Configure Queries
- Capella Operational
You can configure the Query Service using request-level query parameters.
Request-Level Parameters
To set a request-level parameter, do one of the following:
-
Use the Query Options window in the Query tab.
-
Use the cbq shell at the command line.
-
Make a REST API call to the Data API (Query Service passthrough).
-
Use an SDK client program.
Generally, use the cbq shell or the Query tab as a sandbox to test queries in your Capella cluster.
Use a REST API call or an SDK client program for your production queries.
-
Capella UI
-
Command Line
-
REST API
To set request-level preferences in the Query tab:
-
Go to and click Query Options to display the Query Options window.
-
Specify the preferences — if a preference is not explicitly listed, click + next to Named Parameters and add its name and value.
-
Click Save.
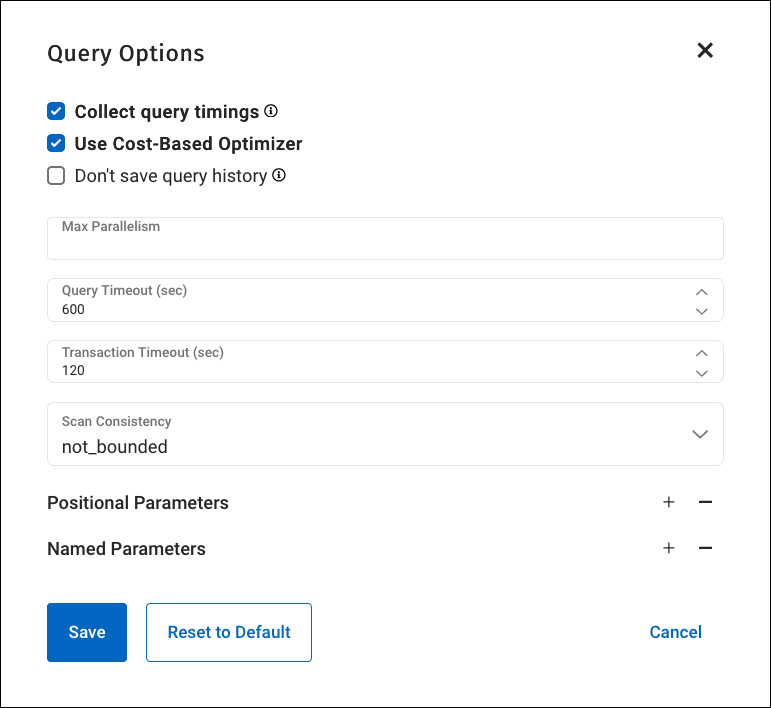
For more information, see Modify Query Settings.
To set request-level parameters in cbq, use the \SET command.
The parameter name must be prefixed by a hyphen.
This example sets the request-level timeout, pretty-print, and max parallelism parameters, and runs a query:
\SET -timeout "30m";
\SET -pretty true;
\SET -max_parallelism 3;
SELECT * FROM "world" AS hello;For more information, see Parameter Manipulation in the cbq documentation.
To set request-level parameters with the Data API, specify the parameters in the request body or the query URI.
In the following examples:
-
$BASEURLis the base URL for the Data API. -
$USERis the cluster access username. -
$PASSWORDis the cluster access secret.
This example sets the request-level timeout, pretty-print, and max parallelism parameters, and runs a query:
curl $BASEURL/_p/query/query/service -u $USER:$PASSWORD \
-d 'statement=SELECT * FROM "world" AS hello;
& timeout=30m
& pretty=true
& max_parallelism=3'The table below contains details of all request-level parameters, along with examples.
| Property | Schema | |
|---|---|---|
args |
Supplies the values for positional parameters in the statement. Applicable if the statement or prepared statement contains 1 or more positional parameters. The value is an array of JSON values, one for each positional parameter in the statement. Refer to Named Parameters and Positional Parameters for details. Example: |
Any Type array |
atrcollection |
Specifies the collection where the active transaction record (ATR) is stored. The collection must be present. If not specified, the ATR is stored in the default collection in the default scope in the bucket containing the first mutated document within the transaction. The value must be a string in the form Example: |
String |
auto_execute |
Specifies that prepared statements should be executed automatically as soon as they are created. This saves you from having to make two separate requests in cases where you want to prepare a statement and execute it immediately. Refer to Auto-Execute for more information. Default: |
Boolean |
client_context_id |
A piece of data supplied by the client that is echoed in the response, if present. SQL++ is agnostic about the content of this parameter; it is just echoed in the response.
|
String |
compression |
Compression format to use for response data on the wire. Values are case-insensitive. Values: |
String |
controls |
Specifies if there should be a controls section returned with the request results. When set to If the request qualifies for caching, these values will also be cached in the Example: |
Boolean |
creds |
In the Data API, this parameter is ignored and has no effect. In the cbq shell, this parameter specifies credentials within a session. For more information, see Switch Between Credentials. Nullable: yes |
Any Type |
durability_level |
The level of durability for mutations produced by the request. If the request contains a Durability is also supported for non-transactional DML statements.
