ALTER VECTOR INDEX
- Capella Operational
- Couchbase Server 8.0
The ALTER VECTOR INDEX statement increases or decreases the number of index replicas and partition replicas.
The ALTER INDEX statement is a synonym for the ALTER VECTOR INDEX statement. Both statements have the same functionality.
Purpose
You can use the ALTER VECTOR INDEX statement to increase or decrease the number of replicas, or to drop a specified index replica temporarily.
You can also use it to perform the same alterations to a partitioned index and any replica partitions.
You may use this statement when you encounter any of the following situations:
-
An imbalance occurs due to a particular index growing faster than expected, and a replica is needed on a different node.
-
An imbalance occurs due to a cluster of indexes being dropped on a single node.
-
A node is scheduled for removal, and its index replicas need to be dropped.
-
The automated process of rebalancing does not give the expected results.
-
Other types of scaling up or scaling down are needed.
If a node goes down while an ALTER VECTOR INDEX operation is happening, then the index would rollback to its original node (not affecting queries) and a notification would appear.
Prerequisites
Only users with the RBAC role of Administrator are allowed to run the ALTER VECTOR INDEX directive.
Syntax
alter-vector-index ::= 'ALTER' 'VECTOR' 'INDEX' ( index-path '.' index-name |
index-name 'ON' keyspace-ref ) index-using? index-with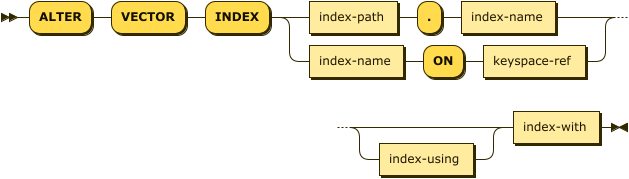
The ALTER VECTOR INDEX statement provides 2 possible syntaxes for specifying the index and the keyspace where the index is located.
| index-name |
(Required) A unique name that identifies the index. |
| index-path |
(Optional) One possible syntax for specifying the keyspace. See Index Path. |
| keyspace-ref |
(Optional) The other possible syntax for specifying the keyspace. See Index Name ON Keyspace Reference. |
| index-using |
(Optional) Specifies the index type. See USING Clause. |
| index-with |
(Required) Specifies options for the index. See WITH Clause. |
Index Path
index-path ::= keyspace-full | keyspace-prefix | keyspace-partial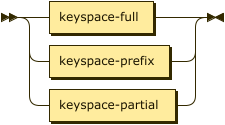
You can use a dotted notation to specify the index and the keyspace on which the index is built. This syntax provides compatibility with legacy versions of Couchbase Server. The index path may be a full keyspace path, a keyspace prefix, or a keyspace partial.
| If there is a hyphen (-) inside the index name or any part of the index path, you must wrap the index name or that part of the index path in backticks (` `). See the examples on this page. |
Index Path: Full Keyspace
keyspace-full ::= namespace ':' bucket '.' scope '.' collection
If the index is built on a named collection, the index path may be a full keyspace path, including namespace, bucket, scope, and collection, followed by the index name. In this case, the query context is ignored.
| namespace |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
| scope |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the scope name of the keyspace. |
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, default:`travel-sample`.inventory.airline.`idx-name` indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection in the inventory scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Index Path: Keyspace Prefix
keyspace-prefix ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket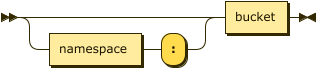
If the index is built on the default collection in the default scope within a bucket, the index path may be just an optional namespace and the bucket name, followed by the index name. In this case, the query context should not be set.
| namespace |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
For example, default:`travel-sample`.def_type indicates the def_type index on the default collection in the default scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Index Path: Keyspace Partial
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Alternatively, if the keyspace is a named collection, the index path may be just the collection name, followed by the index name. In this case, you must set the query context to indicate the required namespace, bucket, and scope.
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, airline.`idx-name` indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection, assuming that the query context is set.
Index Name ON Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
You can use the index name with the ON keyword and a keyspace reference to specify the keyspace on which the index is built.
The keyspace reference may be a keyspace path or a keyspace partial.
| If there is a hyphen (-) inside the index name or any part of the keyspace reference, you must wrap the index name or that part of the keyspace reference in backticks (` `). See the examples on this page. |
Keyspace Reference: Keyspace Path
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?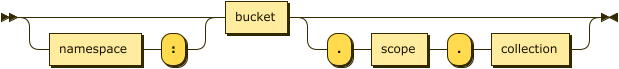
If the keyspace is a named collection, or the default collection in the default scope within a bucket, the keyspace reference may be a keyspace path. In this case, the query context should not be set.
| namespace |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
| scope |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the scope name of the keyspace. If omitted, the bucket’s default scope is used. |
| collection |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. If omitted, the default collection in the bucket’s default scope is used. |
For example, def_type ON default:`travel-sample` indicates the def_type index on the default collection in the default scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Similarly, `idx-name` ON default:`travel-sample`.inventory.airline indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection in the inventory scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Keyspace Reference: Keyspace Partial
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Alternatively, if the keyspace is a named collection, the keyspace reference may be just the collection name. In this case, you must set the query context to indicate the required namespace, bucket, and scope.
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, `idx-name` ON airline indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection, assuming the query context is set.
USING Clause
index-using ::= 'USING' 'GSI'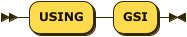
The index type for a secondary index must be Global Secondary Index (GSI).
The USING GSI keywords are optional and may be omitted.
