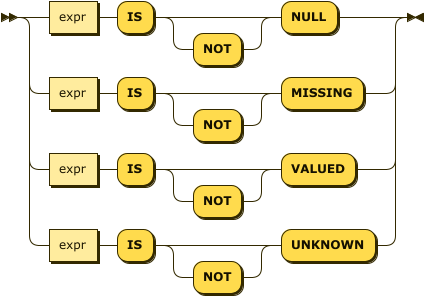
| Operator | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|
IS NULL |
Field has value of NULL. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS NOT NULL |
Field has value or is missing. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS MISSING |
No value for field found. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS NOT MISSING |
Value for field found or value is NULL. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS VALUED |
Value for field found. Value is neither missing nor NULL. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS NOT VALUED |
Value for field not found. Value is NULL. |
TRUE or FALSE |
IS UNKNOWN |
Value for field is unknown, NULL, or missing. |
TRUE OR FALSE |
IS NOT UNKNOWN |
Value for field is known. Value is neither NULL nor missing. |
TRUE OR FALSE |
SELECT fname, children
FROM tutorial
WHERE children IS NULL{
"results": [
{
"children": null,
"fname": "Fred"
}
]
} SELECT fname, children
FROM tutorial
WHERE children IS MISSING {
"results": [
{
"fname": "Harry"
},
{
"fname": "Jane"
}
]
}SELECT NULL IS UNKNOWN,
NULL IS NOT UNKNOWN,
missing IS UNKNOWN,
missing IS NOT UNKNOWN,
"Harry" IS UNKNOWN,
"Harry" IS NOT UNKNOWN{
"results": [
{
"$1": true,
"$2": false,
"$3": true,
"$4": false,
"$5": false,
"$6": true
}
]
}Comparison of Data Types
Strings
String comparison is done using a raw-byte collation of UTF-8 encoded strings — sometimes referred to as binary, C, or memcmp. This collation is case sensitive. Case-insensitive comparisons can be performed using the UPPER() or LOWER() functions. See String Functions for more information.
Arrays and Objects
Arrays are compared element-wise. Objects are first compared by length; objects of equal length are compared pairwise, with the pairs sorted by name.
NULL and MISSING
Except when using the IS family of operators, comparison of the MISSING or NULL data types produces the following results.
-
If either operand in a comparison is MISSING, the result is MISSING.
-
If either operand in a comparison is NULL, the result is NULL.
-
If either operand is MISSING or NULL, the result is MISSING or NULL.