In this case, the If not specified, the default durability level is Values: |
String |
encoded_plan |
In clusters running Couchbase Server 6.5 and later, this parameter is ignored and has no effect. It is included for compatibility with previous versions. |
String |
encoding |
Desired character encoding for the query results. Only possible value is Default: |
String |
format |
Desired format for the query results. Values are case-insensitive. Values: |
String |
kvtimeout |
The approximate time to wait for a KV get operation before timing out.
This applies to statements within a transaction, and to non-transactional statements, whether If The value for this parameter is a string.
Its format includes an amount and a mandatory unit, e.g.
Specify a duration of Default: |
String |
max_parallelism |
Specifies the maximum parallelism for the query. The default value is the same as the number of partitions of the index selected for the query. Example: |
Integer (int32) |
memory_quota |
Specifies the maximum amount of memory the request may use, in MB. Specify This parameter enforces a ceiling on the memory used for the tracked documents required for processing a request. It does not take into account any other memory that might be used to process a request, such as the stack, the operators, or some intermediate values. Within a transaction, this setting enforces the memory quota for the transaction by tracking the delta table and the transaction log (approximately). Default: |
Integer (int32) |
metrics |
Specifies that metrics should be returned with query results. Default: |
Boolean |
namespace |
Specifies the namespace to use.
Currently, only the Example: |
String |
natural |
Couchbase Server 8.0 The prompt for a natural language request. The Query Service uses the prompt to generate a SQL++ statement. If the generated statement is a SELECT statement, the generated statement is returned and executed automatically. If the generated statement is not a SELECT statement, the generated statement is returned, but not executed. In this case, you must verify the statement and execute it in a separate request. Natural language requests use the Couchbase Capella iQ service as a backend. To make a natural language request, you must have a Couchbase Capella user account. This parameter is available in clusters running Couchbase Server 8.0 and later. To use this parameter, you must also specify the Example: |
String |
natural_cred |
Couchbase Server 8.0 The Couchbase Capella user account credentials for a natural language request, in the form Natural language requests use the Couchbase Capella iQ service as a backend. To make a natural language request, you must have a Couchbase Capella user account. This parameter is available in clusters running Couchbase Server 8.0 and later. To use this parameter, you must also specify the Example: |
String (password) |
natural_orgid |
Couchbase Server 8.0 The Couchbase Capella organization ID for a natural language request. Natural language requests use the Couchbase Capella iQ service as a backend. To make a natural language request, you must have a Couchbase Capella user account. This parameter is available in clusters running Couchbase Server 8.0 and later. To use this parameter, you must also specify the |
UUID (uuid) |
natural_context |
Couchbase Server 8.0 A list of paths specifying keyspaces for a natural language request. The Query Service infers the schema of each keyspace, in order to give more precise responses from the natural language request. The parameter may contain up to four paths, separated by commas. Spaces are allowed. Each path may be:
Natural language requests use the Couchbase Capella iQ service as a backend. To make a natural language request, you must have a Couchbase Capella user account. This parameter is available in clusters running Couchbase Server 8.0 and later. To use this parameter, you must also specify the Example: |
String |
natural_output |
Couchbase Server 8.0 Specifies the required output for a natural language request.
Natural language requests use the Couchbase Capella iQ service as a backend. To make a natural language request, you must have a Couchbase Capella user account. This parameter is available in clusters running Couchbase Server 8.0 and later. Values: |
String |
numatrs |
Reserved for future use. This parameter is ignored and has no effect. |
Integer (int32) |
pipeline_batch |
Controls the number of items execution operators can batch for Fetch from the KV. Example: |
Integer (int32) |
pipeline_cap |
Maximum number of items each execution operator can buffer between various operators. Example: |
Integer (int32) |
prepared |
Required if The name of the prepared SQL++ statement to be executed. Refer to EXECUTE for examples. If both Example: |
String |
preserve_expiry |
Specifies whether documents should keep their current expiration setting when modified by a DML statement. If If Not supported for statements in a transaction. Default: |
Boolean |
pretty |
Specifies the query results returned in pretty format. Example: |
Boolean |
profile |
Specifies if there should be a profile section returned with the request results. The valid values are:
If Values: |
String |
query_context |
Specifies the namespace, bucket, and scope used to resolve partial keyspace references within the request. The query context may be a full path, containing namespace, bucket, and scope; or a relative path, containing just the bucket and scope.
