Sample Application
- tutorial
Discover how to program interactions with the Couchbase Server via the data, Query, and search services — using the Travel Sample Application with the built-in Travel Sample data Bucket. Discover how to program interactions with Couchbase Server 7.X via the Data, Query, and Search services — using the Travel Sample Application with the built-in Travel Sample data Bucket.
Quick Start
Fetch the Couchbase Go SDK travel-sample Application REST Backend from github:
git clone https://github.com/couchbaselabs/try-cb-golang.git
cd try-cb-golangWith Docker installed, you should now be able to run a bare-bones copy of Couchbase Server, load the travel-sample, add indexes, install the sample-application and its frontend, all by running a single command:
docker-compose --profile local upRunning the code against your own development Couchbase server.
For Couchbase Server 7.2, make sure that you have at least one node each of data; query; index; and search. For a development box, mixing more than one of these on a single node (given enough memory resources) is perfectly acceptable.
If you have yet to install Couchbase Server in your development environment start here.
Then load up the Travel Sample Bucket, using either the Web interface or the command line. You will also need to create a Search Index — Query indexes are taken care of by the Sample Bucket.
See the README at https://github.com/couchbaselabs/try-cb-golang for full details of how to run and tweak the Go SDK travel-sample app.
Using the Sample App
Give yourself a username and password and click Register.
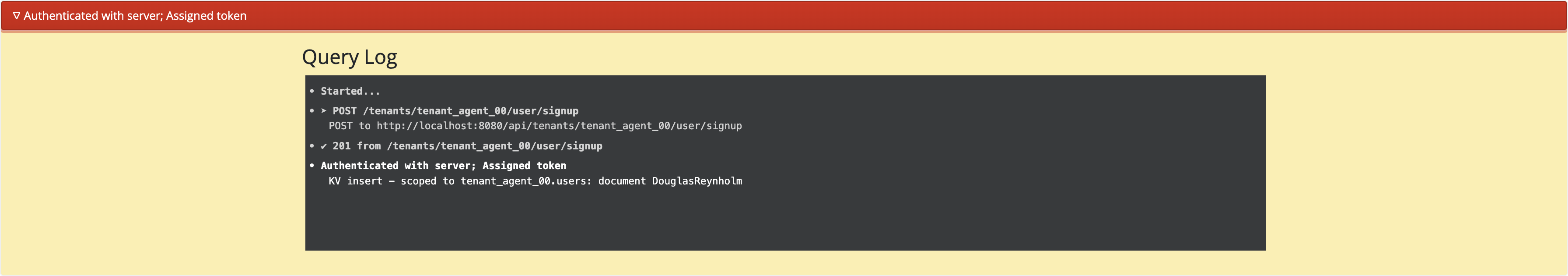
You can now try out searching for flights, booking flights, and searching for hotels. You can see which Couchbase SDK operations are being executed by clicking the red bar at the bottom of the screen:
Sample App Backend
The backend code shows Couchbase Go SDK in action with Query and Search, but also how to plug together all of the elements and build an application with Couchbase Server and the Go SDK.
Here’s the Search code, where AirportSearch checks to see whether the search term is a three or four letter FAA or ICAO abbreviation, and if not searches for it as an airport name:
func AirportSearch(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
var respData jsonAirportSearchResp
searchKey := req.FormValue("search")
var queryStr string
if len(searchKey) == 3 {
queryStr = fmt.Sprintf("SELECT airportname FROM `travel-sample` WHERE faa='%s'", strings.ToUpper(searchKey))
} else if len(searchKey) == 4 && searchKey == strings.ToUpper(searchKey) {
queryStr = fmt.Sprintf("SELECT airportname FROM `travel-sample` WHERE icao ='%s'", searchKey)
} else {
queryStr = fmt.Sprintf("SELECT airportname FROM `travel-sample` WHERE airportname like '%s%%'", searchKey)
}
respData.Context.Add(queryStr)
rows, err := globalCluster.Query(queryStr, nil)
if err != nil {
writeJsonFailure(w, 500, err)
return
}
respData.Data = []jsonAirport{}
var airport jsonAirport
for rows.Next(&airport) {
respData.Data = append(respData.Data, airport)
airport = jsonAirport{}
}
encodeRespOrFail(w, respData)
}The main.go file also contains the functions for handling users, registration, and SQL++ (formerly N1QL) queries.
Data Model
See the Travel App Data Model reference page for more information about the sample data set used.