CREATE INDEX
- reference
The CREATE INDEX statement allows you to create secondary indexes.
Secondary indexes contain a filtered or a full set of keys in a given keyspace.
Secondary indexes are optional but increase query efficiency on a keyspace.
In Couchbase Server 8.0 and later, the CREATE INDEX statement also allows you to create Composite Vector indexes.
To create Hyperscale Vector indexes, use the CREATE VECTOR INDEX statement.
Purpose
CREATE INDEX allows you to make multiple concurrent index creation requests.
The command starts a task to create the index definition in the background.
If there is an index creation task already running, the Index Service queues the incoming index creation request.
CREATE INDEX returns as soon as the index creation phase is complete.
By default, when the index creation phase is complete, the Index Service triggers the index build phase.
If you lose connectivity, the index build operation continues in the background.
You can defer the index build phase using the defer_build clause.
In deferred build mode, CREATE INDEX creates the index definition, but does not trigger the index build phase.
You can then build the index using the BUILD INDEX command.
You can create multiple identical secondary indexes on a keyspace and place them on separate nodes for better index availability.
In Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition, the recommended way to do this is using the num_replica option.
In Couchbase Server Community Edition, you need to create multiple identical indexes and place them using the nodes option.
For more information, see WITH Clause.
Hyperscale Vector indexes and Composite Vector indexes require a codebook for the vector field. The codebook is the result of sampling the dataset and is saved as part of the index metadata.
The codebook is created as part of the BUILD INDEX process, and is not incrementally updated. If the data set changes dramatically, you must drop and rebuild the index to update the codebook.
Prerequisites
RBAC Privileges
To execute the CREATE INDEX statement, you must have the Query Manage Index privilege granted on the keyspace.
For more information about user roles, see
Authorization.
Syntax
create-index ::= 'CREATE' 'INDEX' ( index-name ( 'IF' 'NOT' 'EXISTS' )? |
'IF' 'NOT' 'EXISTS' index-name ) 'ON' keyspace-ref
'(' index-keys-and-attribs ')'
index-partition? where-clause? index-using? index-with?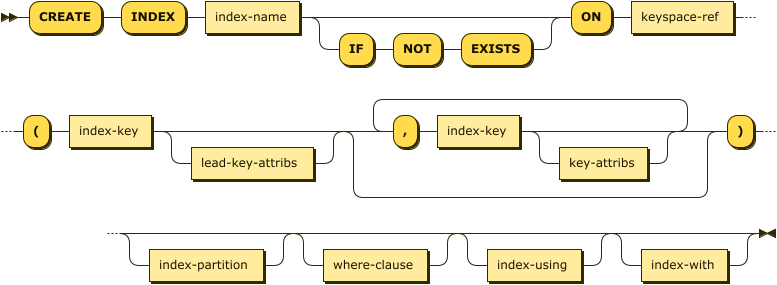
| index-name |
(Required) A unique name that identifies the index. Valid GSI index names can contain any of the following characters: |
| keyspace-ref |
(Required) Specifies the keyspace where the index is created. See Keyspace Reference. |
| index-keys-and-attribs |
(Required) Specifies the index keys and index key attributes. See Index Keys and Attributes. |
| index-partition |
(Optional) Specifies index partitions. See PARTITION BY HASH Clause. |
| where-clause |
(Optional) Specifies filters for a partial index. See WHERE Clause. |
| index-using |
(Optional) Specifies the index type. See USING Clause. |
| index-with |
(Optional) Specifies options for the index. See WITH Clause. |
IF NOT EXISTS Clause
The optional IF NOT EXISTS clause enables the statement to complete successfully when the specified index already exists.
If an index with the same name already exists within the specified keyspace, then:
-
If this clause is not present, an error is generated.
-
If this clause is present, the statement does nothing and completes without error.
Keyspace Reference
keyspace-ref ::= keyspace-path | keyspace-partial
Specifies the keyspace for which the index needs to be created. The keyspace reference may be a keyspace path or a keyspace partial.
| If there is a hyphen (-) inside any part of the keyspace reference, you must wrap that part of the keyspace reference in backticks (` `). See the examples on this page. |
Keyspace Path
keyspace-path ::= ( namespace ':' )? bucket ( '.' scope '.' collection )?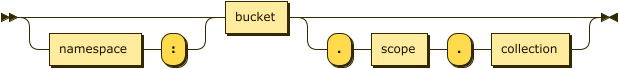
If the keyspace is a named collection, or the default collection in the default scope within a bucket, the keyspace reference may be a keyspace path. In this case, the query context should not be set.
| namespace |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the namespace of the keyspace.
