Cluster Scaling
- Capella Operational
Clusters can be multi-dimensionally scaled by adding or removing Service instances and whole Services, and by adjusting Service instance sizes.
This page walks you through Multi-Dimensional Scaling. It includes information about cluster Services, rebalancing, statuses, events, and jobs.
The dimensions of Multi-Dimensional Scaling are:
-
Adding and removing Service instances
-
Increasing and decreasing the size of Service instances
-
Adding and removing whole Services
| To minimize the risk and severity of cluster outages, Couchbase Capella clusters using Couchbase Server 7.6 or later have guardrails that limit some cluster operations when cluster conditions meets certian thresholds. To learn more, see Couchbase Server Guardrails. |
| For scaling a Single Node cluster, see the limitations of different cluster configuration options. |
Cluster Services
Couchbase clusters comprise multiple independent Services. Cluster capacity is determined by the capacity of each Service running on the cluster. Scaling a cluster means scaling the capacities of each Service. Capella sets up Services on a per-node basis. Each node runs one instance of a Service.
You can determine the capacity of an individual Service by multiplying these factors:
-
The number of instances, or nodes, that make up a Service
-
The size of those instances, including VM instance type and storage.
Each of these factors can be independently scaled. Adding additional instances to a Service is scaling out. Increasing the size of a Service’s instances is scaling up. Removing instances is scaling in. Reducing the size of instances is scaling down. These scaling techniques, together with the ability to add and remove whole Services within a cluster, enable Multi-Dimensional Scaling.
|
Node RAM Allocations
If you deploy multiple Services in a Service Group, Capella distributes the memory allocated to each node in that group between the operating system and all deployed Services. Capella gives 20% of the available RAM on a node to the operating system. It divides the remaining RAM evenly between Services in the Service Group. For example, if there was 25 GB of RAM available on a node in a Service Group that needed to run 3 Services, each Service would get 8.3 GB of RAM (25/3). If you plan to run more than 1 Service on the nodes in your Service Groups, make sure to size your nodes with appropriate compute resources. For production clusters, consider running each of your Services with their own dedicated nodes to give them enough RAM. |
Rebalance
Many of the scaling actions result in the addition or removal of nodes from a cluster. Even changing a Service instance size adds new nodes to the cluster, since Capella swaps out the underlying virtual machines for new ones. After performing any of these procedures, the cluster rebalances to accommodate the new number of active member nodes.
Cluster rebalance is a process that’s required for redistributing data and indexes among available nodes whenever nodes are added or removed. During rebalance, the cluster continues to Service requests for data while the cluster map is correspondingly updated and distributed to clients.
Capella maintains consistent availability and performance during rebalancing. See the rebalance documentation to learn about how each Service behaves during a rebalance. It can help you assess the impacts of this process on your deployments.
Storage Auto-Expansion
Couchbase Capella’s storage auto-expansion can prevent downtime and Service interruptions by automatically expanding your storage when it starts to get full. Capella manages the entire scaling process and underlying infrastructure changes without manual intervention.
Auto-expansion behaves differently depending on the chosen cloud provider:
-
When your usage exceeds 75% on AWS and GCP clusters, Capella triggers a 50% increase in the current storage capacity. Storage increases are in place without any data movement or performance impact. To learn more about how Capella handles AWS storage change limitations, see AWS Storage Scaling Limitations.
-
When your usage exceeds 75% on Azure clusters, Capella doubles the current storage capacity. Storage increases for Azure use the replacement and rebalancing of nodes, which can affect performance until the process completes. To learn more about how Capella handles Azure storage change limitations, see Azure Storage Scaling Limitations.
When auto-expansion occurs, Capella adjusts the IOPS to match the recommended default IOPS for the new storage capacity. If an existing IOPS value is above the recommended default IOPS value for the new storage capacity, the IOPS value remains unchanged.
When deploying a new cluster with AWS or GCP, storage auto-expansion is always on, and you cannot turn it off. Clusters deploying with Azure have auto-expansion off by default with the option to turn it on. Before turning auto-expansion on for Azure clusters, you need to consider possible performance impacts during an auto-expansion. For more information, see Azure Storage Scaling Limitations.
