CREATE a Remote Collection
- Capella Analytics
- reference
This topic describes how you use the CREATE statement to create a collection that shadows OLTP data from a remote data source.
You use different statement syntax to create collections that shadow data located on a Couchbase data service than you do for collections that shadow data from a data service that uses a Kafka pipeline.
Create a Remote Couchbase Collection
| To create a link to a remote data source, you use the Capella Analytics UI. See Stream Data from Remote Sources. |
Syntax
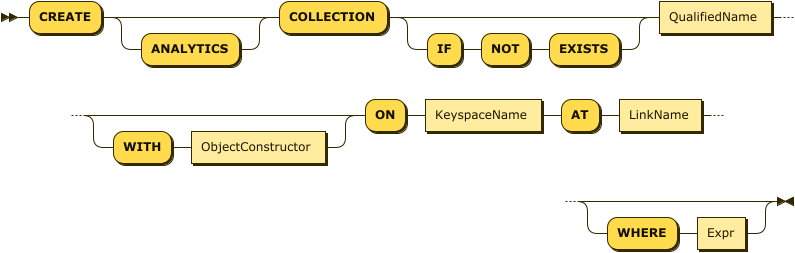
CreateRemoteCouchbaseCollection EBNF
CreateRemoteCouchbaseCollection ::= "CREATE" "ANALYTICS"? "COLLECTION" ("IF" "NOT" "EXISTS")?
QualifiedName
( "WITH" ObjectConstructor )?
"ON" KeyspaceName
"AT" LinkName
("WHERE" Expr | "APPLY" "FUNCTION" QualifiedName)?CreateRemoteCouchbaseCollection Diagram
For all collections, the QualifiedName is the fully qualified name of the collection to create.
Show QualifiedName Diagram
Show ObjectConstructor Diagram
Show KeyspaceName Diagram
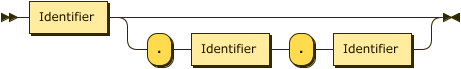
Example
This example adds a collection for French breweries and associates it with the remote link to Capella. As a prerequisite for running this example yourself, follow the add sample data procedures to add a remote link and collections to Capella Analytics.
CREATE COLLECTION remoteCapella.remoteBeer.beerFrance
ON `beer-sample`._default._default
AT capellaLink
WHERE country = "France";This following example creates a new collection named analytics.Commerce.customers that shadows data from a remote source using the capellaLink.
The CustomerTransform function must be created with a CREATE TRANSFORM FUNCTION statement before it can be used here.
It then applies the CustomerTransform function to automatically transform incoming data before storing it in the collection.
CREATE TRANSFORM FUNCTION analytics.Commerce.CustomerTransform (cust) {
SELECT
c.*,
(c.address.street || ', ' || c.address.city || ', ' || c.address.zipcode) AS location
FROM [cust] AS c
};
CREATE COLLECTION analytics.Commerce.customers
ON `donc-book-sample`.Commerce.customers AT capellaLink
APPLY FUNCTION analytics.Commerce.CustomerTransform;Arguments
- WITH
-
The optional
WITHclause enables you to specify parameters for the remote Couchbase collection. ItsObjectConstructorrepresents a JSON object containing key-value pairs.The optional
storage-block-compressionparameter determines the storage compression used for this collection. This parameter takes a nested object value,scheme. Possible values forschemearesnappyornone. The default storage compression scheme issnappy.
- ON
-
The
ONclause specifies the data source for the collection. The `Identifier`s in this clause represent a bucket name, followed by an optional scope name and collection name, on the remote Couchbase Server or Capella cluster.
- AT
-
The
ATclause specifies the name of the link that contains credentials for the bucket. The specified link must have a type of Couchbase.
- WHERE
-
The optional
WHEREclause provides the option to filter the documents in the collection. TheExprin this clause must be deterministic, and it cannot contain a user-defined function. For example, you could filter content by specifying a predicate on the values for one or more of the fields in the objects.
The WHERE clause and the APPLY FUNCTION clause are mutually exclusive; you can use one or the other, but not both when creating a remote collection.
|
- APPLY FUNCTION
-
The
APPLY FUNCTIONclause allows you to attach aTRANSFORM FUNCTIONto a remote collection. When you use theAPPLY FUNCTIONkeyword in theCREATE COLLECTIONstatement, Capella Analytics applies your specified SQL++ user-defined function (UDF) to each incoming document before storing it in the remote collection. This enables you to filter, modify, or reshape data automatically as it arrives from the remote source.