Currently, only the |
| bucket |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the bucket name of the keyspace. |
| scope |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the scope name of the keyspace. If omitted, the bucket’s default scope is used. |
| collection |
(Optional) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. If omitted, the default collection in the bucket’s default scope is used. |
For example, default:`travel-sample` indicates the default collection in the default scope in the travel-sample bucket in the default namespace.
Similarly, default:`travel-sample`.inventory.airline indicates the airline collection in the inventory scope in the travel-sample bucket in the default namespace.
Keyspace Partial
keyspace-partial ::= collection
Alternatively, if the keyspace is a named collection, the keyspace reference may be just the collection name with no path. In this case, you must set the query context to indicate the required namespace, bucket, and scope.
| collection |
(Required) An identifier that refers to the collection name of the keyspace. |
For example, airline indicates the airline collection, assuming the query context is set.
Index Keys and Attributes
index-keys-and-attribs ::= index-key lead-key-attribs? ( ( ',' index-key key-attribs? )+ )?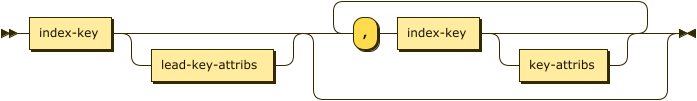
Secondary indexes and Composite Vector indexes can have many keys. Each key may have index attributes, which define the behavior of the index key.
| index-key |
(Required) Specifies an index key. See Index Key. |
| lead-key-attribs |
(Optional) Specifies attributes for the leading index key. See Index Key Attributes. |
| key-attribs |
(Optional) Specifies attributes for a non-leading index key. See Index Key Attributes. |
Index Key
index-key ::= expr | array-expr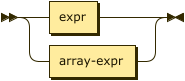
The index key is a SQL++ expression referring to a field in the document, or an ARRAY expression on the field.
For a Composite Vector index, one index key must refer to a vector field in the document. The index key that refers to a vector field may be the only index key. If there are multiple index keys, the index key referring to the vector field may be any of the index keys, including the leading index key.
| expr |
A field name or a scalar function over any field in the document. This cannot use constant expressions, aggregate functions, or sub-queries. For a vector field, the expression may be the field name, or a BASE64_DECODE() function on the vector field — this is necessary if the embedded vectors are stored as a base64-encoded string. |
| array-expr |
An array expression. Array indexing enables you to create global indexes on array elements and optimize the execution of queries involving array elements. For a vector field, only ALL ARRAY is supported. The FLATTEN_KEYS() function is supported, but more than one key in FLATTEN_KEYS() is not permitted. For more information, see Array Indexing. |
Index Key Attributes
lead-key-attribs ::= index-order include-missing? |
include-missing index-order? |
index-vector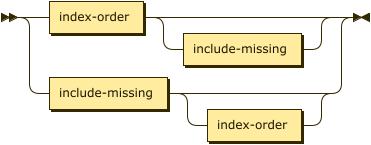
key-attribs ::= index-order | index-vector
Specifies attributes for the index key.
| index-order |
(Optional) Any index key on a non-vector field may include an index order clause. See Index Order. |
| include-missing |
(Optional) If the leading index key is a non-vector field, it may also include the |
| include-vector |
(Optional) In a Composite Vector index, one index key must include the |
Index Order
index-order ::= 'ASC' | 'DESC'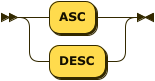
Specifies the sort order of the index key. For non-vector fields only.
ASC
|
The index key is sorted in ascending order. |
DESC
|
The index key is sorted in descending order. |
This clause is optional; if omitted, the default is ASC.
INCLUDE MISSING Clause
include-missing ::= 'INCLUDE' 'MISSING'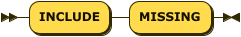
The optional INCLUDE MISSING clause ensures that documents which do not include the index key field are indexed regardless.
If this clause is not present, then documents without the index key field are not indexed.
The INCLUDE MISSING clause can only be applied to the leading index key for non-vector fields.
The INCLUDE MISSING clause may be included before or after the ASC or DESC keyword.
