Upgrading Sync Gateway
This page documents various implementation details and functionalities to consider when performing an upgrade to Sync Gateway 3.0.
Related Application Deployment topics: Prepare | Install | Release Notes
Upgrade Approaches
A rolling upgrade is the recommended method to upgrade a Sync Gateway cluster. At a high level, a rolling upgrade consists of the following steps:
-
The load balancer configuration is updated to stop any HTTP traffic going to the node that will be upgraded.
-
The upgrade is performed on the given node
-
The load balancer configuration is updated to re-balance the HTTP traffic across all nodes.
Those steps are then repeated for each node in the sync gateway cluster.
Upgrade to 3.0
Use Persistent Configuration
The use of 3.0’s Persistent Configuration feature is strongly recommended. It is the default operational mode when starting sync gateway.
The feature provides a smooth upgrade path for existing users by automatically converting their existing configuration files to the new persistent configuration format.
|
One Way Upgrade
The migration to 3.0 configuration is a ONE WAY process; to continue using legacy-mode configuration see: Use Legacy-mode Configuration |
Considerations
Before commencing your upgrade consider your requirements for Configuration Groups although most users will likely find the default group sufficient, Secure Server Connection and Secure Administration.
You should also:
-
Ensure Sync Gateway has write access to the directory containing the existing configuration (the one to be converted). It will be used to backup the existing configuration, and to write the upgraded config.
-
Ensure that, if your existing configuration has multiple databases, all of the server fields used to connect to Couchbase Server match.
Although the connection credentials used may differ between databases, Sync Gateway will only use the first set of credentials for the bootstrap configuration file.Automatic upgrade cannot be done if you have multiple distinct server fields within the configuration file and you will need to manually create their own bootstrap configuration.
Process
Just start up a sync gateway node using your existing configuration properties file.
On starting, Sync Gateway will take the appropriate upgrade path as shown in Table 1.
| Configuration Status | Inference | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
No configuration exists |
This is first node in the default group or with this group ID to start |
Sync gateway uses the configuration file to derive and persist a configuration for this node. |
Configuration exists in the Server bucket |
A node in the default group, or with this group ID, has already started |
Sync gateway ignores the configuration file and uses the configuration associated with the default group, or group ID provided. |
Configuration Groups
Whilst the provided default group will suffice for most deployments sync gateway does allow for the configuration of more complex node groupings.
So, before commencing your upgrade consider your requirements for grouping sync gateway nodes within your sync gateway cluster — see: Configuration Groups
If you want the sync gateway to associate with a specific configuration group Id, you must add the bootstrap_group_id value to the configuration file prior to startup — see: bootstrap.group_id
Failing to do so may result in the configuration being overridden by one configured on a different sync gateway node that has already started and registered its own configuration.
Secure Server Connection
Secure TLS Connection to Couchbase Server is enabled out-of-the-box in 3.0.
If you wish to use non-secure connection, perhaps in a test environment, you need to run sync gateway with
bootstrap.use_tls_server set to false — see: Secure Sync Gateway Access
Secure Administration
Secure Administration is under-pinned by the use of Couchbase Server RBAC-users to authenticate and authorize access to Admin (and Metrics) API functionality. This requires you set-up and configure appropriate users — see: REST API Access.
To opt out of this, you can configure api.api.admin_interface_authentication and-or api.metrics_interface_authentication as false
Use Legacy-mode Configuration
To continue using legacy Pre-3.0 configuration you should start sync gateway with disable-persistent-config set true either in the configuration file or in Command Line Options.
1.x to 2.x No Views
From: Sync Gateway 1.x, 2.0
To: Sync Gateway 2.1+ (use_views: false)
Downtime: No — a rolling upgrade
Steps
-
Upgrade one node in the cluster, and wait for it to be reachable via the REST API (for example, at http://localhost:4985/).
-
Upgrade the rest of the nodes in the cluster.
