USING AI
- reference
- Couchbase Server 8.0
The USING AI statement allows you to generate SQL++ queries from natural language prompts.
Purpose
You can use the USING AI statement to convert a natural language prompt into a SQL++ query. When executed, the statement passes the input to Large Language Models (LLMs), which interpret the request and return the equivalent SQL++ query.
For example, you can input prompts such as How many airlines are based in Europe or List the names of all hotels in the same city as an airport, and the statement generates the corresponding SQL++ query.
If the generated statement is a SELECT query, the Query Service automatically executes it and returns the results. For all other query types, it returns the generated statement as a string without executing it. However, you can modify this behavior by using the execute option.
The word AI is recognized as a keyword, but only when used as part of the USING AI statement.
When used by itself as a field name or identifier, you do not need to escape the word AI by enclosing it in backticks.
For example, in a query like SELECT ai FROM XYZ, you can use ai as a field name without needing to escape it.
|
Prerequisites
Before using the USING AI statement, make sure you have:
-
A Couchbase Capella account.
-
Your Capella account credentials and organization ID readily available.
| Although the USING AI statement requires a Capella account, you can use it with any Couchbase Server 8.0 instances. |
Syntax
using-ai ::= 'USING' 'AI' ( 'FOR' ( 'FLEXINDEX' | 'FTS' ) )? ( 'WITH' options )? prompt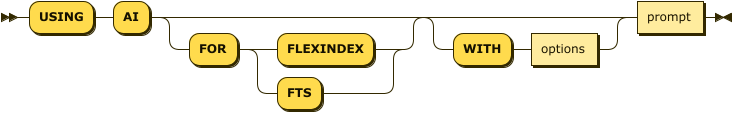
- prompt
-
[Required] A natural language request that you want to convert into a SQL++ query.
- options
-
[Optional] A JSON object specifying additional options for the statement.
By default, the statement uses the natural_orgid, natural_cred, and natural_context request-level parameters to determine the organization ID, credentials, and keyspaces for the request. You can override them by specifying the relevant parameters in the options object.
FLEXINDEX / FTS
Use the optional FLEXINDEX or FTS keyword to generate a query that uses an FTS or flex index.
This hint appends a USE INDEX (USING FTS) clause to all FROM keyspaces in the generated query.
See Example 6.
Options
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
creds |
Couchbase Capella account credentials to authenticate the request. Can be one of the following:
If specified, this value overrides the natural_cred request-level parameter. This parameter does not support Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), or social login credentials (such as Google or GitHub). To ensure your credentials are passed securely, see Handling Passwords. |
String or object |
keyspaces |
One or more keyspaces for the request. Can be one of the following:
If specified, this value overrides the natural_context request-level parameter. |
String or an array of strings |
orgId |
Couchbase Capella organization ID for the request. If specified, this value overrides the natural_orgid request-level parameter. To find your organization ID, log in to your Couchbase Capella account and check the URL in your web browser.
The organization ID is the For example, in the URL |
String |
execute |
Indicates if the generated statement should be executed automatically. If If Default: |
Boolean |
output |
A string specifying the type of output to generate. Possible values are:
The statement returns an error if you specify a value not included in this list. Default: |
String |
| You can prefix a USING AI statement with EXPLAIN or ADVISE to get the query plan or index recommendations for your generated query. See Example 9. |
Usage
To use a USING AI statement, you must provide your Capella credentials, Capella organization ID, and one or more keyspaces. You can provide these details in two ways:
Set Parameters at the Request Level
You can set natural_cred, natural_orgid, and natural_context as request-level parameters, outside the USING AI statement.
When set, these parameters apply to all subsequent USING AI statements in that session.
For example, in the cbq shell, you can set these parameters using the \set command.
See Example 1.
Once configured, you do not need to specify creds, orgId, or keyspaces in the WITH clause.
Set Parameters Inline
You can set the creds, orgId, and keyspaces options directly in the WITH clause of the USING AI statement.
If specified, these values override the natural_cred, natural_orgid, and natural_context parameters.
See Example 3.
Result
A JSON object containing the generated statement, execution status, and metrics.
If the generated statement is a SELECT query and the execute option is TRUE (default), the output includes the query results as well.
Handling Passwords Securely
Use creds and natural_cred parameters with caution to avoid exposing password information through history files or logs.
When working with the cbq shell, avoid passing passwords directly on the command line.
Instead, use the \set command to specify only the username, and then enter the password at the terminal prompt.
This ensures that the password is not recorded in the shell history.