PARTITION BY HASH Clause
Used to partition the index. Index partitioning helps increase the query performance by dividing and spreading a large index of documents across multiple nodes, horizontally scaling out an index as needed. For more information, see Index Partitioning.
With Hyperscale Vector indexes and Composite Vector indexes, training is done for each index node independently, and the codebook is provided to all partitions on that node. If there are multiple partitions for an index on a node, training is only done once for all partitions. See The Importance of Index Training.
WHERE Clause
where-clause ::= 'WHERE' cond
| cond |
Specifies WHERE clause predicates to qualify the subset of documents to include in the index. |
USING Clause
index-using ::= 'USING' 'GSI'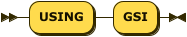
The index type for a secondary index must be Global Secondary Index (GSI).
The USING GSI keywords are optional and may be omitted.
WITH Clause
index-with ::= 'WITH' expr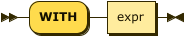
Use the WITH clause to specify additional options.
| expr |
An object with the following properties. |
| Name | Description | Schema |
|---|---|---|
nodes |
An array of strings, each of which represents a node name. In Couchbase Server Community Edition, a single secondary index of type In Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition, you can specify multiple nodes to distribute replicas of an index across nodes running the Indexing Service: for example, If If you specify the If you specify both A node name passed to the Example: |
String array |
defer_build |
Whether the index should be created in deferred build mode. When set to When set to Default: |
Boolean |
num_replica |
This property is only available in Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition. The number of replicas of the index to create. The indexer will automatically distribute these replicas amongst index nodes in the cluster for load-balancing and high availability purposes. The indexer will attempt to distribute the replicas based on the server groups in use in the cluster where possible. The number of replicas must be lower than the number of index nodes in the cluster.
If Default: |
Integer |
Composite Vector indexes support the following additional options.
| Name | Description | Schema | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
dimension |
The number of dimensions in the vector. The embedded model you use to embed the vectors determines the number of dimensions in the vector. |
Integer |
||||||||
similarity |
Sets the distance metric to use when comparing vectors during index creation. Couchbase Server uses the following strings to represent the distance metrics:
For the greatest accuracy, use the distance metric you plan to use to query the data. Default: |
String |
||||||||
description |
The settings for the quantization and index algorithms. The string is made up of the following settings:
For more information, see Quantization and Centroid Settings. Pattern: |
String |
||||||||
scan_nprobes |
The number of cells to search for each scan. Default: |
Integer |
||||||||
train_list |
The size of the sample set of vectors to be used for index training. If the index count is < 10000, the default is to sample everything. Otherwise, the default value is 10% of the index count, or 10 × the number of centroids, whichever is higher. Maximum: |
Integer |
Partitioned indexes support further options. See Index Partitioning.
Usage
|
Attention
Do not create (or drop) secondary indexes, Composite Vector indexes, or Hyperscale Vector indexes when any Index service node is down, as this may result in duplicate index names. |
Monitoring Indexes
Index metadata provides a state field.
This state field and other index metadata can be queried using system:indexes.
The index state may be scheduled for creation, deferred, building, pending, online, offline, or abridged.
You can also monitor the index state using the Couchbase Web Console.
|
If you kick off multiple index creation operations concurrently, you may sometimes see transient errors similar to the following. If this error occurs, the Index Service tries to run the failed operation again in the background until it succeeds, up to a maximum of 1000 retries. If the Index Service still cannot create the index after the maximum number of retries, the index state is marked as |
Indexing Metadata
You can create indexes on metadata using the META() function.
For more information, see Indexing Metadata Information.
Using Indexes for Aggregates
If you have an index on a simple expression, such as geo.alt, you can use that index to satisfy a query on an aggregate of that expression, such as MIN(geo.alt) or MAX(geo.alt).
For more information and examples, see Operator Pushdowns.
Index Replicas
In the Indexes screen in the Couchbase Web Console, index replicas are marked with their replica ID.

If you select view by server node from the drop-down menu, you can see the server node where each index and index replica is placed.
You can also query the system:indexes catalog to find the ID of an index replica and see which node it’s placed on.
|
By default, index replicas are used to serve index scans. The system automatically load-balances an index scan across the index and all its replicas. Adding index replicas enables you to scale scan throughput, in addition to providing high availability. |
With Hyperscale Vector indexes and Composite Vector indexes, training is done by each replica index independently, and the codebook is stored as part of index metadata. See The Importance of Index Training.
Defer Index Builds by Default
Usually, the default setting for the defer_build option is false.
In Couchbase Server 7.6.2 and later, you can change the default setting for the defer_build option.
If you change the default setting for defer_build to true, index creation operates in deferred build mode by default.
To change the default setting for deferred builds, use the Index Settings REST API to set the indexer.settings.defer_build property.
For an example, see Defer Index Builds by Default.
Examples
To try the examples in this section, you must set the query context as described in each example.
For this example, unset the query context. For more information, see Query Context.
Create a secondary index that contains airports with an alt value greater than 1000 on the node 127.0.0.1.
CREATE INDEX idx_default_over1000
ON `travel-sample`(geo.alt)
WHERE geo.alt > 1000
USING GSI
WITH {"nodes": ["127.0.0.1:8091"]};For this example, the path to the required keyspace is specified by the query, so you do not need to set the query context.
Create a secondary index that contains airports with an alt value greater than 1000 on the node 127.0.0.1.
CREATE INDEX idx_airport_over1000
ON `travel-sample`.inventory.airport(geo.alt)
WHERE geo.alt > 1000
USING GSI
WITH {"nodes": ["127.0.0.1:8091"]};For this example, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
Create a secondary index with the defer_build option.
CREATE INDEX idx_landmark_country
ON landmark(country)
USING GSI
WITH {"defer_build":true};Query system:indexes for the status of the index.
SELECT * FROM system:indexes WHERE name="idx_landmark_country";[
{
"indexes": {
"bucket_id": "travel-sample",
"datastore_id": "http://127.0.0.1:8091",
"id": "d079aec40eb0c6cc",
"index_key": [
"`country`"
],
"keyspace_id": "landmark",
"name": "idx_landmark_country",
"namespace_id": "default",
"scope_id": "inventory",
"state": "deferred", (1)
"using": "gsi"
}
}
]| 1 | The index is in the deferred state. |
For this example, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
Kick off a deferred build using the index name.
BUILD INDEX ON landmark(idx_landmark_country) USING GSI;Query system:indexes for the status of the index.
SELECT * FROM system:indexes WHERE name="idx_landmark_country";[
{
"indexes": {
"bucket_id": "travel-sample",
"datastore_id": "http://127.0.0.1:8091",
"id": "d079aec40eb0c6cc",
"index_key": [
"`country`"
],
"keyspace_id": "landmark",
"name": "idx_landmark_country",
"namespace_id": "default",
"scope_id": "inventory",
"state": "online", (1)
"using": "gsi"
}
}
]| 1 | The index has now been created. |
For this example, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
The following statement will not index airports where the district field is missing.
CREATE INDEX idx_airport_missing
ON airport(district, name);The following statement will index all airports, even if the district field is not included in the document.
CREATE INDEX idx_airport_include
ON airport(district INCLUDE MISSING, name);For more examples of indexes where the leading key may be missing, see Index Selection.
For this example, you must install the vector sample data as described in Prerequisites. The path to the required keyspace is specified by the query, so you do not need to set the query context.
Create a Composite Vector index that indexes the vector field named colorvect_l2, as well as the scalar color and brightness fields.
CREATE INDEX `color_vectors_idx` ON `vector-sample`.`color`.`rgb`
(`colorvect_l2` VECTOR, color, brightness)
WITH { "dimension":3 , "similarity":"L2", "description":"IVF,SQ8"};For this example, you must install the vector sample data as described in Prerequisites. The path to the required keyspace is specified by the query, so you do not need to set the query context.
Create a Composite Vector index that indexes the vector field named embedding-vector-dot, as well as the scalar color and brightness fields.
CREATE INDEX `color_desc_idx` ON `vector-sample`.`color`.`rgb`
(`embedding_vector_dot` VECTOR, color, brightness)
WITH { "dimension":1536, "similarity":"DOT", "description":" IVF,SQ8" }For this example, you must install the vector sample data as described in Prerequisites. The path to the required keyspace is specified by the query, so you do not need to set the query context.
Create a Composite Vector index that indexes the scalar color and brightness fields, as well as the vector field named embedding-vector-dot.
CREATE INDEX `color_name_idx` ON `vector-sample`.`color`.`rgb`
(color, brightness, `embedding_vector_dot` VECTOR)
WITH { "dimension":1536, "similarity":"DOT", "description":" IVF,SQ8" }