-
Clean up obsolete views:
-
Optional Issue a call to
/_post_upgrade?preview=trueon any node to preview which design documents will be removed. -
Issue a call to
/post_upgradeto remove the obsolete design documents. The response should indicate that "sync_gateway" and "sync_housekeeping" were removed.
-
Upgrade Notes
The upgrade, from using views to using Global Secondary Indexes and N1QL, happens automatically when starting a Sync Gateway 2.1 or above node in a cluster that was previously using views.
By default, Sync Gateway requires the Couchbase Server cluster to be running Couchbase Server 5.5, with at least two nodes running the Index and Query Services.
If this is not the case, users must configure the use_views and/or num_index_replicas properties in their Sync Gateway configuration during upgrade.
Installation follows the same general approach used in 2.0. On startup, Sync Gateway will check for the existence of the required indexes, and only attempt to create them if they do not already exist.
Then, Sync Gateway will wait until indexes are available before starting to serve requests.
Tidy-up
Sync Gateway 2.1 or above will not automatically remove the previously used design documents.
Removal of the obsolete design documents is done via a call to the /_post_upgrade endpoint in Sync Gateway’s Admin REST API.
This endpoint can be run in preview mode (?preview=true) to see which design documents would be removed.
1.x to 2.x Using Views
From: Sync Gateway 1.x
To: Sync Gateway 2.x (use_views: true)
Downtime: No — a rolling upgrade
Steps
-
Upgrade one node in the cluster to 2.0, and wait for it to be reachable via the REST API (for example at http://localhost:4985/).
-
Upgrade the rest of the nodes in the cluster.
-
Clean up obsolete views:
-
Optional Issue a call to
_post_upgrade?preview=trueon any node to preview which design documents will be removed. To upgrade to 2.0, expect to see "sync_gateway" and "sync_housekeeping" listed. -
Issue a call to
_post_upgradeto remove the obsolete design documents. The response should indicate that "sync_gateway" and "sync_housekeeping" were removed.
-
Notes
In 2.0, Sync Gateway’s design documents include the version number in the design document name.
In this release for example, the design documents are named _design/sync_gateway_2.0 and _design/sync_housekeeping_2.0.
On startup, Sync Gateway will check for the existence of these design documents, and only attempt to create them if they do not already exist.
Then, Sync Gateway will wait until views are available and indexed before starting to serve requests.
To evaluate this, Sync Gateway will issue a stale=false&limit=1 query against the Sync Gateway views (channels, access and role_access).
If the view request exceeds the default timeout of 75s (which would be expected when indexing large buckets), Sync Gateway will log additional messages and retry — see Example 1.
14:26:41.039-08:00 Design docs for current SG view version (2.0) found.
14:26:41.039-08:00 Verifying view availability for bucket default...
14:26:42.045-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "access" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:42.045-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "channels" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:42.045-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "role_access" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:44.065-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "access" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:44.065-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "role_access" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:44.065-08:00 Timeout waiting for view "channels" to be ready for bucket "default" - retrying...
14:26:44.072-08:00 Views ready for bucket default.Tidy-up
Sync Gateway 2.0 will not automatically remove the previous design documents.
Removal of the obsolete design documents is done via a call to the new _post_upgrade endpoint in Sync Gateway’s Admin REST API.
This endpoint can be run in preview mode (?preview=true) to see which design documents would be removed.
1.x to 1.5
From: Sync Gateway 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4
To: Sync Gateway 1.5
Downtime: Possible downtime in a rolling upgrade; follow the steps below to avoid any downtime.
Upgrade Notes
In this upgrade path, the upgrade process will trigger views in Couchbase Server to be re-indexed. During the re-indexing, operations that are dependent on those views will not be available. The main operations relying on views to be indexed are:
-
A user requests data that doesn’t reside in the channel cache.
-
A new channel or role is granted to a user in the Sync Function.
The unavailability of those operations may result in some requests not being processed. The duration of the downtime will depend on the data set and frequency of replications with mobile clients. To avoid this downtime, it is possible to pre-build the view index before directing traffic to the upgraded node.
