How to use the Cost-Based Optimizer and manage optimizer statistics.
This guide is for Couchbase Server.
Introduction
In Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition, the Cost-Based Optimizer enables the Query Service to create the most efficient plan to execute a query. The Cost-Based Optimizer analyzes keyspace statistics, index statistics, and distribution statistics to select the optimal indexes and create the query execution plan.
The Cost-Based Optimizer can generate a query plan for SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, MERGE, and INSERT INTO with SELECT queries.
| If the Cost-Based Optimizer is unavailable or inactive, or if statistics are not available, the Query Service falls back on the legacy rules-based optimizer to generate the query execution plan. |
If you want to try out the examples in this section, follow the instructions given in Do a Quick Install to install Couchbase Server, configure a cluster, and load a sample dataset. Read the following for further information about the tools available for editing and executing queries:
Activating the Cost-Based Optimizer
The Cost-Based Optimizer is active by default. This section shows how to activate or deactivate the Cost-Based Optimizer for a request. You can also activate or deactivate the Cost-Based Optimizer for a query node, or for all the query nodes in the cluster.
-
Query Workbench
-
CBQ Shell
To activate or deactivate the Cost-Based Optimizer for a request, use the Query Run-Time Preferences window.
-
Click the cog icon to display the Run-Time Preferences window.
-
Check or uncheck the Use Cost-Based Optimizer box as required.
-
Choose Save Preferences to save the preferences and return to the Query Workbench.
The following setting deactivates the Cost-Based Optimizer for subsequent requests on this Query node.
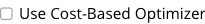
The following setting activates the Cost-Based Optimizer for subsequent requests on this Query node.
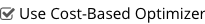
To activate or deactivate the Cost-Based Optimizer for a request, use \SET command with the use_cbo parameter.
The parameter name must be prefixed by a hyphen.
The parameter is set to true by default.
|
For example, the following code deactivates the Cost-Based Optimizer for subsequent requests on this Query node.
\SET -use_cbo false;The following code activates the Cost-Based Optimizer for subsequent requests on this Query node.
\SET -use_cbo true;For more information and examples, see Settings and Parameters.
Updating Statistics
Before you can use the Cost-Based Optimizer with a query, you must first gather the statistics that it needs.
When you use an index with a query, you typically create the index on the fields which the query uses to filter. To use the cost-based optimizer with that query, you must collect statistics on the same fields that you used to create the index.
A query may have predicates on non-indexed fields, and you can collect statistics on those fields also to help the optimizer.
For a query which filters on an array or array of objects, you must collect the statistics using exactly the same expression that you used to create the index.
Updating Statistics for Expressions
To gather statistics for specified expressions, use the UPDATE STATISTICS command.
The following example creates two indexes, gathers statistics for the index key expressions and for predicate required by the query, and then runs the query.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
CREATE INDEX idx_country_city ON hotel(country, city);
CREATE INDEX idx_city_country ON hotel(city, country);UPDATE STATISTICS FOR hotel(city, country, free_breakfast);SELECT COUNT(*) FROM hotel
WHERE country = 'United States' AND free_breakfast = true;For more information and examples, see Update Statistics for Index Expressions.
Updating Statistics for an Index
To gather statistics for all the index key expressions used by an index, use the UPDATE STATISTICS command with the INDEX clause.
For example, the following query gathers statistics for all the index expressions used by the specified index.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
UPDATE STATISTICS FOR
INDEX airport.def_inventory_airport_city;For more information and examples, see Update Statistics for a Single Index.
Updating Statistics for Multiple Indexes
To gather statistics for all the index key expressions used by multiple indexes, use the UPDATE STATISTICS command with the INDEX clause and a list of index names.
For example, the following query gathers statistics for the index expressions used by the specified indexes.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
UPDATE STATISTICS FOR airport
INDEX (def_inventory_airport_faa, def_inventory_airport_city);The following query gathers statistics for the index expressions used by all indexes in the specified keyspace.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
UPDATE STATISTICS FOR airport INDEX ALL;For more information and examples, see Update Statistics for Multiple Indexes.
Deleting Statistics
To delete statistics, use the UPDATE STATISTICS command with the DELETE clause.
| Deleting statistics for a set of index expressions effectively turns off the Cost-Based Optimizer for queries which use predicates on those expressions. |
For example, the following query deletes statistics for the specified index expressions.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
UPDATE STATISTICS FOR hotel
DELETE (city, country, free_breakfast);The following query deletes statistics for the index expressions used by all indexes in the specified keyspace.
Set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Setting the Query Context.
UPDATE STATISTICS FOR airport DELETE ALL;For more information and examples, see Delete Statistics.