CREATE FUNCTION
- Capella Operational
- reference
The CREATE FUNCTION statement enables you to create a user-defined function.
Purpose
Capella supports 2 types of user-defined function in SQL++ for Query:
-
Inline functions are defined using SQL++ or JavaScript expressions. Use an inline function to reuse complex or repetitive expressions, including subqueries, and simplify your SQL++ queries.
-
External functions are defined using an external language and stored in a user-defined function (UDF) library. External functions can be collectively managed through their UDF library. Capella supports defining external functions using JavaScript.
You can use inline or external JavaScript functions to run expressions or queries that may be difficult or impossible to define using built-in SQL++ expressions.
JavaScript functions in SQL++ support most of the language constructs available in ECMAScript. For more information about the restrictions and extensions that come with the Couchbase implementation, see JavaScript Functions for Query Reference.
Global Functions and Scoped Functions
You can create user-defined functions at two different levels of the SQL++ logical hierarchy.
-
A global function is created within a namespace, at the same level as the buckets within the namespace. When you call a global function, any partial keyspace references within the function definition are resolved against the function’s namespace, regardless of the current query context.
For example, when you call a global function
default:global()which contains the keyspace reference`travel-sample`, the keyspace reference is always resolved within the context of the function to thedefault:`travel-sample`bucket. -
A scoped function is created within a scope, at the same level as the collections within the scope. When you call a scoped function, any partial keyspace references within the function definition are resolved against the function’s scope, regardless of the current query context.
For example, when you call a scoped function
default:`travel-sample`.inventory.scope()which contains the keyspace referenceroute, the keyspace reference is always resolved within the context of the function todefault:`travel-sample`.inventory.route.
When you create a user-defined function, the current query context determines whether it is created as a global function or a scoped function. If you want to create a user-defined function outside of the current query context, you must include the full path to the function when you specify the function name.
Similarly, when you call a user-defined function, the current query context determines the path to the function. If you want to call a user-defined function outside of the current query context, you must include the full path to the function when you specify the function name.
Finally, it is important to note that a global function is not the same as a scoped function stored in the default scope in a bucket.
You cannot create 2 functions that have the same name inside the same scope. You can create 2 functions with the same name inside different scopes.
External Libraries
You can store JavaScript functions in a user-defined function (UDF) library. This enables you to share external function code for use in more than one SQL++ user-defined function. A library can contain 1 or more JavaScript functions.
For more information about how to create a UDF library, see Create a User-Defined Function Library.
UDF libraries, like SQL++ user-defined functions, may be scoped or global. Set a UDF library or user-defined function as Scoped to keep the code for external functions separate.
Any code that you store in a global library is available to all users with read and write permissions on your operational cluster.
A global library may have the same name as a scoped library, and scoped libraries may have the same name as each other.
For example, you can have a global math library, and a math library in each scope.
SQL++ Managed User-Defined Functions
Couchbase Server 7.6
For operational clusters using Couchbase Server 7.6 and later, you can create the code for a JavaScript function and the corresponding SQL++ user-defined function in a single operation in the Query Tab or cbq. You do not have to create a UDF library before creating a SQL++ user-defined function.
With a SQL++ managed user-defined function, the JavaScript function code is stored inline, along with the SQL++ user-defined function. You cannot share this JavaScript function code with other user-defined functions, or access it from a UDF library.
Prerequisites
-
To manage user-defined functions on your operational cluster, you must have the
Project Owneror theCluster Data Reader/Writerrole.
Syntax
The CREATE FUNCTION statement takes a different syntax depending on the type of function you are creating.
Refer to Inline Functions or JavaScript Functions below.
create-function ::= create-function-inline | create-function-external
Inline Functions
There are two alternative syntaxes for defining an inline function: a syntax with braces {} and a syntax using the LANGUAGE keyword.
The two syntaxes are synonymous.
create-function-inline ::= 'CREATE' ( 'OR' 'REPLACE' )? 'FUNCTION' function '(' params? ')'
( 'IF' 'NOT' 'EXISTS' )?
( '{' body '}' | 'LANGUAGE' 'INLINE' 'AS' body )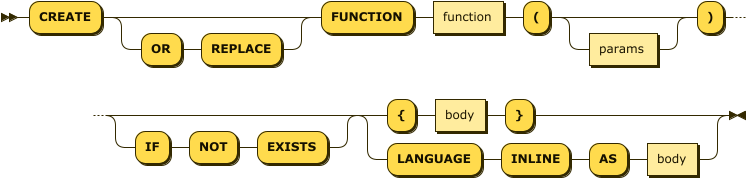
| function | |
| params | |
| body |
OR REPLACE / IF NOT EXISTS
The optional OR REPLACE clause enables you to redefine a user-defined function if it already exists, whereas the optional IF NOT EXISTS clause enables the statement to complete successfully without replacing the function.
When a function with the same name already exists within the same context: [1]
-
If the
OR REPLACEclause is present, the existing function is replaced. -
If the
IF NOT EXISTSclause is present, the statement does nothing and completes without error. -
If neither of these two clauses is present, an error is generated.
These clauses are exclusive.
If the statement contains both the OR REPLACE clause and the IF NOT EXISTS clause, an error is generated.
|
Function Name
function ::= ( namespace ':' ( bucket '.' scope '.' )? )? identifier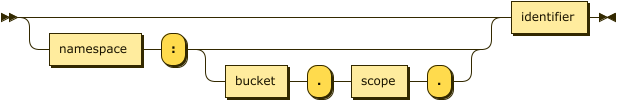
The function name specifies the name of the function to create.
It is recommended to use an unqualified identifier for the function name, such as func1 or `func-1`.
In this case, the function is created as a global function or a scoped function, depending on the current query context.
To create a global function in a particular namespace, the function name must be a qualified identifier with a namespace, such as default:func1.
Similarly, to create a scoped function in a particular scope, the function name must be a qualified identifier with the full path to a scope, such as default:`travel-sample`.inventory.func1.
If the function name is an unqualified identifier, it may not be the same as a reserved keyword. A function name with a specified namespace or scope may have the same name as a reserved keyword.
Your function name must be unique inside your specified scope. You cannot have 2 functions with the same name inside the same scope. You can have 2 functions with the same name across different scopes.
Function Parameters
params ::= identifier ( "," identifier )* | "..."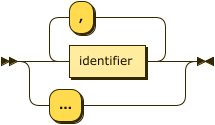
[Optional] The function parameter list specifies parameters for the function.
If you specify named parameters for the function, then you must call the function with exactly the same number of arguments at execution time.
If you specify no parameters, then you must call the function with no arguments.
To create a variadic function, that is, a function which you can call with any number of arguments or none, specify ... as the only parameter.
Function Body
The function body defines the function.
You can use any valid SQL++ expression.
If you specified named parameters for the function, you can use these in the expression to represent arguments passed to the function at execution time.
If you specified that the function is variadic, any arguments passed to the function at execution time are held in an array named args.
|
JavaScript Functions
There are two alternative syntaxes for defining a JavaScript function: one where the function code is stored in an external library, and one for creating a SQL++ managed user-defined function.
create-function-external ::= 'CREATE' ( 'OR' 'REPLACE' )? 'FUNCTION' function '(' params? ')'
( 'IF' 'NOT' 'EXISTS' )?
'LANGUAGE' 'JAVASCRIPT' 'AS' ( obj 'AT' library | javascript )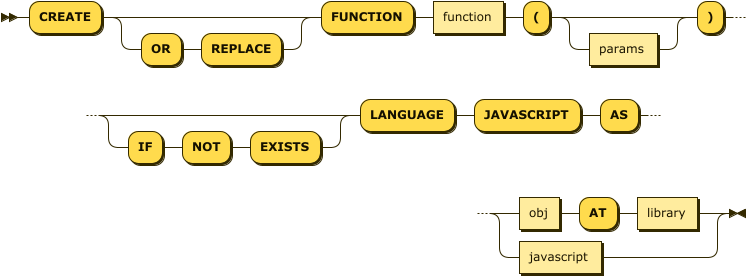
| function | |
| params | |
| obj | |
| library | |
| javascript |
OR REPLACE / IF NOT EXISTS
The optional OR REPLACE clause enables you to redefine a user-defined function if it already exists, whereas the optional IF NOT EXISTS clause enables the statement to complete successfully without replacing the function.
When a function with the same name already exists within the same context: [1]
-
If the
OR REPLACEclause is present, the existing function is replaced. -
If the
IF NOT EXISTSclause is present, the statement does nothing and completes without error. -
If neither of these two clauses is present, an error is generated.
These clauses are exclusive.
If the statement contains both the OR REPLACE clause and the IF NOT EXISTS clause, an error is generated.
|
Function Name
function ::= ( namespace ':' ( bucket '.' scope '.' )? )? identifier
The function name specifies the name of the function to create.
It is recommended to use an unqualified identifier for the function name, such as func1 or `func-1`.
In this case, the function is created as a global function or a scoped function, depending on the current query context.
To create a global function in a particular namespace, the function name must be a qualified identifier with a namespace, such as default:func1.
Similarly, to create a scoped function in a particular scope, the function name must be a qualified identifier with the full path to a scope, such as default:`travel-sample`.inventory.func1.
If the function name is an unqualified identifier, it may not be the same as a reserved keyword. A function name with a specified namespace or scope may have the same name as a reserved keyword.
Your function name must be unique inside your specified scope. You cannot have 2 functions with the same name inside the same scope. You can have 2 functions with the same name across different scopes.
Function Parameters
params ::= identifier ( "," identifier )* | "..."
[Optional] The function parameter list specifies parameters for the function.
If you specify named parameters for the function, then you must call the function with exactly the same number of arguments at execution time.
