SQL++ for Query Reference
- reference
This reference guide describes the syntax and structure of SQL++ for Query. It provides information about the basic elements which can be combined to build SQL++ statements. The Couchbase implementation of SQL++ was formerly known as N1QL.
The SQL++ language is composed of statements, expressions, and comments.
Statements
SQL++ statements are categorized into the following groups:
-
Data Definition Language (DDL) statements enable you to create and modify database objects, such as users, keyspaces, and indexes.
-
Data Control Language (DCL) statements enable you to control which users or groups have access to data, and what they are permitted to do with that data.
-
Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements enable you to create, read, update, and delete data. Some DML statements may be further subcategorized as data query language, transaction control language, or utility statements.
For more details, see Statements.
Expressions
The following are the different types of SQL++ expressions:
Nested Path Expressions
In SQL++, nested paths indicate an expression to access nested sub-documents within a JSON document or expression.
For example, in the document below, the latitude of an airport is stored within the geo sub-document, and can be addressed using the nested path geo.lat:
[
{
"airportname": "Calais Dunkerque",
"city": "Calais",
"geo": {
"alt": 12,
"lat": 50.962097,
"lon": 1.954764
},
"latitude": 51,
// ...
}
]You can use nested operators to access sub-document fields within a document.
Comments
SQL++ supports block comments and line comments.
Block Comments
block-comment ::= '/*' ( text | newline )* '*/'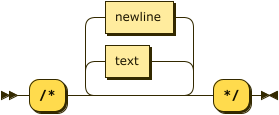
A block comment starts with /* and ends with */.
The query engine ignores the start and end markers /* */, and any text between them.
A block comment may start on a new line, or in the middle of a line after other SQL++ statements. A block comment may contain line breaks.
There may also be further SQL++ statements on the same line after the end of a block comment — the query engine does not ignore these.
Line Comments
line-comment ::= '--' text?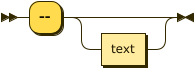
You can use line comments in Couchbase Server 6.5 and later.
A line comment starts with two hyphens --.
The query engine ignores the two hyphens, and any text following them up to the end of the line.
A line comment may start on a new line, or in the middle of a line after other SQL++ statements. A line comment may not contain line breaks.
Optimizer Hints
You can supply hints to the optimizer within a specially-formatted hint comment. For further details, refer to Optimizer Hints.