UPSERT
- reference
UPSERT is used to insert a new record or update an existing one. If the document doesn’t exist it will be created. UPSERT is a combination of INSERT and UPDATE.
Please note that the examples on this page will alter the data in your sample buckets.
To restore your sample data, remove and reinstall the travel-sample bucket.
Refer to Sample Buckets for details.
|
Prerequisites
RBAC Privileges
User executing the UPSERT statement must have the Query Update and Query Insert privileges on the target keyspace. If the statement has any RETURNING clauses, then the Query Select privilege is also required on the keyspaces referred in the respective clauses. For more details about user roles, see Authorization.
| A user with the Data Writer privilege may set documents to expire. When the document expires, the data service deletes the document, even though the user may not have the Query Delete privilege. |
RBAC Examples
For this example, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Update and Query Insert privileges on hotel.
UPSERT INTO hotel (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("key1", { "type" : "hotel", "name" : "new hotel" });To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Update and Query Insert privileges on hotel and the Query Select privilege on hotel also (for RETURNING clause).
UPSERT INTO hotel (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("key1", { "type" : "hotel", "name" : "new hotel" })
RETURNING *;[
{
"hotel": {
"name": "new hotel",
"type": "hotel"
}
}
]To execute the following statement, you must have the Query Update and Query Insert privileges on landmark and Query Select privilege on `beer-sample`.
UPSERT INTO landmark (KEY foo, VALUE bar)
SELECT META(doc).id AS foo, doc AS bar FROM `beer-sample` AS doc WHERE type = "brewery";Syntax
upsert ::= 'UPSERT' 'INTO' target-keyspace ( insert-values | insert-select )
returning-clause?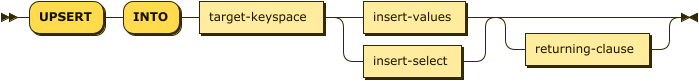
| target-keyspace | |
| insert-values | |
| insert-select | |
| returning-clause |
Insert Target
target-keyspace ::= keyspace-ref ( 'AS'? alias )?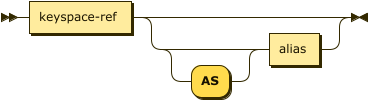
Specifies the keyspace into which to upsert documents.
| keyspace-ref | |
| alias |
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?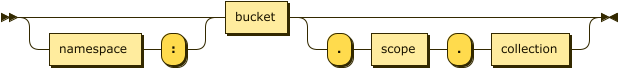
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Keyspace reference for the insert target. For more details, refer to Keyspace Reference.
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the keyspace reference. For details, refer to AS Clause.
Assigning an alias to the keyspace reference is optional.
If you assign an alias to the keyspace reference, the AS keyword may be omitted.
Insert Values
insert-values ::= ( '(' 'PRIMARY'? 'KEY' ',' 'VALUE' ( ',' 'OPTIONS' )? ')' )? values-clause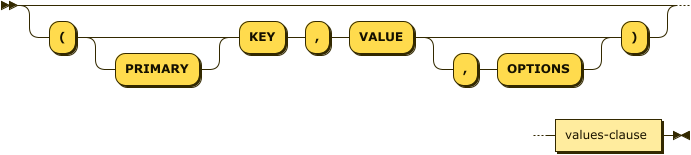
Specifies one or more documents to be upserted using the VALUES clause. For details, refer to Insert Values.
| values-clause |
VALUES Clause
values-clause ::= 'VALUES' '(' key ',' value ( ',' options )? ')'
( ',' 'VALUES'? '(' key ',' value ( ',' options )? ')' )*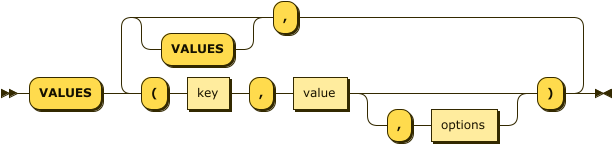
Specify the values as well-formed JSON. Also enables you to set the expiration of the upserted documents. For details, refer to VALUES Clause.
When updating a document, if the document expiration is not specified, the document expiration is set according to the request-level preserve_expiration parameter.
If this is true, the existing document expiration is preserved; if false, the document expiration defaults to 0, meaning the document expiration is the same as the bucket expiration.
|
Insert Select
insert-select ::= '(' 'PRIMARY'? 'KEY' key ( ',' 'VALUE' value )?
( ',' 'OPTIONS' options )? ')' select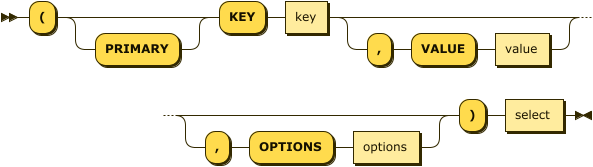
Specifies the documents to be upserted as a SELECT statement. Also enables you to set the expiration of the upserted documents. For details, refer to Insert Select.
When updating a document, if the document expiration is not specified, the document expiration is set according to the request-level preserve_expiration parameter.
If this is true, the existing document expiration is preserved; if false, the document expiration defaults to 0, meaning the document expiration is the same as the bucket expiration.
|
RETURNING Clause
returning-clause ::= 'RETURNING' (result-expr (',' result-expr)* |
('RAW' | 'ELEMENT' | 'VALUE') expr)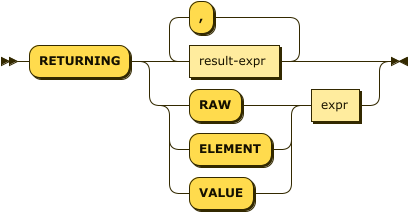
Specifies the fields that must be returned as part of the results object.
| result-expr |
Result Expression
result-expr ::= ( path '.' )? '*' | expr ( 'AS'? alias )?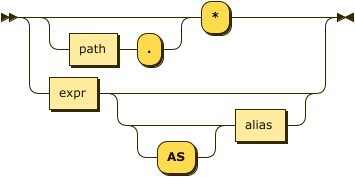
Specifies an expression on the data you upserted, to be returned as output. For details, refer to Result Expression.
Example
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
The following statement upserts documents with type landmark-pub into the landmark keyspace.
UPSERT INTO landmark (KEY, VALUE)
VALUES ("upsert-1", { "name": "The Minster Inn", "type": "landmark-pub"}),
("upsert-2", {"name": "The Black Swan", "type": "landmark-pub"})
RETURNING VALUE name;[
"The Minster Inn",
"The Black Swan"
]