For example:
cbq> \set -natural_cred username@example.com; Enter password for "natural_cred": <enter password> cbq> \set; Query Parameters : Parameter name : natural_cred Value : [username@example.com:***] Parameter name : profile Value : ["timings"] ...
Similarly, if you’re sending requests directly to a REST endpoint from a shell, be mindful of how you provide the password and whether it will be recorded in the shell history. Consider using a method like the following to prompt for the password:
echo -n "Enter your password: "
read -s p
echo
curl -s -d "natural_cred=<your-username>:${p}" ...
If you choose to reuse the password by setting an environment variable, it might be visible to other users on the system with sufficient privileges for process inspection (for example, through /proc).
If security is a concern, consider using an HTTPS connection.
Examples
In the following examples:
-
Replace
<USER>with your Couchbase Capella username. -
Replace
<PASSWORD>with your Couchbase Capella password. -
Replace
<ORGID>with your Couchbase Capella organization ID.
To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_context travel-sample.inventory.hotel;
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI How many hotels provide free parking?;{
"requestID": "097f9cbf-57f2-4832-986d-4f85041c91dc",
"generated_statement": "SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel`
AS `h` WHERE `h`.`free_parking` = TRUE",
"signature": {
"$1": "number"
},
"results": [
{
"$1": 253
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.244083167s",
"executionTime": "55.577625ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 25,
"serviceLoad": 3,
"usedMemory": 16511,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.188224375s"
}
}To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.airline"],"execute":false} \
How many airlines are based in United Kingdom?;{
"requestID": "a6dfea34-6445-4e66-9127-9bdfbe5f7585",
"status": "success",
"generated_statement": "SELECT COUNT(*) AS `airlines_based_in_uk`
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`airline`
AS `a` WHERE `a`.`country` = \"United Kingdom\"",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.485615126s",
"executionTime": "0s",
"resultCount": 0,
"resultSize": 0,
"serviceLoad": 0,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.484809668s"
}
}To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
USING AI WITH
{
"creds": {
"user": "<USER>",
"pass": "<PASSWORD>"
},
"orgId": "<ORGID>",
"keyspaces": [
"travel-sample.inventory.hotel",
"travel-sample.inventory.airport"
],
"execute": false
}
List the names of all hotels in the same city as an airport;{
"requestID": "e154f6d5-0fa0-4de3-8824-3ebb73cb49f2",
"status": "success",
"generated_statement": "SELECT `h`.`name`
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel` AS `h`
JOIN `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`airport` AS `a`
ON `h`.`city` = `a`.`city`",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "4.032734417s",
"executionTime": "0s",
"resultCount": 0,
"resultSize": 0,
"serviceLoad": 0,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "4.032041335s"
}
}echo -n "Enter your password: "
read -s p
echo
curl -s -d "natural_cred=<USER>:${p}" \
-d 'pretty=true&statement=USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":"travel-sample.inventory.landmark",
"orgId":"<ORGID>"} \
How many landmarks are in the western hemisphere?' \
http://localhost:8093/query/service -u username:password{
"requestID": "325457b8-9cf4-477b-aaf5-7609f2ae79bf",
"generated_statement": "SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`landmark`
AS `l` WHERE `l`.`geo`.`lon` \u003c 0",
"signature": {
"$1": "number"
},
"results": [
{
"$1": 4033
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "1.811586709s",
"executionTime": "73.500333ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 26,
"serviceLoad": 3,
"usedMemory": 659994,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "1.736891542s"
}
}To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.hotel"], "execute": true} \
Insert a new hotel named "Sunset Inn" in "Miami, Florida" with a rating of 4;{
"requestID": "28a3f92e-0595-4a80-b35f-0606751e4d51",
"status": "success",
"generated_statement": "INSERT INTO `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel`
(KEY, VALUE) VALUES (UUID(),
{\"name\": \"Sunset Inn\",
\"city\": \"Miami\",
\"state\": \"Florida\",
\"rating\": 4,
\"type\": \"hotel\"})",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.007107125s",
"executionTime": "0s",
"resultCount": 0,
"resultSize": 0,
"serviceLoad": 0,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.005838959s"
}
}If you examine the hotel keyspace, you’ll see that this document was not inserted, even though execute was set to TRUE.
This is because the Query Service executes the generated statement only if it’s a SELECT query.
To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI FOR FLEXINDEX WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.hotel"]} \
How many hotels are located in California?;{
"requestID": "d5746585-4589-4703-a4cd-5acac3897c6f",
"generated_statement": "SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel` AS `h`
USE INDEX (USING FTS) WHERE `h`.`state` = \"California\"",
"signature": {
"$1": "number"
},
"results": [
{
"$1": 361
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.528830585s",
"executionTime": "67.032959ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 25,
"serviceLoad": 3,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.46060671s"
}
}ftssqlTo try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
This example uses the same prompt as Example 5, but specifies the output option instead of the FLEXINDEX keyword.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.hotel"], "output":"ftssql"} \
How many hotels are located in California?;{
"requestID": "c6fcaed5-23fa-4dc5-936c-febc6b5cb222",
"generated_statement": "SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel`
AS `h`
USE INDEX (USING FTS) WHERE `h`.`state` = \"California\"",
"signature": {
"$1": "number"
},
"results": [
{
"$1": 361
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.921005918s",
"executionTime": "29.772792ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 25,
"serviceLoad": 3,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.889671542s"
}
}jsudfTo try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.hotel"], "output":"jsudf"} \
Create a function to list all hotels in California;{
"requestID": "731a896e-f4b8-4b3b-893a-2fbf38dfedc8",
"status": "success",
"generated_statement": "CREATE FUNCTION listHotelsInCalifornia()
LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT AS 'function listHotelsInCalifornia() {
/* Define the query to select hotels in California */
var q = SELECT `name`, `city`, `state`, `country`
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel`
AS `h` WHERE `h`.`state` = \"CA\";
/* Initialize an empty array to store the results */
var res = [];
/* Iterate over the query results and
push each hotel into the results array */
for (const doc of q) {
var hotel = {};
hotel.name = doc.name;
hotel.city = doc.city;
hotel.state = doc.state;
hotel.country = doc.country;
res.push(hotel);
}
/* Return the array of hotels in California */
return res;
}'",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "4.10252771s",
"executionTime": "0s",
"resultCount": 0,
"resultSize": 0,
"serviceLoad": 0,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "4.102134168s"
}
}To try this example, use cbq shell with Couchbase Server version 8.0 or later.
\set -natural_cred <USER>:<PASSWORD>;
\set -natural_orgid <ORGID>;
EXPLAIN USING AI WITH {"keyspaces":["travel-sample.inventory.hotel"]} \
List the names and cities of hotels with a rating greater than 4;{
"requestID": "98ea3e33-7ad9-4606-ae95-26b68463498e",
"generated_statement": "explain SELECT `h`.`name`, `h`.`city`
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel` AS `h`
WHERE ANY `review` IN `h`.`reviews`
SATISFIES `review`.`rating` \u003e 4 END",
"signature": "json",
"results": [
{
"plan": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "PrimaryScan3",
"as": "h",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"index": "def_inventory_hotel_primary",
"index_projection": {
"primary_key": true
},
"keyspace": "hotel",
"namespace": "default",
"optimizer_estimates": {
"cardinality": 917,
"cost": 303.73468119182434,
"fr_cost": 12.318140328453461,
"size": 11
},
"scope": "inventory",
"using": "gsi"
},
{
"#operator": "Fetch",
"as": "h",
"bucket": "travel-sample",
"early_projection": [
"city",
"name",
"reviews"
],
"keyspace": "hotel",
"namespace": "default",
"optimizer_estimates": {
"cardinality": 917,
"cost": 6989.182886677501,
"fr_cost": 31.59561928754362,
"size": 4377
},
"scope": "inventory"
},
{
"#operator": "Parallel",
"~child": {
"#operator": "Sequence",
"~children": [
{
"#operator": "Filter",
"condition": "any `review` in (`h`.`reviews`)
satisfies (4 \u003c (`review`.`rating`))
end"
},
{
"#operator": "InitialProject",
"discard_original": true,
"preserve_order": true,
"result_terms": [
{
"expr": "(`h`.`name`)"
},
{
"expr": "(`h`.`city`)"
}
]
}
]
}
}
]
},
"text": "SELECT `h`.`name`, `h`.`city`
FROM `travel-sample`.`inventory`.`hotel` AS `h`
WHERE ANY `review` IN `h`.`reviews`
SATISFIES `review`.`rating` \u003e 4 END"
}
],
"status": "success",
"metrics": {
"elapsedTime": "2.524200293s",
"executionTime": "7.078542ms",
"resultCount": 1,
"resultSize": 2825,
"serviceLoad": 3,
"naturalLanguageProcessingTime": "2.516578959s"
}
}Limitations
When using the statement, consider the following:
-
To execute the statement on Couchbase Server, use the cbq shell, an SDK, or the Query REST API. The statement does not function when run directly through the Query Workbench or Couchbase Shell (cbsh).
-
You cannot use the
credsandnatural_credparameters with the following types of credentials:-
Single Sign-On (SSO)
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
-
Social logins (such as Google or GitHub)
-