For more information about how to create a TRANSFORM FUNCTION, see Create Transform Function.
The following example uses the APPLY FUNCTION clause to apply a TRANSFORM FUNCTION when creating a remote collection:
CREATE COLLECTION analytics.Commerce.customers
ON `donc-book-sample`.Commerce.customers
AT capellaLink
APPLY FUNCTION analytics.Commerce.CustomerTransform;The CustomerTransform TRANSFORM FUNCTION processes each record before storing it in the analytics.Commerce.customers collection.
To create a link to a remote data source, you use the Capella Analytics UI. See Stream Data from Couchbase Capella.
Create a Remote Kafka Collection
| To create a link to a remote data source, you use the Capella Analytics UI. See Stream Data from Remote Sources. |
Syntax
CreateRemoteKafkaCollection EBNF
CreateRemoteKafkaCollection ::= "CREATE" "ANALYTICS"? "COLLECTION"
("IF" "NOT" "EXISTS")?
QualifiedName
"PRIMARY" "KEY" "(" FieldList ")"
"ON" TopicName ("," TopicName)*
"AT" LinkName
"WITH" KafkaObjectConstructor
("WHERE" Expr | "APPLY" "FUNCTION" QualifiedName)?CreateRemoteKafkaCollection Diagram
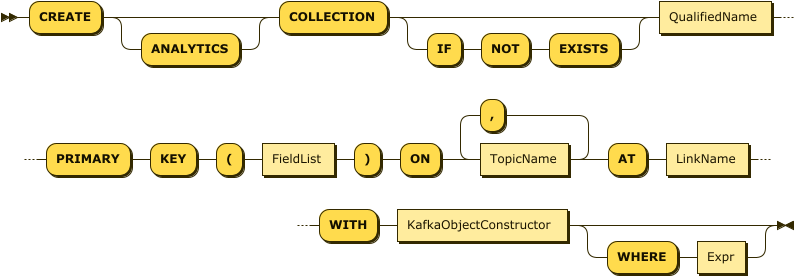
For all collections, the QualifiedName is the fully qualified name of the collection to create.
Show QualifiedName Diagram

Show FieldList Diagram
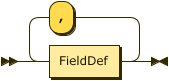
Show FieldDef Diagram

Show FieldName Diagram
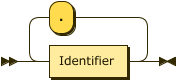
Show FieldType Diagram

Examples
This statement uses the JSON Commerce customers dataset as an example.
It assumes that this data is in a Kafka topic named remote-topic-1 for a MongoDB dataset that uses CDC.
The primary key for the MongoDB dataset is _id, with string values.
In addition, this example assumes that a link named confluentLink has the credentials for accessing the MongoDB dataset.
CREATE COLLECTION sampleAnalytics.Commerce.customers
PRIMARY KEY (_id:string)
ON `remote-topic-1`
AT confluentLink
WITH {
"keySerializationType":"JSON",
"valueSerializationType":"JSON",
"cdcEnabled": "true"
"cdcDetails": {
"cdcSource": "MONGODB"
"cdcSourceConnector":"DEBEZIUM"
},
"deadLetterQueue":"dlq_topic-1"
};Show additional example
This statement uses the JSON Commerce orders dataset as an example.
It assumes that the data is in a Kafka topic named non_cdc_5m_json.mongo_database.mongo_collection for a MongoDB dataset that does not use CDC.
In addition, you have a link set up named mskLink with the credentials for accessing the dataset.
CREATE COLLECTION sampleAnalytics.Commerce.orders
PRIMARY KEY (orderno:int)
ON `non_cdc_5m_json.mongo_database.mongo_collection`
AT mskLink
WITH {
"keySerializationType":"JSON",
"valueSerializationType":"JSON"
};The following example creates a new collection named analytics.Commerce.orders that uses orderno as the primary key and ingests data from a remote MongoDB source via the mskLink.
The WHERE clause filters the documents in the collection to include only those where the category field has the value Apparel.
CREATE TRANSFORM FUNCTION OrderTransform (ord)
{ SELECT orderno, custid, order_date, ship_date
FROM [ord] AS o };
CREATE COLLECTION analytics.Commerce.orders
PRIMARY KEY (orderno:int)
ON `non_cdc_5m_json.mongo_database.mongo_collection` AT mskLink
WITH {
"keySerializationType":"JSON",
"valueSerializationType":"JSON"
}
WHERE category = "Apparel";Show additional example
The following example creates a new collection named analytics.Commerce.lineitems with a composite primary key of orderno and itemno, ingesting data from a remote MongoDB source via the mskLink.
