DROP VECTOR INDEX
- reference
- Couchbase Server 8.0
The DROP VECTOR INDEX statement allows you to drop a Hyperscale Vector index, a Composite Vector index, or a secondary index. Dropping an index that has replicas will drop all of the replica indexes too.
The DROP INDEX statement is a synonym for the DROP VECTOR INDEX statement. Both statements have the same functionality.
| To drop a primary index, use the DROP PRIMARY INDEX statement. For compatibility with legacy versions of Couchbase Server, you can also use DROP INDEX or DROP VECTOR INDEX to drop a named primary index. |
Prerequisites
RBAC Privileges
To use the DROP VECTOR INDEX statement, you must have the Query Manage Index privilege on the keyspace or bucket.
For more information about user roles, see
Authorization.
Syntax
drop-vector-index ::= 'DROP' 'VECTOR' 'INDEX' ( index-path-and-name | index-name-on-keyspace )
index-using?
The DROP VECTOR INDEX statement provides two possible syntaxes for specifying the index and the keyspace where the index is located.
| index-path-and-name |
(Optional) One possible syntax for specifying the index and keyspace. See Index Path and Name. |
| index-name-on-keyspace |
(Optional) The other possible syntax for specifying the index and keyspace. See Index Name ON Keyspace Reference. |
| index-using |
(Optional) Specifies the index type. See USING Clause. |
Index Path and Name
index-path-and-name ::= index-path '.' index-name ( 'IF' 'EXISTS' )? |
'IF' 'EXISTS' index-path '.' index-name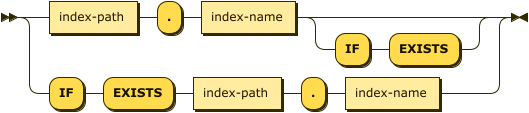
You can use a dotted notation to specify the index and the keyspace on which the index is built. This syntax provides compatibility with legacy versions of Couchbase Server.
| index-name |
(Required) A unique name that identifies the index. |
| index-path |
(Required) See Index Path. |
| If there is a hyphen (-) inside the index name or any part of the index path, you must wrap the index name or that part of the index path in backticks (` `). See the examples on this page. |
Index Path
index-path ::= keyspace-full | keyspace-prefix | keyspace-partial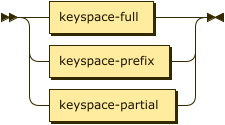
The index path may be a full keyspace path, a keyspace prefix, or a keyspace partial.
Index Path: Full Keyspace
keyspace-full ::= namespace ':' bucket '.' scope '.' collection
If the index is built on a named collection, the index path may be a full keyspace path, including namespace, bucket, scope, and collection, followed by the index name. In this case, the query context is ignored.
| namespace |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
| scope |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the scope name of the keyspace. |
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, default:`travel-sample`.inventory.airline.`idx-name` indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection in the inventory scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Index Path: Keyspace Prefix
keyspace-prefix ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket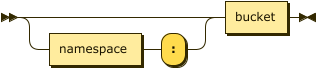
If the index is built on the default collection in the default scope within a bucket, the index path may be just an optional namespace and the bucket name, followed by the index name. In this case, the query context should not be set.
| namespace |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
For example, default:`travel-sample`.def_type indicates the def_type index on the default collection in the default scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Index Path: Keyspace Partial
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Alternatively, if the keyspace is a named collection, the index path may be just the collection name, followed by the index name. In this case, you must set the query context to indicate the required namespace, bucket, and scope.
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, airline.`idx-name` indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection, assuming that the query context is set.
Index Name ON Keyspace Reference
index-name-on-keyspace ::= ( index-name ( 'IF' 'EXISTS' )? | 'IF' 'EXISTS' index-name )
'ON' keyspace-ref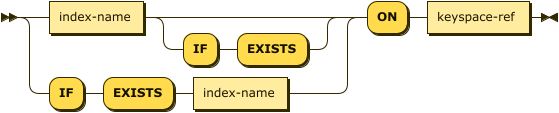
You can use the index name with the ON keyword and a keyspace reference to specify the index and the keyspace on which the index is built.
| index-name |
(Required) A unique name that identifies the index. |
| keyspace-ref |
(Required) See Keyspace Reference. |
| If there is a hyphen (-) inside the index name or any part of the keyspace reference, you must wrap the index name or that part of the keyspace reference in backticks (` `). See the examples on this page. |
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
The keyspace reference may be a keyspace path or a keyspace partial.
Keyspace Reference: Keyspace Path
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?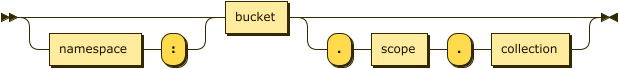
If the keyspace is a named collection, or the default collection in the default scope within a bucket, the keyspace reference may be a keyspace path. In this case, the query context should not be set.
| namespace |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
| scope |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the scope name of the keyspace. If omitted, the bucket’s default scope is used. |
| collection |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. If omitted, the default collection in the bucket’s default scope is used. |
For example, def_type ON default:`travel-sample` indicates the def_type index on the default collection in the default scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Similarly, `idx-name` ON default:`travel-sample`.inventory.airline indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection in the inventory scope in the default:`travel-sample` bucket.
Keyspace Reference: Keyspace Partial
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Alternatively, if the keyspace is a named collection, the keyspace reference may be just the collection name. In this case, you must set the query context to indicate the required namespace, bucket, and scope.
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, `idx-name` ON airline indicates the idx-name index on the airline collection, assuming the query context is set.
IF EXISTS Clause
The optional IF EXISTS clause enables the statement to complete successfully when the specified index does not exist.
If the index does not exist within the specified keyspace, then:
-
If this clause is not present, an error is generated.
-
If this clause is present, the statement does nothing and completes without error.
Usage
When using memory-optimized indexes, DROP VECTOR INDEX is an expensive operation and may take a few minutes to complete.
If you drop an index with replicas while one of the index nodes is failed over, then only the replicas in the active index nodes are dropped. If the failed-over index node is recovered, then the orphan replica will be dropped when this failed-over indexer is added back to cluster.
If you drop an index with replicas when one of the index nodes is unavailable but not failed over, the drop index operation may fail.
If you drop an index which is scheduled for background creation, a warning message is generated, but the drop index operation succeeds.
|
Attention
Do not drop (or create) secondary indexes, Composite Vector indexes, or Hyperscale Vector indexes when any Index service node is down, as this may result in duplicate index names. |
Examples
To try the examples in this section, you must install the vector sample data as described in Prerequisites.
For this example, the path to the required keyspace is specified by the query, so you do not need to set the query context.
Drop the Hyperscale Vector index called color_desc_hyperscale, if it exists.
DROP VECTOR INDEX `color_desc_hyperscale`
IF EXISTS
ON `vector-sample`.color.rgbThe following command would drop the index in exactly the same way, but uses alternative syntax.
DROP VECTOR INDEX IF EXISTS
default:`vector-sample`.color.rgb.`color_desc_hyperscale`