Set up Prometheus to Consume Couchbase Metrics
With Couchbase 7.x, it’s not necessary to write a custom Prometheus Exporter. This page will demonstrate how to enable a Prometheus server to read from Couchbase’s Prometheus-ready endpoints.
Prerequisites
Make sure that you have Docker installed and running on your machine. You should also have an available Couchbase cluster with at least one running node.
1. Prepare the target configuration file
Create a file that contains a list of the cluster’s node targets. This is done by issuing a request to the server from the command line:
wget --content-disposition \
'http://10.112.211.101:8091/prometheus_sd_config.yaml' \
--http-user Administrator --http-password passwordThis will generate a configuration file containing the target addresses of the nodes in your cluster.
| The name and contents of the file will depend on the configuration of the cluster: |
- targets:
- '10.144.220.101:8091'
- '10.144.220.102:8091'Create a new directory on your system and copy the file to the new directory:
mkdir ~/prometheus
cp couchbase_sd_config_my-cluster.yaml ~/prometheus2. Create the Prometheus configuration file
Create a new file called prometheus.yml in the directory containing the targets file.
Populate the file with the following text:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'couchbase_cluster' (1)
basic_auth:
username: 'Administrator' (2)
password: 'password' (3)
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- 'couchbase_sd_config_my-cluster.yml' (4)
refresh_interval: 15s| 1 | This is the name that Prometheus will assign to the process retrieving data from the target nodes. |
| 2 | The username the process can use to log into the cluster. |
| 3 | The password the process will use to log into the cluster. |
| 4 | The name of target file. The process will use this to read th addresses of the target nodes. |
The directory should contain the following files.
📂 ~ (home directory)
+ 📂 prometheus
📄 prometheus.yml
📄 couchbase_sd_config_my-cluster.yaml| The cluster configuration file will have a different name to the one shown here. |
3. Install Prometheus
Open a terminal window and run the following command to provision Prometheus:
docker run \
-p 9090:9090 \ (1)
-v ~/prometheus:/etc/prometheus \ (2)
prom/prometheus| 1 | The port through which the Prometheus server is accessed and takes the form: -p host-port:container-port.
|
||||
| 2 | This is the mapping of the Prometheus configuration directory to the host machine configuration.
~/prometheus will be mapped on to the Prometheus instance configuration directory inside the Docker container. |
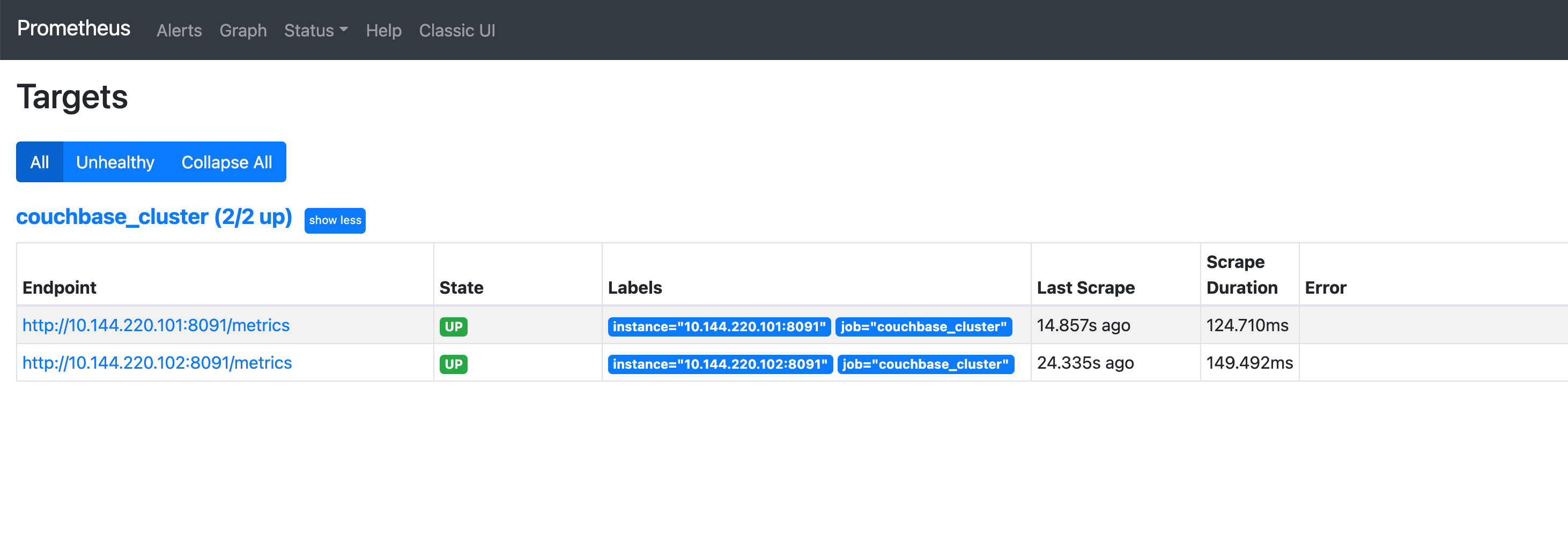
4. Test the configuration
Once the Docker container has started up, visit http://localhost:9090/targets to ensure that Prometheus is accessing the cluster correctly: