DELETE Statements
- Capella Analytics
- reference
This topic describes how you use DELETE statements to delete objects from a standalone collection.
Syntax
Delete EBNF
Delete ::= "DELETE" "FROM" QualifiedName
("AS" OutputAlias)?
("WHERE" Expr)?
("RETURNING" Expr)?Delete Diagram
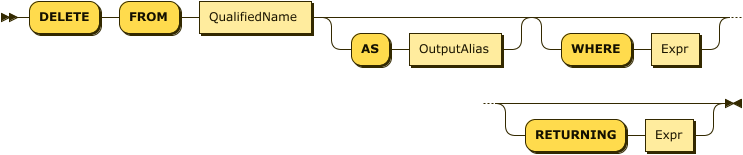
The first QualifiedName must resolve to a standalone collection or synonym.
Examples
This example deletes all orders placed before 2020-07-01 from a standalone collection named Orders:
DELETE FROM database_name.scope_name.Orders
WHERE order_date < "2020-07-01";After you use DELETE, you can run ANALYZE COLLECTION on the collection to update the data sample used by cost-based optimization (CBO).
See Cost-Based Optimizer for Capella Analytics Services.
Show additional example
This example deletes orders made by a customer named T. Cody and returns the values of the orderno field for those deleted orders:
DELETE FROM database_name.scope_name.Orders AS ord
WHERE ord.custid = (
SELECT VALUE cust.custid
FROM Customers AS cust
WHERE cust.name = "T. Cody"
)[0]
RETURNING VALUE ord.orderno;The output of the RETURNING clause is:
1002 1007 1008 1009
Arguments
- WHERE
-
The optional
WHEREclause specifies a condition that the objects in the target collection must satisfy for the statement to delete them. It can include uncomplicated predicates as well as other subqueries referring to other existing collections. The default database for theWHEREexpression is the target collection’s database. There’s one variable in scope for theWHEREexpression. If specified,OutputAliasdefines the variable’s name. Otherwise, the variable’s name is the target collection’s name.
- RETURNING
-
Adding an optional
RETURNINGclause causes the statement to return a result for each object deleted, identified by theOutputAliasor the collection name. The clause can contain subqueries, although they cannot refer to any collections in their FROM clauses, making them object-local in nature.Errors encountered during
DELETEcancels the action and leaves the target dataset in its pre-DELETE state.