Sync Gateway uses Couchbase Server views to index and query documents. When Sync Gateway starts, it will publish a Design Document which contains the View definitions (map/reduce functions) — see Example 2.
{
"views":{
"access":{
"map":"function (doc, meta) { ... }"
},
"channels":{
"map":"function (doc, meta) { ... }"
},
...
},
"index_xattr_on_deleted_docs":true
}Avoiding Downtime
Potential Downtime: Following the Design Document creation, it must run against all the documents in the Couchbase Server bucket to build the index. An index rebuild may also be required during a Sync Gateway upgrade, if the Design Document definition has changed.
To avoid this downtime, you can publish the Design Document and build the index before starting Sync Gateway by using the Couchbase Server REST API. The following curl commands refer to a Sync Gateway 1.3 → Sync Gateway 1.4 upgrade but they apply to any upgrade of Sync Gateway or Accelerator.
-
Start Sync Gateway 1.4 with Couchbase Server instance that isn’t your production environment. Then, copy the Design Document to a file with the following.
$ curl localhost:8092/<BUCKET_NAME>/_design/sync_gateway/ > ddoc.json -
Create a Development Design Document on the cluster where Sync Gateway is going to be upgraded from 1.3:
$ curl -X PUT http://localhost:8092/<BUCKET_NAME>/_design/dev_sync_gateway/ -d @ddoc.json -H "Content-Type: application/json"This should return:
{"ok":true,"id":"_design/dev_sync_gateway"} -
Run a View Query against the Development Design Document. By default, a Development Design Document will index one vBucket per node, however we can force it to index the whole bucket using the
full_setparameter:$ curl "http://localhost:8092/sync_gateway/_design/dev_sync_gateway/_view/role_access_vbseq?full_set=true&stale=false&limit=1"This may take some time to return, and you can track the index’s progress in the Couchbase Server UI. Note that this will consume disk space to build an almost duplicate index until the switch is made.
-
Upgrade Sync Gateway. When Sync Gateway 1.4 starts, it will publish the new Design Document to Couchbase Server. This will match the Development Design Document we just indexed, so will be available immediately.
Couchbase Server Upgrade Paths
| When upgrading your Couchbase Server from 4.x to 5.x, remember to create a Sync Gateway RBAC user on the server — see: Configure Server for Sync Gateway — and to include the user’s credentials username/password in you Sync-Gateway-Config.json file. |
All of the different upgrade paths mentioned above assume that you are running a compatible Couchbase Server version — see Compatibility Matrix.
There are three commonly used upgrade approaches for Couchbase Server. Depending on the one you choose, there may be additional consideration to keep in mind when using Sync Gateway:
| Approach | Downtime | Additional Machine Requirements | Impact when using Sync Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
Rolling Online Upgrade |
None |
Low |
Potential transient connection errors: The Couchbase Server re-balance operations can result in transient connection errors between Couchbase Server and Sync Gateway, which could result in Sync Gateway performance degradation. Potential for unexpected server errors during re-balance: There is an increased potential to lose in-flight ops during a fail-over. |
Upgrade Using Inter-Sync Gateway Replication |
Small amount during switchover |
High - duplicate entire cluster |
Using an XDCR (Cross Data Center Replication) approach will incur some Sync Gateway downtime, but less than other approaches where Sync Gateway is shutdown during the entire Couchbase Server upgrade. It’s important to note that the XDCR replication must be a one way replication from the existing (source) Couchbase Server cluster to the new (target) Couchbase Server cluster, and that no other writes can happen on the new (target) Couchbase Server cluster other than the writes from the XDCR replication, and no Sync Gateway instances should be configured to use the new (target) Couchbase Server cluster until the last step in the process.
Caveats:
|
Offline Upgrade |
During entire upgrade |
None |
|
SG Replicate to Inter-Sync Gateway
Out of the box behavior
Any replications (continuous or ad-hoc) pre-configured in the configuration file’s databases section will run using the SG Replicate protocol. This is subject to any compatibility constraints defined in the Compatibility Matrix.