If you specify no parameters, then you must call the function with no arguments.
To create a variadic function, that is, a function which you can call with any number of arguments or none, specify ... as the only parameter.
External Object
[Optional] Use this parameter where the function code is stored in an external library.
The name of the JavaScript function that you want to use for the user-defined function. This parameter is a string and must be wrapped in quotes.
External Library
[Optional] Use this parameter where the function code is stored in an external library.
The name of the JavaScript library that contains the JavaScript function you want to use. This parameter is a string and must be wrapped in quotes.
The name of a scoped external library must include the bucket name, the scope name, and the library name, separated by slashes.
For example, to refer to a scoped library called my-library located in the inventory scope within the travel-sample bucket, you would specify the library name as travel-sample/inventory/my-library.
Function Body
[Optional] Use this parameter to create a SQL++ managed user-defined function.
The external JavaScript function code. This must contain a function with the same name and the same number of parameters as the SQL++ user-defined function. This parameter is a string and must be wrapped in quotes.
The JavaScript code can contain multiple function definitions, but these functions can only be referenced within the JavaScript code for this SQL++ user-defined function, and cannot be shared.
Examples
For simplicity, none of these examples implement any data validation or error checking. If necessary, you can use conditional operators to check the parameters of a user-defined function, and the ABORT() function to generate an error if something is wrong.
This statement creates a function called celsius, which converts Fahrenheit to Celsius.
The function is variadic.
For purposes of illustration, this expression converts just the first argument supplied at execution time, which is stored in the first member in the args array.
A more realistic variadic function would make use of all the supplied arguments.
CREATE FUNCTION celsius(...) LANGUAGE INLINE AS (args[0] - 32) * 5/9;EXECUTE FUNCTION celsius(100);[
37.77777777777778
]This statement creates a function called fahrenheit, which converts Celsius to Fahrenheit.
The function is variadic.
For purposes of illustration, this expression converts just the first argument supplied at execution time, which is stored in the first member in the args array.
A more realistic variadic function would make use of all the supplied arguments.
CREATE FUNCTION fahrenheit(...) { (args[0] * 9/5) + 32 };EXECUTE FUNCTION fahrenheit(100, "ignore this");[
212
]As the function is variadic, you can use any number of arguments when you call the function. Arguments which are not used by the function expression are ignored.
The following statement creates a function called lstr, which returns the specified number of characters from the left of a string.
The expression expects two named arguments: vString, which is the string to work with, and vLen, which is the number of characters to return.
CREATE FUNCTION lstr(vString, vLen) LANGUAGE INLINE AS SUBSTR(vString, 0, vLen);EXECUTE FUNCTION lstr("Couchbase", 5, "ignore this");[
{
"code": 10104,
"msg": "Incorrect number of arguments supplied to function lstr - cause: lstr"
}
]As the arguments were specified by the function definition, you must use the same number of arguments when you call the function. If you supply the wrong number of arguments, an error is generated.
The following statement creates a function called rstr, which returns the specified number of characters from the right of a string.
The expression expects two named arguments: vString, which is the string to work with, and vLen, which is the number of characters to return.
CREATE FUNCTION rstr(vString, vLen) { SUBSTR(vString, LENGTH(vString) - vLen, vLen) };EXECUTE FUNCTION rstr("Couchbase", 4);[
"base"
]The following statement creates a function called locations, which selects name and address information from all documents with the specified activity in the landmark keyspace.
CREATE FUNCTION locations(vActivity) { (
SELECT id, name, address, city
FROM landmark
WHERE activity = vActivity) };EXECUTE FUNCTION locations("see");[
[
{
"address": "Prince Arthur Road, ME4 4UG",
"city": "Gillingham",
"id": 10019,
"name": "Royal Engineers Museum"
},
{
"address": "84 rue Claude Monet",
"city": "Giverny",
"id": 10061,
"name": "Monet's House"
},
...This statement creates a function which returns the mathematical constant φ. The function takes no arguments.
CREATE FUNCTION phi() { 2 * SIN(RADIANS(54)) };EXECUTE FUNCTION phi();[
1.618033988749895
]The following statement redefines the function so that it calculates φ using a different method.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION phi() { (1 + SQRT(5)) / 2 };EXECUTE FUNCTION phi();[
1.618033988749895
]The following statement creates external JavaScript function code and the corresponding SQL++ user-defined function in one operation.
CREATE FUNCTION add100(num) LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT AS
"function add100(param1) {return param1+100;}";EXECUTE FUNCTION add100(100);[
200
]Related Links
-
To manage UDF libraries and JavaScript functions, see Create a User-Defined Function Library.
-
To execute a user-defined function, see EXECUTE FUNCTION.
-
To see the execution plan for a user-defined function, see EXPLAIN FUNCTION.
-
To include a user-defined function in an expression, see User-Defined Functions.
-
To monitor user-defined functions, see Monitor Functions.
-
To drop a user-defined function, see DROP FUNCTION.