WITH Clause
index-with ::= 'WITH' expr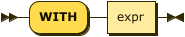
Use the WITH clause to specify additional options.
| expr |
An object with the following properties. |
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
action |
A string denoting the operation to be performed. The possible values are:
|
enum (move, replica_count, drop_replica) |
num_replica |
Required if An integer specifying the number of replicas of the index. The index service will automatically distribute these indexes amongst the index nodes in the cluster for load balancing and high availability purposes. The index service attempts to distribute the replicas based on the server groups in use in the cluster where possible. (In Couchbase Capella, you cannot restrict the placement of index replicas to specified nodes.) |
Integer |
nodes |
You cannot use this property in Couchbase Capella, as it defaults to file-based index rebalancing. |
String array |
replicaId |
Required if An integer, specifying a replica ID. |
Integer |
Usage
If you attempt to alter an index which is still scheduled for background creation, the request fails.
The statement will not work while the cluster is undergoing a rebalance.
Moving an Index or Index Replicas
You cannot use this statement to move indexes or index replicas in Couchbase Capella, as it defaults to file-based index rebalancing.
Likewise, you cannot use this statement to repartition an index across a different number of nodes.
Changing the Replica Count
When changing the number of replicas, the specified number of replicas must be less than the number of index nodes available for placement. If the specified number of replicas is greater than or equal to the number of index nodes available for placement, then the operation will fail.
In Couchbase Capella, you cannot restrict the placement of index replicas to specified nodes.
When increasing the number of replicas, no single index node will host more than 1 replica of the same index, or the same partition of the same index. Replicas are distributed across the available server groups.
When reducing the number of replicas, the index service will first drop unhealthy replicas, where an unhealthy replica is a replica with missing partitions. After all unhealthy replicas are dropped, the index service will if necessary drop replicas with the highest replica ID. An unhealthy replica may not have the highest replica ID, so after an index reduction there may be gaps in the sequence of replica IDs — for example, 1, 2, 4, where replica ID 3 was dropped.
Dropping a Specific Replica
When dropping a replica, the index topology does not change. The indexing service remembers the number of partitions and replicas specified for this index. Given sufficient capacity, the dropped replica is rebuilt after the next rebalance — although it may be placed on a different index node, depending on the resource usage statistics of the available nodes.
To find the ID of an index replica and see which node it’s placed on, you can use the Indexes page in the Couchbase Capella UI or query the system:indexes catalog.
When dropping a replica, it’s possible to leave a server group with no replica. For a partitioned index, run a rebalance to move a replica into the vacant server group.
Index Redistribution
Couchbase Capella redistributes indexes automatically on rebalance. For more information, see Rebalance.
Return Value
If the statement succeeds, then:
-
The query returns an empty array.
-
The index alteration is visible in the Indexes tab.
-
After the alteration is complete, the new indexes begin to service query scans.
If the statement fails, then:
-
The original indexes continue to service query scans.
-
The UI Log and Query tab have the appropriate error message.
-
Some common errors include:
Error Message Possible Cause GSI index xxxxxxxx not found-
Mistyped an index name
move index is disabled-
Attempted to move a replica
"nodes" clause is disabled with alter index as file based rebalance (shard affinity) is enabled-
Attempted to restrict replicas to specified nodes when altering the number of replicas
syntax error - at \",\"-
Missed a double-quote mark (
")
Fail to alter index: Fail to drop replica-
Replica does not exist or was mistyped
Unsupported action value-
Mistyped the
"action"
-
Examples
To try the examples in this section, you must do the following:
-
Create a cluster of 3 nodes. The examples in this section assume that the 3 nodes have the names
svc-dqi-node-001,svc-dqi-node-002, andsvc-dqi-node-003. The nodes in your cluster may have different names or IP addresses. -
Install the
color-vector-sampledata as described in Prerequisites. -
Set the query context to the
colorscope in thecolor-vector-sampledataset. For more information, see Query Context.
Create a Hyperscale Vector index on node svc-dqi-node-001 with a replica on node svc-dqi-node-002, then increase the number of replicas to 2.
New replicas may be placed on any available index nodes in the cluster.
CREATE VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_multi
ON rgb(embedding_vector_dot VECTOR)
WITH {"dimension": 1536,
"similarity": "L2",
"description": "IVF8,SQ4",
"nodes": ["svc-dqi-node-001:18091",
"svc-dqi-node-002:18091"]};
ALTER VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_multi ON rgb
WITH {"action": "replica_count", "num_replica": 2};Create a Hyperscale Vector index on node svc-dqi-node-001 with replicas on nodes svc-dqi-node-002 and svc-dqi-node-003, then decrease the number of replicas to 1.
CREATE VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_decrease
ON rgb(embedding_vector_dot VECTOR)
WITH {"dimension": 1536,
"similarity": "L2",
"description": "IVF8,SQ4",
"nodes": ["svc-dqi-node-001:18091",
"svc-dqi-node-002:18091",
"svc-dqi-node-003:18091"]};
ALTER VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_decrease ON rgb
WITH {"action": "replica_count", "num_replica": 1};Create a Hyperscale Vector index with 2 replicas, and specify that nodes svc-dqi-node-001, svc-dqi-node-002, and svc-dqi-node-003 should be available for index and replica placement.
Then delete replica 2.
CREATE VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_drop
ON rgb(embedding_vector_dot VECTOR)
WITH {"dimension": 1536,
"similarity": "L2",
"description": "IVF8,SQ4",
"num_replica": 2,
"nodes": ["svc-dqi-node-001:18091",
"svc-dqi-node-002:18091",
"svc-dqi-node-003:18091"]};
ALTER VECTOR INDEX hyperscale_rep_drop ON rgb
WITH {"action": "drop_replica", "replicaId": 2};