Existing replications implementing custom conflict resolution strategies (via the REST endpoint) will continue to function in the same manner as for SG Replicate replications after upgrade
Upgrading existing replications
To upgrade existing SG Replicate replications to Inter-Sync Gateway Replication, reconfigure them using Inter-Sync Gateway Replication’s replications property in the configuration file or the REST API — see Upgrade Scenarios for more.
Post-upgrade behavior
- General
-
-
The system supports a rolling upgrade from SG Replicate to inter-Sync Gateway replication.
-
One-shot replications configured at database level will continue as SG Replicate replications.
-
Any configured SG Replicate replications that you want to upgrade to Inter-Sync Gateway must be re-configured using the Inter-Sync Gateway configuration (at database rather than global level) or REST API endpoint (
_replication). -
An pre-2.8 systems using their own custom resolution strategy (via the REST endpoint) will function as they did for SG Replicate replications after upgrading.
-
- Restarting Replications
-
The
replicationIdis used to ensure that any replications previously setup with SG Replicate, automatically restart using inter-Sync Gateway replication. The restart point will be the last checkpoint used, unless over-ridden. - Over-riding restart point
-
To restart a sync from zero: After the upgrade reconfigure the inter-Sync Gateway replication replications to use a different replication_id
Constraints
- Minimum Version for Inter-Sync Gateway Replication
-
In order to support Inter-Sync Gateway Replication, all active nodes in active cluster must be running Sync Gateway 2.8+.
- Replication between two remote databases
-
Replication between two remote databases is no longer supported.
Sync Gateway will log an error and fail to start if a replication defined at the configuration’s root level does not involve at least one local database (source or target).
- Pushing to SG Replicate targets
-
-
Push replications do not support SG Replicate targets with
"allow_conflicts": falseset; the target must use"allow_conflicts": truefor a replication to work. -
Push replications do not use Delta Sync when pushing to a SG Replicate targets
-
Upgrade Scenarios
This section describes recommended upgrade strategies for implementing Inter-Sync Gateway Replication
-
Scenario 1 — Continue with SG Replicate (no conflict resolution)
-
Scenario 2 — Continue with SG Replicate (custom conflict resolution)
-
Scenario 3 — Change to SGR-Replicate 2.0 (default conflict resolution)
-
Scenario 4 — Change to SGR-Replicate 2.0 (custom conflict resolution)
- From
-
-
Source Cluster — Active peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Target Cluster — Passive peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Replication - SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Not implemented
-
- To
-
-
Source Cluster — Active node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Target Cluster — Passive node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Replication — SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Not implemented
-
- Strategy
-
-
Upgrade sequence — Either cluster can be upgraded first
-
Restart point — When the active node restarts it will use SG Replicate and will continue from where it last left off
-
Upgrade Constraint — Replication will be down for the duration of the active node restart
-
- From
-
-
Source Cluster — Active peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Target Cluster — Passive peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Replication — SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Custom conflict resolution with
allow_conflicts=true
-
- To
-
-
Source Cluster — Active node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Target Cluster — Passive node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Replication — SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Custom conflict resolution with
allow_conflicts=true
-
- Strategy
-
-
Upgrade sequence — Either cluster can be upgraded first
-
Restart point — When the active node restarts it will use SG Replicate and will continue from where it last left off
-
Conflict Resolution — Will continue to be handled by the app
-
Upgrade Constraints
-
Replication will be down for the duration of the active node restart
-
The
allow_conflictsflag is ignored for any inter-Sync Gateway replication replications configured.
-
-
- From
-
-
Source Cluster — Active peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Target Cluster — Passive peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Replication — SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Not implemented
-
- To
-
-
Source Cluster — Active node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Target Cluster — Passive node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Replication — Inter-Sync Gateway replication configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Not implemented
-
- Strategy
-
-
Upgrade sequence
-
Stop SG Replicate replications
-
Upgrade each cluster to 2.8.
-
-
Restart Outcomes
-
When The active cluster is restarted it will automatically switch to Inter-Sync Gateway Replication
-
Replication will continue from the last checkpoint, unless over-ridden.
-
ENTERPRISE EDITION The replication will distribute automatically
-
-
Conflict resolution — Default
-
Upgrade Constraint — The
allow_conflictsflag is ignored for any inter-Sync Gateway replication replications configured.
-
- From
-
-
Source Cluster — Active peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Target Cluster — Passive peer running Sync Gateway 2.x or 1.5 (Pre-2.8)
-
Replication — SG Replicate configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Custom conflict resolution with
allow_conflicts=true
-
- To
-
-
Source Cluster — Active node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Target Cluster — Passive node running Sync Gateway 2.8+
-
Replication — inter-Sync Gateway replication configured in continuous or one-shot mode
-
Conflict resolution — Apply custom conflict resolution
-
- Strategy
-
-
Upgrade sequence
-
Stop SG Replicate replications
-
Add the Inter-Sync Gateway replication configuration, including Javascript function as custom_conflict_resolver
-
Upgrade each cluster to 2.8
-
-
Restart Outcomes
-
When the active cluster is restarted it will automatically switch to Inter-Sync Gateway Replication
-
Replication will continue from the last checkpoint, unless over-ridden.
-
ENTERPRISE EDITION The replication will distribute automatically
-
-
Conflict resolution — Conflicts will be handled by the function specified as the as custom_conflict_resolver
-
Upgrade Constraint — The
allow_conflictsflag is ignored for any inter-Sync Gateway replication replications configured.
-
Re-using SG Replicate Checkpoints
You are able to use SG Replicate checkpoint![]() as a starting point for Inter-Sync Gateway replications.
This can save time on larger buckets by avoiding re-processing documents that have previously been replicated.
as a starting point for Inter-Sync Gateway replications.
This can save time on larger buckets by avoiding re-processing documents that have previously been replicated.
To be eligible for re-use use in this way
-
These replication parameters MUST match:
-
Replication ID
-
Direction (push or pull only)
-
Previous Source/Target URLs match Remote URL
-
Channel filters
-
DocID filters
-
-
The new replication must be configured to be unidirectional (there was no bidirectional support prior to 2.8)
Upgrade Steps
-
Have both SG Replicate and Inter-Sync Gateway replications defined in the same config file.
-
Ensure prerequisites from previous slide are fulfilled (matching IDs, params, etc.)
-
On startup, Sync Gateway will determine if replications match, and log:
[DBG] Replicate+: Matched replication IDs for SGR1 checkpoint fallback: &{...} [INF] Replicate: Got SGR1 checkpoint ID for fallback in replication "repl1-push": b8da8486df3093141f7ed225eb2b2afae88ca9ce -
This prevents the SG Replicate replication from running, even though it’s configured.
[INF] Replicate: Replication "repl1-push" was upgraded, preventing startup of SG Replicate replication. [INF] Replicate: Replication "repl1-pull" was upgraded, preventing startup of SG Replicate replication. [INF] Replicate: Starting sg-replicate replications... -
When the Inter-Sync Gateway replication is assigned (even on a different node), the SG Replicate checkpoint is used if no Inter-Sync Gateway checkpoint can be found. Logs:
[DBG] SGCluster+: Replication repl1-pull is assigned to node debbc9ed92243c01 (local node is debbc9ed92243c01) [INF] Replicate: Initializing replication repl1-pull [INF] Replicate: Attempting to fetch SGR1 checkpoint as fallback: 58782a013091ffc0e7e4ae3c4b6abd8baa7149c6 [INF] Replicate: c:repl1-pull-pull using checkpointed seq from SGR1: "3" -
Once the SG Replicate checkpoint is used, it is deleted to ensure it cannot be used as a fallback again in the event Inter-Sync Gateway replication checkpoints
 are removed.
are removed.
Upgrade from Views to GSI
Prior to 2.1, Sync Gateway used system views for a variety of internal operations, including authentication and replication. Starting in 2.1, Sync Gateway will use GSI and N1QL to perform those tasks.
The upgrade, from using views to using Global Secondary Indexes and N1QL, happens automatically when starting a Sync Gateway 2.1 or above node in a cluster that was previously using views.
Use of GSI requires Couchbase Server 5.5, with at least one node running the Query and Index Services.
Users wanting to run Sync Gateway 2.1 or above with an older version of Couchbase Server will need to continue to use views, by setting the use_views property.
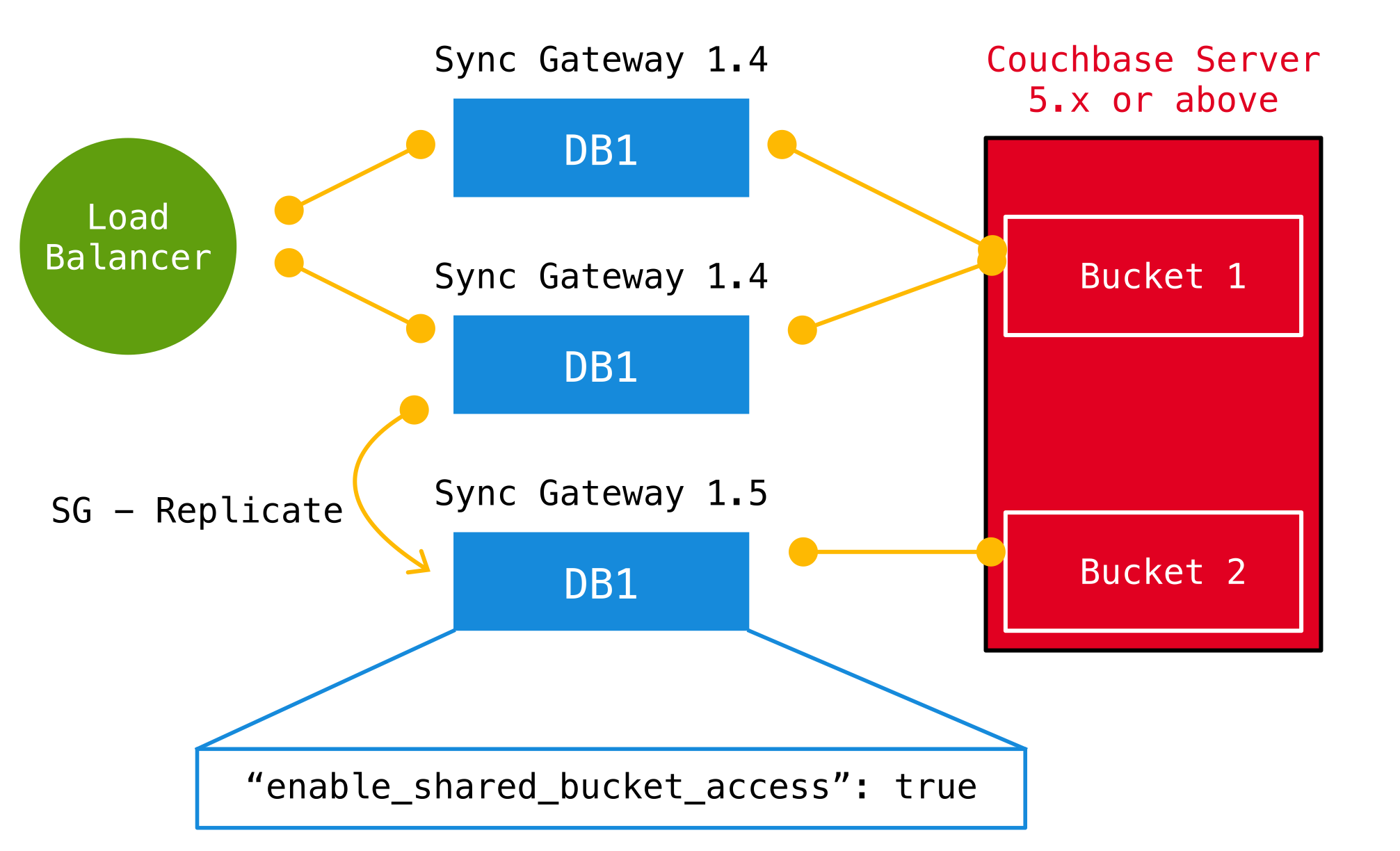
Upgrade to Shared Bucket
Implementation notes for XATTRs:
Mobile applications require additional metadata in order to manage security and replication. In previous versions of Sync Gateway, this information has always been stored in the document body. Sync Gateway 1.5 utilizes a new feature of Couchbase Server 5.0 called XATTRs (x-attributes) to store that metadata into an external document fragment.
