MERGE
- reference
A MERGE statement provides the ability to update, insert into, or delete from a keyspace based on the results of a join with another keyspace or subquery. It is possible to specify actions (insert, update, delete) on the keyspace based on a match or no match in the join. Multiple actions can be specified in the same query.
Couchbase Server supports two types of merge clause, which are described in the sections below: ANSI Merge and Lookup Merge.
| The ANSI merge clause has much more flexible functionality than its earlier legacy equivalent. Since it is standard compliant and more flexible, we recommend you to use ANSI merge exclusively, where possible. |
Privileges
User executing the MERGE statement must have the following privileges:
-
Query Select privileges on the source keyspace
-
Query Insert, Query Update, or Query Delete privileges on the target keyspace as per the MERGE actions
-
Query Select privileges on the keyspaces referred in the RETURNING clause
For more details about user roles, refer to Authorization.
| A user with the Data Writer privilege may set documents to expire. When the document expires, the data service deletes the document, even though the user may not have the Query Delete privilege. |
Syntax
merge ::= 'MERGE' 'INTO' ( ansi-merge | lookup-merge ) limit-clause? returning-clause?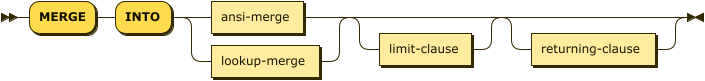
| ansi-merge | |
| lookup-merge | |
| limit-clause | |
| returning-clause |
ANSI Merge
ansi-merge ::= target-keyspace use-index-clause 'USING' ansi-merge-source
ansi-merge-predicate ansi-merge-actions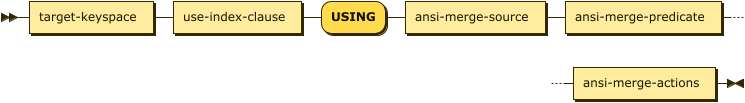
| target-keyspace | |
| use-index-clause | |
| ansi-merge-source | |
| ansi-merge-predicate | |
| ansi-merge-actions |
ANSI Merge Target
target-keyspace ::= keyspace-ref ( 'AS'? alias )?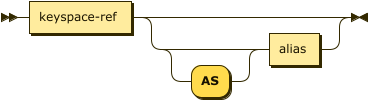
The merge target is the keyspace which you want to update, insert into, or delete from.
| keyspace-ref | |
| alias |
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?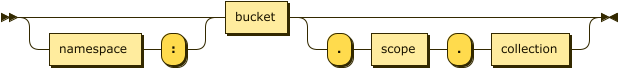
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Keyspace reference for the merge target. For more details, refer to Keyspace Reference.
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the keyspace reference. For details, refer to AS Clause.
Assigning an alias to the keyspace reference is optional.
If you assign an alias to the keyspace reference, the AS keyword may be omitted.
ANSI Merge Target Hint
You can use a USE INDEX hint on the merge target to specify that the merge should use a particular index.
For details, refer to USE INDEX Clause.
The USE INDEX hint is the only hint allowed on the target.
You cannot specify a USE KEYS hint or a join hint (USE NL or USE HASH) on the target of a merge statement.
|
ANSI Merge Source
ansi-merge-source ::= ( merge-source-keyspace | merge-source-subquery | merge-source-expr )
ansi-join-hints?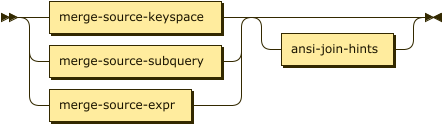
The merge source is the recordset that you want to merge with the merge target. It can be a keyspace reference, a subquery, or a generic expression.
| merge-source-keyspace | |
| merge-source-subquery | |
| merge-source-expr | |
| ansi-join-hints |
ANSI Merge Keyspace
merge-source-keyspace ::= keyspace-ref ( 'AS'? alias )?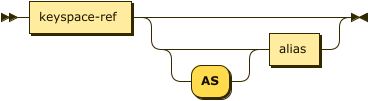
| keyspace-ref | |
| alias |
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Keyspace reference for the merge source. For details, refer to Keyspace Reference.
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the keyspace reference. For details, refer to AS Clause.
Assigning an alias to the keyspace reference is optional.
If you assign an alias to the keyspace reference, the AS keyword may be omitted.
ANSI Merge Subquery
merge-source-subquery ::= subquery-expr 'AS'? alias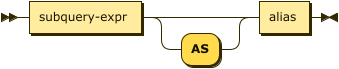
| subquery-expr | |
| alias |
Subquery Expression
subquery-expr ::= '(' select ')'
Use parentheses to specify a subquery for the merge source. For details, refer to Subqueries.