Currently, only the Default: |
String |
readonly |
Controls whether a query can change a resulting recordset. If
When using GET requests, it's best to set Default: |
Boolean |
scan_cap |
Maximum buffered channel size between the indexer client and the query service for index scans. This parameter controls when to use scan backfill. Use Example: |
Integer (int32) |
scan_consistency |
Specifies the consistency guarantee or constraint for index scanning. The valid values are:
Values are case-insensitive. For multi-statement requests, the default behavior is RYOW within each request.
If you want to disable RYOW within a request, add a separate If the request contains a Values: |
String |
scan_vector |
Required if Specify the lower bound vector timestamp for one keyspace when using Scan vectors are built of two-element [
Scan vectors have two forms:
Note that For queries referencing multiple keyspaces, use Example: |
Object |
scan_vectors |
Required if A map from keyspace names to scan vectors.
See The scan vectors can be Full or Sparse. |
Object |
scan_wait |
Can be supplied with Specifies the maximum time the client is willing to wait for an index to catch up to the vector timestamp in the request. Specifies how much time the client is willing to wait for the indexer to satisfy the required Its format includes an amount and a mandatory unit, e.g.
Specify Default: |
String (duration) |
signature |
Include a header for the results schema in the response. Default: |
Boolean |
sort_projection |
If If Default: |
Boolean |
statement |
Required if Any valid SQL++ statement for a POST request, or a read-only SQL++ statement (SELECT, EXPLAIN) for a GET request. If both When specifying the request parameters as form data, the statement may not contain an unescaped semicolon ( This restriction does not apply when specifying the request parameters in JSON format. Example: |
String |
timeout |
Maximum time to spend on the request before timing out (s). The value for this parameter is a string.
Its format includes an amount and an optional unit: for example,
Specify a duration of If Example: |
String (duration) |
txdata |
Transaction data. For internal use only. |
Object |
txid |
Required for statements within a transaction. Transaction ID. Specifies the transaction to which a statement belongs. For use with DML statements within a transaction, rollbacks, and commits. The transaction ID should be the same as the transaction ID generated by the Example: |
UUID (UUID) |
tximplicit |
Specifies that a DML statement is a singleton transaction. When this parameter is true, the Query service starts a transaction and executes the statement. If execution is successful, the Query service commits the transaction; otherwise the transaction is rolled back. The statement may not be part of an ongoing transaction.
If the Default: |
Boolean |
txstmtnum |
Transaction statement number. The transaction statement number must be a positive integer, and must be higher than any previous transaction statement numbers in the transaction. If the transaction statement number is lower than the transaction statement number for any previous statement, an error is generated. Example: |
Integer (int32) |
txtimeout |
Maximum time to spend on a transaction before timing out.
Only applies to Within a transaction, the request-level The value for this parameter is a string.
Its format includes an amount and a mandatory unit, e.g.
Specify a duration of The default is Example: |
String (duration) |
use_cbo |
Specifies whether the cost-based optimizer is enabled. Example: |
Boolean |
use_fts |
Specifies that the query should use a Search index. If the query contains a If the query does not contain a Refer to Flex Indexes for more information. Default: |
Boolean |
use_replica |
Specifies whether a query can fetch data from a replica vBucket if active vBuckets are inaccessible. The possible values are:
Do not enable read from replica when you require consistent results. Only SELECT queries that are not within a transaction can read from replica. Reading from replica is only possible if the cluster uses Couchbase Server 7.6.0 or later. Note that KV range scans cannot currently be started on a replica vBucket. If a query uses sequential scan and a data node becomes unavailable, the query might return an error, even if read from replica is enabled for the request. Values: |
String |
<$identifier> |
Supplies the value for a named parameter in the statement. Applicable if the statement or prepared statement contains 1 or more named parameters. The name of this property consists of two parts:
If the named parameter contains sensitive information, start and end the name of the parameter (after the initial The value of the named parameter can be any JSON value. Refer to Named Parameters and Positional Parameters for details. Nullable: yes |
Any Type |
Transactional Scan Consistency
If the request contains a BEGIN TRANSACTION statement, or a DML statement with the tximplicit parameter set to true, then the scan_consistency parameter sets the transactional scan consistency.