With storage auto-expansion turned on, Couchbase bills you only for the additional storage capacity when the limit increase triggers.
|
To minimize the risk of disruptions to your cluster, review all cloud provider limitations before making any storage configuration changes. Monitor your systems after making adjustments to make sure they function as expected. If you have questions about storage auto-expansion for your cluster, contact Support. |
AWS Storage Scaling Limitations
If you’re hosting your cluster on AWS, you must be aware of the storage scaling limitations. AWS allows you to change your IOPS or increase storage capacity once every 6 hours. For more information about storage scaling limitations, see the AWS Limitations Documentation.
If you need to scale your storage during these 6 hours, Capella replaces and rebalances the nodes. Rebalancing can result in data movement. Depending on the size of your data and available computing resources, this can affect performance until the process completes.
| Couchbase Capella does not automatically decrease storage capacity. However, Capella allows for manual decreases in storage capacity by replacing and rebalancing nodes. While this approach provides greater flexibility, it can result in data movement and a slower process depending on the size of your data and available computing resources. It’s essential to consider the effects of decreasing storage capacity before making any changes to make sure the stability and performance of your systems are not compromised. |
Azure Storage Scaling Limitations
| Auto-expansion for Azure requires replacing and rebalancing nodes, which results in data movement. Depending on the amount of your data and available computing, this may affect performance until the auto-scaling process completes. |
All Azure clusters have auto-expansion turned off by default. You can turn on Azure storage auto-expansion during cluster creation or after you create a cluster. To change the storage auto-expansion settings for an existing cluster in the Capella UI, open the cluster page and click . Each Service Group has its own Auto-Expansion toggle.
When a cluster hosted with Azure auto expands, Capella doubles the current storage up to the maximum available per node. For the maximum storage that’s available for clusters hosted with Azure, see Microsoft Azure — Storage.
IOPS Defaults
The following tables contain recommended default IOPS values for AWS gp3, AWS io2, and Azure Ultra Disk. These defaults are based on disk utilization for typical enterprise workloads. When creating or modifying a cluster and choosing a storage option, Capella uses these defaults for the IOPS field. You can replace the default IOPS value with one higher than the default but not lower.
| Couchbase recommends that you review your current IOPS values for your existing clusters against these default values. |
| Storage Size Range (GB) | IOPS |
|---|---|
50-99 |
3000 |
100-199 |
4370[1] |
200-299 |
5740 |
300-399 |
7110 |
400-499 |
8480 |
500-599 |
9850 |
600-699 |
11220 |
700-799 |
12590 |
800-899 |
13960 |
900-999 |
15330 |
1000 & Up |
16000 |
[1] When application workloads require lower IOPS values, you can reduce IOPS to a minimum of 3,000 for 100-199 GB disks.
| Storage Size Range (GB) | IOPS |
|---|---|
64 |
3000 |
128 |
4000 |
256 |
6000 |
512 |
8000 |
1024 & Up |
16000 |
Cluster Scaling Statuses
When you create, delete, or modify a cluster, you can see its status when you open its project.
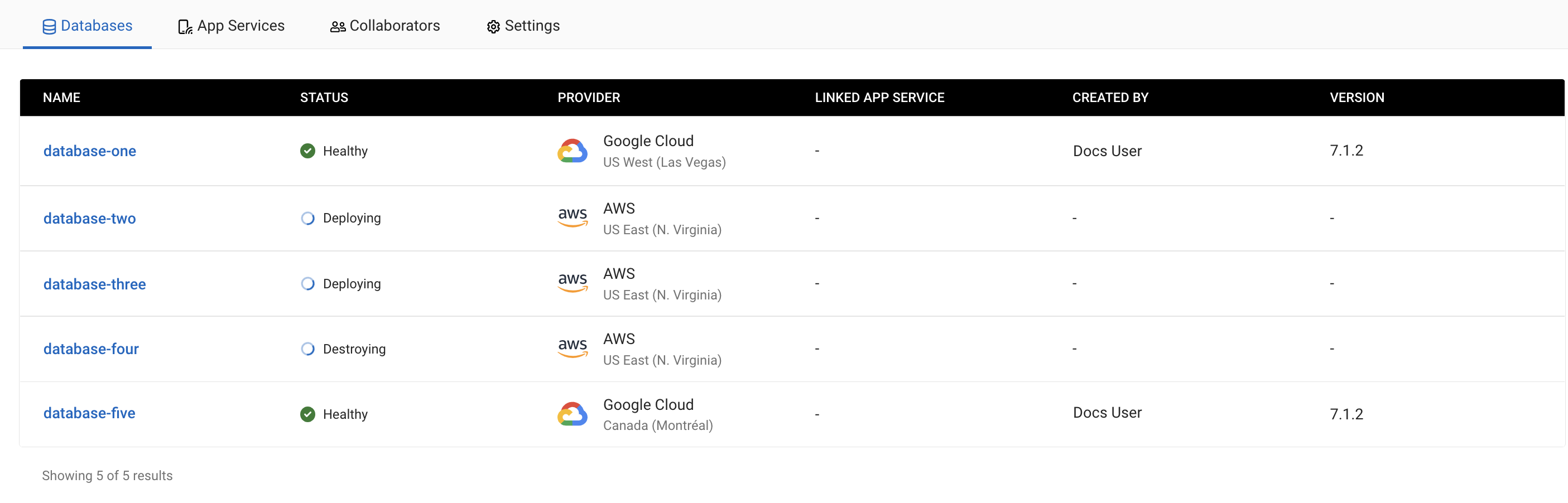
A cluster status can be:
-
Deploying -
Deployment Failed -
Healthy -
Unhealthy -
Scaling -
Scaling Failed -
Rebalance Failed -
Destroying -
Destroy Failed
Cluster Events
You can find a list of all your cluster events by opening the Activity Log:
-
In the navigation breadcrumbs in the Capella UI, do 1 of the following:
-
Click your organization name and go to Operational.
-
Click your current project name or search for a project and go to Operational.
-
Expand the cluster breadcrumb and search for a cluster.
-
-
Select the cluster where you want to view the Activity Log.
-
Go to .
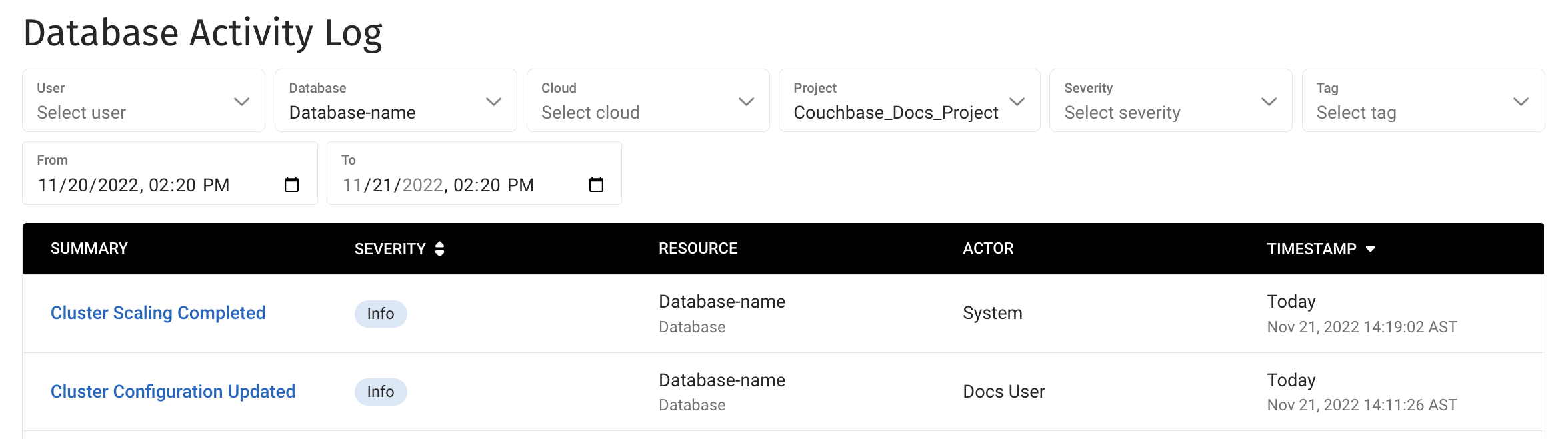
When scaling your cluster, you’ll see these events:
-
A Cluster Configuration Updated event when you first request any changes.
-
A Cluster Scaling Complete event when Capella has finished applying the new configuration.
See Also
-
To add and remove nodes in a cluster, or increase and decrease the size of existing nodes, see Modify the Cluster Configuration.
-
To add a new Service to a cluster, see Add a Service.
-
To remove a Service from a cluster, see Remove a Service.