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the subquery. For details, refer to AS Clause.
You must assign an alias to a subquery on the merge source.
However, when you assign an alias to the subquery, the AS keyword may be omitted.
ANSI Merge Expression
merge-source-expr ::= expr ( 'AS'? alias )?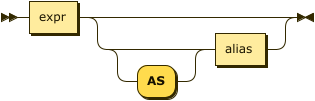
| expr |
A SQL++ expression generating JSON documents or objects for the merge source. |
| alias |
AS Alias
Assigns another name to the generic expression. For details, refer to AS Clause.
Assigning an alias to the generic expression is optional.
If you assign an alias to the generic expression, the AS keyword may be omitted.
ANSI Merge Source Hints
You can specify ANSI join hints (USE HASH or USE NL) on the source of an ANSI merge.
For details, refer to ANSI JOIN Hints.
|
If the merge source is a keyspace, you can also specify a If the merge action is update or delete, you can specify any of the join methods: If the merge action is insert, the only join methods you can specify are The ANSI join hint is optional.
If omitted, the default hint is If you are using a nested-loop join, i.e. |
ANSI Merge Predicate
ansi-merge-predicate ::= 'ON' expr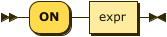
The merge predicate enables you to specify an ANSI join between the merge source and the merge target.
| expr |
Boolean expression representing the join condition. This expression may contain fields, constant expressions, or any complex SQL++ expression. |
ANSI Merge Actions
ansi-merge-actions ::= merge-update? merge-delete? ansi-merge-insert?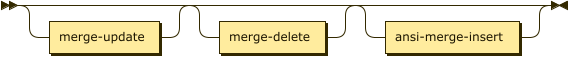
The merge actions enable you to specify insert, update, and delete actions on the target keyspace, based on a match or no match in the join.
| merge-update | |
| merge-delete | |
| ansi-merge-insert |
ANSI Merge Update
merge-update ::= 'WHEN' 'MATCHED' 'THEN' 'UPDATE' set-clause? unset-clause? where-clause?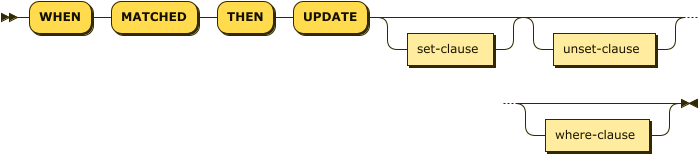
Updates a document that already exists with updated values.
| set-clause | |
| unset-clause | |
| where-clause |
SET Clause
set-clause ::= 'SET' ( meta '=' expiration | path '=' expr update-for? )
( ',' ( meta '=' expiration | path '=' expr update-for? ) )*
Specifies the value for an attribute to be changed. Also enables you to set the expiration of the document. For more details, refer to SET Clause.
| update-for |
UNSET Clause
unset-clause ::= 'UNSET' path update-for? (',' path update-for?)*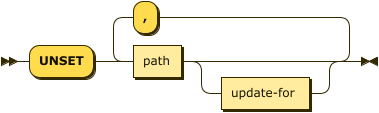
Removes a specified attribute from the document. For more details, refer to UNSET Clause.
| update-for |
FOR Clause
update-for ::= ('FOR' (name-var ':')? var ('IN' | 'WITHIN') path
(',' (name-var ':')? var ('IN' | 'WITHIN') path)* )+
('WHEN' cond)? 'END'
path ::= identifier ( '[' expr ']' )* ( '.' identifier ( '[' expr ']' )* )*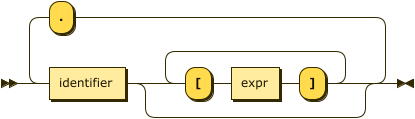
Iterates over a nested array to SET or UNSET the given attribute for every matching element in the array. For more details, refer to FOR Clause.
WHERE Clause
where-clause ::= 'WHERE' cond
Optionally specifies a condition that must be met for data to be updated. For more details, refer to WHERE Clause.
ANSI Merge Delete
merge-delete ::= 'WHEN' 'MATCHED' 'THEN' 'DELETE' where-clause?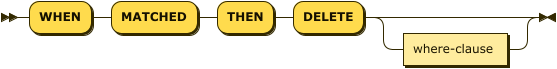
Removes the specified document from the keyspace.
| where-clause |
WHERE Clause
where-clause ::= 'WHERE' cond
Optionally specifies a condition that must be met for data to be deleted. For more details, refer to WHERE Clause.