It applies the OrderTransform function to automatically transform incoming data before storing it in the collection, using JSON serialization for both keys and values.
CREATE COLLECTION analytics.Commerce.lineitems
PRIMARY KEY (orderno:int, itemno:int)
ON `non_cdc_5m_json.mongo_database.mongo_collection` AT mskLink
WITH {
"keySerializationType":"JSON",
"valueSerializationType":"JSON"
}
APPLY FUNCTION analytics.Commerce.OrderTransform;Arguments
- PRIMARY KEY
-
The
PRIMARY KEYclause indicates the field or fields to use as the primary key for the collection. TheFieldTypecan be any of the primitive data types, whereINTis an alias forBIGINT.A common datatype for the MongoDB
_idprimary key is objectId. To specify a primary key with this datatype, you use the following syntax:
PRIMARY KEY (`_id`.`$oid`:String)
If CDC is enabled for the collection, you should specify the primary key of the source collection as the primary key for your Capella Analytics collection.
- ON
-
You specify one or more topics from the Kafka cluster in a comma-separated list.
- WITH
-
The
WITHclause enables you to specify parameters for the collection. ItsObjectConstructorrepresents an object containing key-value pairs, one for each parameter. The configuration that you supply applies to all of the topics listed by the ON clause. You can define the following parameters.Name Description Schema keySerializationType
RequiredSpecifies the format of the keys in the remote data. Accepts one of the following string values:
JSON— JSON
PROTOBUF— Protocol Buffers
AVRO— Apache Avro
For information about the mapping that Capella Analytics performs for Avro data types, see Data Type Mapping: Parquet and Avro.enum: json, protobuf, avro
valueSerializationType
RequiredSpecifies the format of the values in the remote data. Accepts one of the following string values:
JSON— JSON
PROTOBUF— Protocol Buffers
AVRO— Apache Avro
For information about the mapping that Capella Analytics performs for Avro data types, see Data Type Mapping: Parquet and Avro.enum: json, protobuf, avro
cdcEnabled
RequiredIdentifies whether the Kafka pipeline uses Change Data Capture (CDC) processing.
Whentrue, you also specify acdcDetailsobject with thecdcSourceandcdcSourceConnectorparameters.
Whentrue, you should specify the primary key of the source collection as the primary key for your Capella Analytics collection. The Debezium source connector sends the primary key of the source collection as the key for records in the Kafka topic.Boolean
cdcSource
OptionalOnly used if cdcEnabled is true.
Identifies the data source that uses CDC in the Kafka pipeline.enum: MONGODB, MYSQLDB, POSTGRESQL
cdcSourceConnector
OptionalOnly used if cdcEnabled is true.
Identifies the type of source data connector used in the pipeline.enum: DEBEZIUM
deadLetterQueue
OptionalSpecifies a remote Kafka topic as the destination for failed messages. If you do not define a topic, failed messages are dropped.
string
- WHERE
-
The optional
WHEREclause provides the option to filter the documents in the collection. TheExprin this clause must be deterministic, and it cannot contain a user-defined function. For example, you could filter content by specifying a predicate on the values for one or more of the fields in the objects.
The WHERE clause and the APPLY FUNCTION clause are mutually exclusive; you can use one or the other, but not both when creating a remote collection.
|
- APPLY FUNCTION
-
The
APPLY FUNCTIONclause allows you to attach aTRANSFORM FUNCTIONto incoming data during collection creation. When you use theAPPLY FUNCTIONkeyword in theCREATE COLLECTIONstatement, Capella Analytics automatically processes each incoming record with your specified SQL++ user-defined function (UDF) before storing it in the collection. This enables you to filter, modify, or reshape data as it arrives from Kafka.
For more information about how to create a TRANSFORM FUNCTION, see Create Transform Function.
See the following example:
CREATE COLLECTION analytics.Commerce.orders
PRIMARY KEY (orderno:int)
ON `non_cdc_5m_json.mongo_database.mongo_collection` AT mskLink
WITH {
"keySerializationType":"JSON",
"valueSerializationType":"JSON"
}
APPLY FUNCTION analytics.Commerce.OrderTransform;The OrderTransform TRANSFORM FUNCTION processes each record before storing it in the analytics.Commerce.orders collection.
To create a link to a remote data source, you use the Capella Analytics UI. See Create a Kafka Pipeline Link.