Negative Keyspace Hints
- reference
- Couchbase Server 8.0
Negative hints direct the optimizer not to use certain indexes or join methods.
A negative hint is a type of optimizer hint that applies to a specific keyspace. Unlike positive keyspace hints, which direct the optimizer to use specific indexes or join methods, negative hints instruct it what not to use.
Negative hints are of two types: index hints and join hints. Index hints direct optimizer not to use specific indexes, and join hints direct it not to use specific join methods.
For each negative hint, you must specify the keyspace or keyspaces that the hint applies to. If a keyspace is given an explicit alias in the query, then the hint must refer to the explicit alias, not the keyspace name. This is to avoid confusion in situations where the same keyspace can be used multiple times (with different aliases) in the same query.
If the keyspace is not given an explicit alias in the query, the hint must refer to the keyspace using the keyspace name. (If the keyspace name is a dotted path, the hint must refer to the keyspace using its implicit alias, which is the last component in the keyspace path.)
Negative hints support two prefixes: NO_ and AVOID_.
You can specify them using either simple syntax or JSON syntax, but you cannot mix the two in the same hint comment.
NO_INDEX
This hint is the negative equivalent of the INDEX hint. It directs the optimizer not to use a specific secondary index for a keyspace. You can add one or more secondary indexes in the hint. If you do not specify this hint, the optimizer selects the optimal available index.
Simple Syntax
no-gsi-hint-simple ::= ( 'NO_INDEX' | 'AVOID_INDEX' ) '(' keyspace index* ')'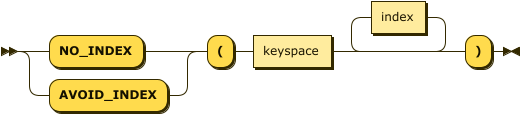
With the simple syntax, this hint specifies a single keyspace expression along with zero, one, or more indexes to avoid.
You can either use NO_INDEX or AVOID_INDEX as the hint keyword.
You can also use this hint multiple times within a hint comment to apply it to more than one keyspace.
| For this hint to work effectively, you must specify at least one index. The optimizer ignores the hint if you do not specify any indexes. |
JSON Syntax
no-gsi-hint-json ::= ( '"no_index"' | '"avoid_index"' ) ':' ( index-array | index-object )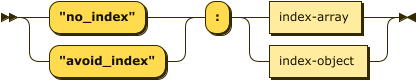
With the JSON syntax, this hint takes the form of a no_index or avoid_index property.
You can only use this property once within a hint comment.
The value of this property can be an Index Array or an Index Object.
Index Array
index-array ::= '[' index-object ( ',' index-object )* ']'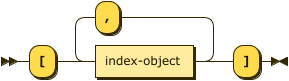
Use this array to specify indexes for multiple keyspaces. Each element must be an Index Object.
Index Object
index-object ::= '{' keyspace-property ',' indexes-property '}'
Use this object to specify indexes for a single keyspace. It must contain a Keyspace Property and an Indexes Property. The order of the properties within the object is not significant.
Keyspace Property
keyspace-property ::= ( '"keyspace"' | '"alias"' ) ':' '"' keyspace '"'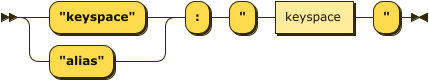
Synonym for "keyspace": "alias"
The value of this property is the keyspace or alias to which this hint applies.
Indexes Property
indexes-property ::= '"indexes"' ':' ( 'null'
| '"' index '"'
| '[' '"' index '"' ( ',' '"' index '"' )* ']' )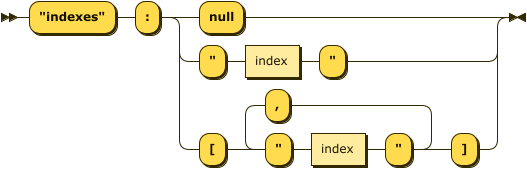
The value of this property can be:
| null |
The optimizer ignores the hint when the value is |
| An index string |
A secondary index that the optimizer must not use for the given keyspace. |
| An array of index strings |
An array of secondary indexes that the optimizer must not use for the given keyspace. |
Examples
For the examples in this section, it’s assumed that the cost-based optimizer is active, and all optimizer statistics are up-to-date.
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
The following query does not include an index hint.
SELECT id
FROM route
WHERE sourceairport = "SFO"
LIMIT 1;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the optimizer has selected the index def_inventory_route_sourceairport, which is installed with the travel sample dataset.
{
"#operator": "IndexScan3",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"index": "def_inventory_route_sourceairport",The following query hints the optimizer to avoid using the index def_inventory_route_sourceairport for the keyspace route.
SELECT /*+ NO_INDEX (route def_inventory_route_sourceairport) */ id
FROM route
WHERE sourceairport = "SFO"
LIMIT 1;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the query omits the specified index, forcing the optimizer to consider other available indexes.