ANSI Merge Insert
ansi-merge-insert ::= 'WHEN' 'NOT' 'MATCHED' 'THEN' 'INSERT' '(' 'KEY'? key
( ',' 'VALUE'? value )? ( ',' 'OPTIONS'? options )? ')' where-clause?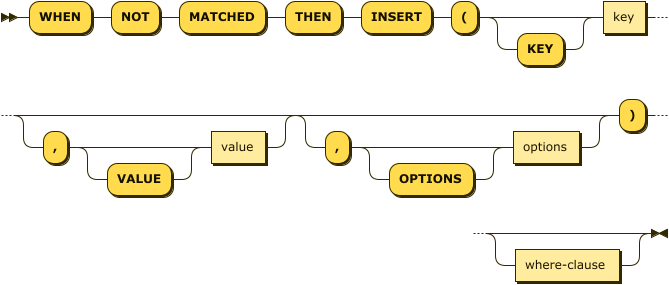
Inserts a new document into the keyspace. Use parentheses to specify the key and value for the inserted document, separated by a comma.
| Use the UUID() function to generate a random, unique document key. |
| key |
An expression specifying the key for the inserted document. The |
| value |
[Optional] An expression specifying the value for the inserted document. If the value is omitted, an empty document is inserted. The |
| options |
[Optional] An object representing the metadata to be set for the inserted document.
Only the
The |
| where-clause |
WHERE Clause
where-clause ::= 'WHERE' cond
Optionally specifies a condition that must be met for data to be inserted. For more details, refer to WHERE clause.
Lookup Merge
lookup-merge ::= target-keyspace 'USING' lookup-merge-source lookup-merge-predicate
lookup-merge-actions
| target-keyspace | |
| lookup-merge-source | |
| lookup-merge-predicate | |
| lookup-merge-actions |
Lookup Merge Target
Keyspace reference for the merge target. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Target.
Lookup Merge Source
lookup-merge-source ::= merge-source-keyspace use-clause? |
merge-source-subquery |
merge-source-expr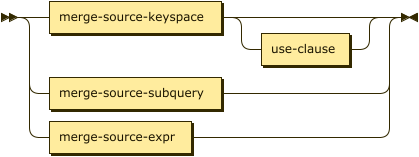
The merge source is the recordset that you want to merge with the merge target. It can be a keyspace reference, a subquery, or a generic expression.
| merge-source-keyspace | |
| use-clause | |
| merge-source-subquery | |
| merge-source-expression |
Lookup Merge Keyspace
Keyspace reference for the merge source. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Keyspace.
Lookup Merge Source Hint
If the merge source is a keyspace, you can specify a USE KEYS or USE INDEX hint on the merge source. For details, refer to USE clause.
Lookup Merge Subquery
Specifies a subquery for the merge source. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Subquery.
Lookup Merge Expression
Specifies a generic expression for the merge source. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Expression.
Lookup Merge Predicate
lookup-merge-predicate ::= 'ON' 'PRIMARY'? 'KEY' expr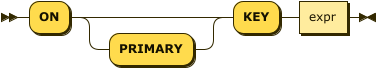
The merge predicate produces a document key for the target of the lookup merge.
| expr |
[Required] String or expression representing the primary key of the documents for the target keyspace. |
Lookup Merge Actions
lookup-merge-actions ::= merge-update? merge-delete? lookup-merge-insert?
The merge actions enable you to specify insert, update, and delete actions on the target keyspace, based on a match or no match in the join.
| merge-update | |
| merge-delete | |
| lookup-merge-insert |
Lookup Merge Update
Updates a document that already exists with updated values. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Update.
Lookup Merge Delete
Removes the specified document from the keyspace. The syntax is the same as for an ANSI merge. Refer to ANSI Merge Delete for details.
Lookup Merge Insert
lookup-merge-insert ::= 'WHEN' 'NOT' 'MATCHED' 'THEN' 'INSERT' expr where-clause?
Inserts a new document into the keyspace. The key specified in the Lookup Merge Predicate is used as the key for the newly inserted document.
| expr |
An expression specifying the value for the inserted document. |
| where-clause |
| The Lookup Merge Insert syntax does not enable you to specify the document expiration. If you need to specify the document expiration, rewrite the query using the ANSI Merge Insert syntax. |
WHERE Clause
where-clause ::= 'WHERE' cond
Optionally specifies a condition that must be met for data to be inserted. For more details, refer to WHERE clause.
Common Clauses
The following clauses are common to both ANSI Merge and Lookup Merge.
LIMIT Clause
limit-clause ::= 'LIMIT' expr
Specifies the minimum number of records to be processed. For more details, refer to LIMIT Clause.
RETURNING Clause
returning-clause ::= 'RETURNING' (result-expr (',' result-expr)* |
('RAW' | 'ELEMENT' | 'VALUE') expr)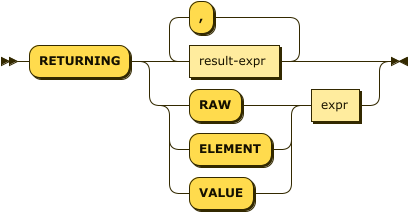
Specifies the information to be returned by the operation as a query result. For more details, refer to RETURNING Clause.
Examples
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
Please note that the examples below will alter the data in your sample buckets.
To restore your sample data, remove and reinstall the travel-sample bucket.
Refer to Sample Buckets for details.
|
This example updates the vacancy field based on the source expression.
MERGE INTO hotel t
USING [
{"id":"21728", "vacancy": true},
{"id":"21730", "vacancy": true}
] source
ON meta(t).id = "hotel_" || source.id
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET t.old_vacancy = t.vacancy,
t.vacancy = source.vacancy
RETURNING meta(t).id, t.old_vacancy, t.vacancy;This example finds all BA routes whose source airport is in France. If any flights are using equipment 319, they are updated to use 797. If any flights are using equipment 757, they are deleted.
MERGE INTO route
USING airport
ON route.sourceairport = airport.faa
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE
SET route.old_equipment = route.equipment,
route.equipment = "797",
route.updated = true
WHERE airport.country = "France"
AND route.airline = "BA"
AND CONTAINS(route.equipment, "319")
WHEN MATCHED THEN DELETE
WHERE airport.country = "France"
AND route.airline = "BA"
AND CONTAINS(route.equipment, "757")
RETURNING route.old_equipment, route.equipment, airport.faa;This example compares a source set of airport data with the airport keyspace data.
If the airport already exists in the airport keyspace, the record is updated.
If the airport does not exist in the airport keyspace, a new record is created.
MERGE INTO airport AS target
USING [
{"iata":"DSA", "name": "Doncaster Sheffield Airport"},
{"iata":"VLY", "name": "Anglesey Airport / Maes Awyr Môn"}
] AS source
ON target.faa = source.iata
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET target.old_name = target.airportname,
target.airportname = source.name,
target.updated = true
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT (KEY UUID(),
VALUE {"faa": source.iata,
"airportname": source.name,
"type": "airport",
"inserted": true} )
RETURNING *;This example compares a source set of airport data with the airport keyspace data.
If the airport already exists in the airport keyspace, the record is updated, and the existing document expiration is preserved.
If the airport does not exist in the airport keyspace, a new record is created with an expiration of one week.
MERGE INTO airport AS target
USING [
{"iata":"DSA", "name": "Doncaster Sheffield Airport"},
{"iata":"VLY", "name": "Anglesey Airport / Maes Awyr Môn"}
] AS source
ON target.faa = source.iata
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET target.old_name = target.airportname,
target.airportname = source.name,
target.updated = true,
meta(target).expiration = meta(target).expiration
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT (KEY UUID(),
VALUE {"faa": source.iata,
"airportname": source.name,
"type": "airport",
"inserted": true},
OPTIONS {"expiration": 7*24*60*60} );Note that it is possible to preserve the document expiration using the request-level preserve_expiry parameter.
Lookup merge version of Example 1.
MERGE INTO hotel t
USING [
{"id":"21728", "vacancy": true},
{"id":"21730", "vacancy": true}
] source
ON KEY "hotel_"|| source.id
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET t.old_vacancy = t.vacancy, t.vacancy = source.vacancy
RETURNING meta(t).id, t.old_vacancy, t.vacancy;The following statement updates product based on orders.
MERGE INTO product p USING orders o ON KEY o.productId
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET p.lastSaleDate = o.orderDate
WHEN MATCHED THEN
DELETE WHERE p.inventoryCount <= 0;The following statement merges two datasets containing employee information.
It then updates all_empts on match with emps_deptb and inserts when there is no match.
MERGE INTO all_empts a USING emps_deptb b ON KEY b.empId
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET a.depts = a.depts + 1
a.title = b.title || ", " || b.title
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT { "name": b.name,
"title": b.title,
"depts": b.depts,
"empId": b.empId,
"dob": b.dob };