If you specify a transactional scan consistency of request_plus, statement_plus, or at_plus, or if you specify no transactional scan consistency, the transactional scan consistency is set to request_plus; otherwise, the transactional scan consistency is set as specified.
| Scan consistency at start of transaction | Transactional scan consistency |
|---|---|
Not set |
|
|
|
|
|
Any DML statements within the transaction that have no scan consistency set will inherit from the transactional scan consistency.
Individual DML statements within the transaction may override the transactional scan consistency.
If you specify a scan consistency of not_bounded for a statement within the transaction, the scan consistency for the statement is set as specified.
When you specify a scan consistency of request_plus, statement_plus, or at_plus for a statement within the transaction, the scan consistency for the statement is set to request_plus.
However, request_plus consistency is not supported for statements using a full-text index.
If any statement within the transaction uses a full-text index, by means of the SEARCH function or the Flex Index feature, the scan consistency is set to not_bounded for the duration of the Full-Text Search.
| Scan consistency for statement within transaction | Inherited scan consistency |
|---|---|
Not set |
Transactional scan consistency |
|
|
|
|
Named Parameters and Positional Parameters
You can add placeholder parameters to a statement, so that you can safely supply variable values when you run the statement. A placeholder parameter may be a named parameter or a positional parameter.
-
To add a named parameter to a query, enter a dollar sign
$or an at sign@followed by the parameter name. -
To add a positional parameter to a query, enter a dollar sign
$or an at sign@followed by the number of the parameter, or enter a question mark?.
To run a query containing placeholder parameters, you must supply values for the parameters.
-
You can use an additional request-level parameter to supply the value for a named parameter. The name of this property is a dollar sign
$or an at sign@followed by the parameter name. -
The args request-level parameter enables you to supply a list of values for positional parameters.
You can supply the values for placeholder parameters using any of the methods used to specify request-level parameters.
Examples
To try the examples in this section, set the query context to the inventory scope in the travel sample dataset.
For more information, see Query Context.
In the REST API examples:
-
$BASEURLis the base URL for the Data API. -
$USERis the cluster access username. -
$PASSWORDis the cluster access secret.
-
Capella UI
-
Command Line
-
REST API
The following query uses named parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Query Options window.
name |
|
value |
|
name |
|
value |
|
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $country AND geo.alt > @altitude;The named parameters and named parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
The following query uses named parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the cbq shell.
\SET -@country "France";
\SET -$altitude 500;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $country AND geo.alt > @altitude;The named parameters and named parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
The following query uses named parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Data API.
curl -v $BASEURL/_p/query/query/service \
-d 'statement=SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $country AND geo.alt > @altitude
& query_context=travel-sample.inventory
& $country="France" & $altitude=500' \
-u $USER:$PASSWORDThe named parameters and named parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
-
Capella UI
-
Command Line
-
REST API
The following query uses numbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Query Options window.
$1 |
|
$2 |
|
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $1 AND geo.alt > @2;In this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered $1, the second positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered @2, and so on.
The numbered positional parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
The following query uses numbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the cbq shell.
\SET -args ["France", 500];
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $1 AND geo.alt > @2;In this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered $1, the second positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered @2, and so on.
The numbered positional parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
The following query uses numbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Data API.
curl -v $BASEURL/_p/query/query/service \
-d 'statement=SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = $1 AND geo.alt > @2
& query_context=travel-sample.inventory
& args=["France", 500]' \
-u $USER:$PASSWORDIn this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered $1, the second positional parameter value is used for the placeholder numbered @2, and so on.
The numbered positional parameter placeholders in this example use a mixture of @ and $ symbol prefixes.
You can use either of these symbols as preferred.
-
Capella UI
-
Command Line
-
REST API
The following query uses unnumbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Query Options window.
$1 |
|
$2 |
|
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = ? AND geo.alt > ?;In this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the first ? placeholder, the second positional parameter value is used for the second ? placeholder, and so on.
The following query uses unnumbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the cbq shell.
\SET -args ["France", 500];
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = ? AND geo.alt > ?;In this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the first ? placeholder, the second positional parameter value is used for the second ? placeholder, and so on.
The following query uses unnumbered positional parameter placeholders. The parameter values are supplied using the Data API.
curl -v $BASEURL/_p/query/query/service \
-d 'statement=SELECT COUNT(*) FROM airport
WHERE country = ? AND geo.alt > ?
& query_context=travel-sample.inventory
& args=["France", 500]' \
-u $USER:$PASSWORDIn this case, the first positional parameter value is used for the first ? placeholder, the second positional parameter value is used for the second ? placeholder, and so on.
For more information and examples, including examples using SDKs, see the Prepare Statements for Reuse guide.
Related Links
-
For more information about the Data API, see Manage Data with the Data API.