Extended attributes (xattrs) are JSON objects that can be associated with Couchbase documents. Each document can be associated with zero or more extended attributes. There are currently three types (user, system, virtual). Mobile Convergence uses a system extended attribute, which has the following characteristics central to convergence:
-
Shares lifetime with the document metadata - when a document is deleted, system xattrs are preserved with the tombstone.
-
Allocated 1MB of storage, independent of the 20MB available for the document
Extended attributes are stored as part of the document, and are replicated with the document (both intra-cluster replication and XDCR).
Extended attributes can be accessed via the SDKs using the sub-document API, via command-line tools, and via views.
They are also accessible from N1QL in Couchbase Server 5.5 or above with the ().xattrs property. For example, SELECT meta().xattrs._sync from travel-sample where Meta().id = "user::demo";.
| The sync metadata is maintained internally by Sync Gateway and its structure can change at any time. It should not be used to drive business logic of applications. The direct use of the N1QL query is unsupported and must not be used in production environments. |
The raw endpoint on Sync Gateway’s Admin REST API returns both the document and its associated mobile metadata.
Configuration Changes
Before |
After |
Sync Gateway 1.5 or above
|
Sync Gateway 1.5 or above
|
After restarting Sync Gateway with the updated configuration file, the mobile metadata for existing documents is automatically migrated.
To enable shared bucket on incoming documents, one Sync Gateway node in the cluster must also have the Enabling shared bucket access on your existing deployment is not reversible. It is recommended to test the upgrade on a staging environment before upgrading the production environment. The known issue CBG-394, means that the upgrade will require downtime when enabling shared bucket access on an existing deployment that is running with GSI indexing. This is to allow all documents to migrate, using index-based data requests whilst migration is in progress could result in an incomplete data set being returned (containing only those docs migrated at the time of the request). You are advised to schedule a maintenance window to allow time for migration to complete. |
|
Sync Gateway 2.1 or above
|
Sync Gateway 2.1 or above
|
After restarting Sync Gateway with the updated configuration file, the number of Index Replicas in the Couchbase Server cluster is automatically updated. |
|
Migrating from Bucket Shadowing
As of Sync Gateway 1.5, the Bucket Shadowing feature is deprecated and no longer supported. The following steps outline a recommended method for migrating from Bucket Shadowing to the latest version with interoperability between Couchbase Server SDKs and Couchbase Mobile.
-
Follow the recommendations in the Couchbase Server documentation to upgrade all instances to 5.0.
-
Create a new bucket on Couchbase Server (bucket 2).
-
Install Sync Gateway 1.5 on a separate node with shared access enabled and connect it to the new bucket (bucket 2).
-
Setup a push replication from the Sync Gateway instance used for Bucket Shadowing to the Sync Gateway 1.5 instance.
-
Once the replication has completed, test your application is performing as expected.
-
Update the load balancer to direct incoming traffic to the Sync Gateway 1.5 instance when you are ready to upgrade.
-
Delete the first bucket (bucket 1).