"scan": {
"#operator": "IndexScan3",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"index": "def_inventory_route_route_src_dst_day",NO_INDEX_FTS
This hint is the negative equivalent of the INDEX_FTS hint. It directs the optimizer not to use a specific full-text index for a keyspace. You can add one or more full-text indexes in the hint. If you do not specify this hint, the optimizer selects the optimal available index.
Simple Syntax
no-fts-hint-simple ::= ( 'NO_INDEX_FTS' | 'AVOID_INDEX_FTS' ) '(' keyspace index* ')'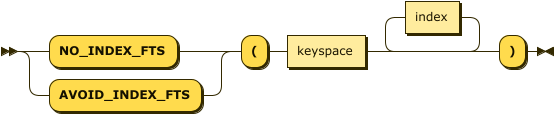
With the simple syntax, this hint specifies a single keyspace expression along with zero, one, or more indexes.
You can either use NO_INDEX_FTS or AVOID_INDEX_FTS as the hint keyword.
You can also use this hint multiple times within a hint comment to apply it to more than one keyspace.
| For this hint to work effectively, you must specify at least one index. The optimizer ignores the hint if you do not specify any indexes. |
JSON Syntax
no-gsi-hint-json ::= ( '"no_index"' | '"avoid_index"' ) ':' ( index-array | index-object )
With the JSON syntax, this hint takes the form of a no_index_fts or avoid_index_fts property.
You can only use this property once within the hint comment.
The value of this property can be an Index Array or an Index Object.
Index Array
index-array ::= '[' index-object ( ',' index-object )* ']'
Use this array to specify indexes for multiple keyspaces. Each element must be an Index Object.
Index Object
index-object ::= '{' keyspace-property ',' indexes-property '}'
Use this object to specify indexes for a single keyspace. It must contain a Keyspace Property and an Indexes Property. The order of the properties within the object is not significant.
Keyspace Property
keyspace-property ::= ( '"keyspace"' | '"alias"' ) ':' '"' keyspace '"'
Synonym for "keyspace": "alias"
The value of this property is the keyspace or alias to which this hint applies.
Indexes Property
indexes-property ::= '"indexes"' ':' ( 'null'
| '"' index '"'
| '[' '"' index '"' ( ',' '"' index '"' )* ']' )
The value of this property can be:
| null |
The optimizer ignores the hint when the value is |
| An index string |
A full-text index that the optimizer must not use for the given keyspace. |
| An array of index strings |
An array of full-text indexes that the optimizer must not use for the given keyspace. |
Examples
This example specifies that the optimizer should not use the FTS index hotel_state_fts_index.
To qualify for this query, you must have this FTS index on state and type, using the keyword analyzer.
(Or alternatively, the FTS index on state, with a custom type mapping on hotel.)
SELECT /*+ NO_INDEX_FTS (hotel hotel_state_fts_index) */
META().id
FROM hotel
WHERE state = "Corse" OR state = "California";The optimizer omits the hotel_state_fts_index index from the query plan.
If a qualified FTS index is available, it’s selected for the query.
If none of the available FTS indexes are qualified, the available GSI indexes are considered instead.
NO_USE_NL
This hint is the negative equivalent of the USE_NL hint. It directs the optimizer not to use a nested loop join for a specified keyspace. This hint must be specified on the keyspace on the right-hand side of the join. If not specified, the optimizer selects the optimal join method.
Simple Syntax
no-nl-hint-simple ::= ( 'NO_USE_NL' | 'AVOID_NL' ) '(' ( keyspace )+ ')'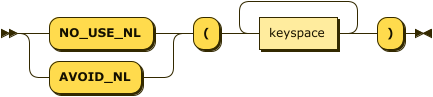
With the simple syntax, this hint specifies one or more keyspaces.
You can either use NO_USE_NL or AVOID_NL as the hint keyword.
You can also use this hint multiple times within the hint comment.
JSON Syntax
no-nl-hint-json ::= ( '"no_use_nl"' | '"avoid_nl"') ':' ( keyspace-array | keyspace-object )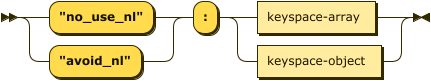
With the JSON syntax, this hint takes the form of a no_use_nl or avoid_nl property.
You can only use this property once within the hint comment.
The value of this property can be a Keyspace Array or a Keyspace Object.
Keyspace Array
keyspace-array ::= '[' keyspace-object ( ',' keyspace-object )* ']'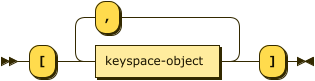
Use this array to apply the hint to multiple keyspaces. Each element must be a Keyspace Object.
Keyspace Object
keyspace-object ::= '{' keyspace-property '}'
Use this object to apply the hint to a single keyspace. It must contain a Keyspace Property.
Examples
The following query does not include a join hint.
SELECT a.airportname AS airport, r.id AS route
FROM route AS r,
airport AS a
WHERE a.faa = r.sourceairport
AND r.sourceairport = "SFO"
LIMIT 4;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the optimizer has selected the nested-loop join method.
{
"#operator": "NestedLoopJoin",
"alias": "a",
"filter": "((`a`.`faa`) = (`r`.`sourceairport`))",
"on_clause": "(((`a`.`faa`) = (`r`.`sourceairport`)))",The following query hints the optimizer to avoid using a nested-loop join.
SELECT /*+ NO_USE_NL (a) */
a.airportname AS airport, r.id AS route
FROM route AS r,
airport AS a
WHERE a.faa = r.sourceairport
AND r.sourceairport = "SFO"
LIMIT 4;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the optimizer avoids using a nested-loop join and considers other join methods. In this case, the optimizer has selected the hash join method.
{
"#operator": "HashJoin",
"build_aliases": [
"r"
],NO_USE_HASH
This hint is the negative equivalent of the USE_HASH hint. It directs the optimizer not to use a hash join for a specified keyspace. This hint must be specified on the keyspace on the right-hand side of the join. If you do not specify this hint, the optimizer selects the optimal join method.
Unlike USE_HASH, this hint does not allow you to specify whether the keyspace should appear on the build or probe side of the hash join. Instead, you can only specify the keyspace name or alias to which this hint applies.
Simple Syntax
no-hash-hint-simple ::= ( 'NO_USE_HASH' | 'AVOID_HASH' ) '(' ( keyspace )+ ')'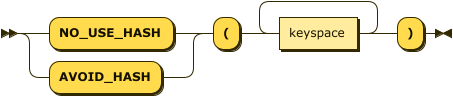
With the simple syntax, this hint specifies one or more keyspaces.
You can either use NO_USE_HASH or AVOID_HASH as the hint keyword.
You may also use this hint multiple times within a hint comment.
JSON Syntax
no-hash-hint-json ::= ( '"no_use_hash"' | '"avoid_hash"' ) ':'
( keyspace-array | keyspace-object )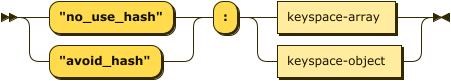
With the JSON syntax, this hint takes the form of a no_use_hash or avoid_hash property.
You can only use this property once within a hint comment.
The value of this property can be a Keyspace Array or a Keyspace Object.
Keyspace Array
keyspace-array ::= '[' keyspace-object ( ',' keyspace-object )* ']'
Use this array to apply the hint to multiple keyspaces. Each element must be a Keyspace Object.
Keyspace Object
keyspace-object ::= '{' keyspace-property '}'
Use this object to apply the hint to a single keyspace. It must contain a Keyspace Property.
Examples
For the examples in this section, it’s assumed that the cost-based optimizer is active, and all optimizer statistics are up-to-date.
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
The following query does not include a join hint.
SELECT COUNT(1) AS Total_Count
FROM route rte
INNER JOIN airline aline
ON rte.airlineid = META(aline).id;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the optimizer has selected to use the hash join method.
{
"#operator": "HashJoin",
"build_aliases": [
"aline"
],
"build_exprs": [
"cover ((meta(`aline`).`id`))"
],
"on_clause": "(((`rte`.`airlineid`) = cover ((meta(`aline`).`id`))))",
// ...
"probe_exprs": [
"(`rte`.`airlineid`)"
],The following query hints the optimizer to avoid using a hash join for the keyspace aline.
SELECT /*+ NO_USE_HASH(aline) */
COUNT(1) AS Total_Count
FROM route rte
INNER JOIN airline aline
ON rte.airlineid = META(aline).id;If you examine the plan for this query, you can see that the optimizer avoids using a hash join and considers other join methods. In this case, the optimizer has selected the lookup join method.
{
"#operator": "Join",
"as": "aline",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"keyspace": "airline",
"namespace": "default",
"on_keys": "(`rte`.`airlineid`)",
"optimizer_estimates": {
"cardinality": 44924.88,
"cost": 343011.9112140067,
"fr_cost": 343011.9112140067,
"size": 800
},
"scope": "inventory"
},Legacy Equivalent
Unlike positive keyspace hints, negative hints do not have legacy equivalents.
However, you cannot specify a negative hint and the USE clause on the same keyspace.
If you do this, the negative hint and the USE clause are both marked as erroneous and ignored by the optimizer.
Interaction between Positive and Negative Hints
As a best practice, avoid using positive and negative hints of the same type on the same keyspace. This can create conflicts and may cause the optimizer to ignore both hints.
Join Hints
You can only specify one join hint per keyspace or alias. This can be either a positive (USE HASH, USE_NL) or a negative (NO_USE_HASH, NO_USE_NL) join hint.
Index Hints
You can specify both positive (INDEX, INDEX_FTS) and negative (NO_INDEX, NO_INDEX_FTS) index hints on the same keyspace or alias, provided the list of indexes are non-overlapping.
If an index is included in both the positive and negative hint lists, the optimizer ignores both hints. Similarly, omitting the index list in either a positive or negative hint may result in conflicts, causing the hints to be ignored.