Goal: When a document in an existing collection is about to expire, a new document is created in a different collection.
Implementation:
Create a JavaScript Function that contains an OnUpdate handler, which runs whenever a document is created (or mutated). The Eventing Function calls a timer routine, which executes a callback function, two minutes prior to any document’s established expiration. This function retrieves a specified value from the document, and stores a document with the same key, in a specified target collection. The original document in the source collection is not changed during the copy (and will be deleted).
Preparations:
For this example, two (2) buckets 'bulk' and 'rr100' are required where the latter is intended to be 100% resident. Create the buckets with a minimum size of 100MB. For information on buckets, see Create a Bucket. Within the buckets we need three (3) keyspaces 'bulk.data.source', 'bulk.data.target', and 'rr100.eventing.metadata' (we loosely follow this organization).
For the Function Scope or RBAC grouping, we will use the 'bulk.data', assuming you have the role of either "Full Admin" or "Eventing Full Admin". For standard or non-privileged users refer to Eventing Role-Based Access Control.
If you run a version of Couchbase prior to 7.0 you can just create the buckets 'source', 'target', and 'metadata' and run this example. Furthermore if your cluster was subsequently upgraded from say 6.6.2 to 7.0 your data would be moved to 'source._default._default', 'target._default._default', and 'metadata._default._default' and your Eventing Function would be seamlessly upgraded to use the new keyspaces and continue to run correctly.
For complete details on how to set up your keyspaces refer to creating buckets and creating scopes and collections.
| The Eventing Storage keyspace, in this case 'rr100.eventing.metadata', is for the sole use of the Eventing system, do not add, modify, or delete documents from it. In addition do not drop or flush or delete the containing bucket (or delete this collection) while you have any deployed Eventing functions. In a single tenancy deployment this collection can be shared with other Eventing functions. |
You will need to run a special SQL++ statement, a cbc (the command-line KV client), or alternatively an SDK python script or Java program to create or update a document in the 'source' bucket with an expiration time of 600 seconds.
Procedure:
-
The example requires a document to be created in the 'source' collection with a key of SampleDocument2, a value of {'a_key': 'a_value'}, and most importantly that the document’s expiration (or TTL) set to 600 seconds or 10 minutes).
There are several methods to make a test document with an expiration set. The easiest is most likely using SQL++. However you can use cbc or any Couchbase SDK (the command-line KV client is compiled from the C SDK). For example you can use a Python script or a complied Java program.
-
SQL++ UPDATE
-
The cbc binary, or KV client
-
Python SDK script
-
Java SDK program
- Using the Query Workbench
UPSERT INTO `bulk`.`data`.`source` (KEY, VALUE) VALUES ("SampleDocument2", {"a_key":"a_value"}, {"expiration":600});Issue the above command in the Query Workbench of the UI.
For information on setting document expiration times via SQL++, refer to Insert a document with expiration
- On Linux
/opt/couchbase/bin/cbc \ create SampleDocument2 -V '{"a_key": "a_value"}' \ -U couchbase://localhost/source \ --scope=data --collection=source \ -u Administrator -P password \ --expiry=600on macOS
/Applications/Couchbase\ Server.app/Contents/Resources/couchbase-core/bin/cbc \ create SampleDocument2 -V '{"a_key": "a_value"}' -U couchbase://localhost/source \ --scope=data --collection=source \ -u Administrator -P password \ --expiry=600on Windows
"C:\Program Files\Couchbase\Server\bin\cbc" ^ create SampleDocument2 -V "{'a_key': 'a_value'}" -U couchbase://localhost/source ^ --scope=data --collection=source ^ -u Administrator -P password ^ --expiry=600Use the command-line KV client, e.g. the cbc binary, and cut-n-paste one of the above commands to create the needed sample document.
We are passing --expiry the number of time in seconds from now at which the item should expire. However if you want an expiry over 30 days you must use the number of seconds since Unix Epoch.
On macOS (or OS-X) if you get a 'dyld: Library not loaded' when running cbc a solution is documented in MB-37768.
For information on the cbc tool, refer to Using the command-line KV client.
#!/usr/bin/python3 import sys import couchbase.collection import couchbase.subdocument as SD from couchbase.cluster import Cluster, ClusterOptions from couchbase_core.cluster import PasswordAuthenticator from couchbase.durability import ServerDurability, Durability from datetime import timedelta pa = PasswordAuthenticator('Administrator', 'password') cluster = Cluster('couchbase://127.0.0.1', ClusterOptions(pa)) bucket = cluster.bucket('bulk') collection = bucket.scope('data').collection('source') try: document = dict( a_key="a_value" ) result = collection.upsert( 'SampleDocument2', document, expiry=timedelta(minutes=10) ) print("UPSERT SUCCESS") print("cas result:", result.cas) except: print("exception:", sys.exc_info())Make an executable script as above and then it. Alternatively run the command python3 to start a Python session then cut-n-paste the above line (without the
#!/usr/bin/python3line) to create the needed sample document and then ^D (or ctrl-D) to close the Python session.For information on the Couchbase Python SDK, refer to Start Using the Python SDK.
A Java 3.0 SDK program example
// Must use the Collections API package com.jonstrabala; import java.time.Duration; import com.couchbase.client.java.*; import com.couchbase.client.java.json.JsonObject; import static com.couchbase.client.java.kv.UpsertOptions.upsertOptions; public class DocExpiryTestCC { public static void main(String... args) throws Exception { // Note, if not on the server you need to change "localhost" to your DNS name or IP Cluster cluster = Cluster.connect("localhost", "Administrator", "password"); Bucket bucket = cluster.bucket("bulk"); // Collection collection = bucket.defaultCollection(); Collection collection = bucket.scope("data").collection("source"); String docID = "SampleDocument2"; Duration dura = Duration.ofMinutes(10); try { collection.upsert( docID, JsonObject.create().put("a_key", "a_value"), upsertOptions().expiry(dura) ); System.out.println("docID: " + docID + " expires in " + dura.getSeconds()); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("upsert error for docID: " + docID + " " + e); } bucket = null; collection = null; cluster.disconnect(Duration.ofSeconds(2000)); } }Download the proper SDK and then compile and run one of the above Java programs
For information on the Couchbase Java SDK, refer to Start Using the Java SDK.
-
-
You now have a document in collection 'source' (keyspace
bulk.data.source) with an expiration set. -
To verify that your new document was created, access the Couchbase Web Console > Documents page and click the Documents then select the keyspace
bulk.data.source. The new document gets displayed automatically (as this page will attempt to list the first few items). You will see one (1) document in thebulk.data.sourcekeyspace (this will disappear on the document’s expiry of 10 minutes).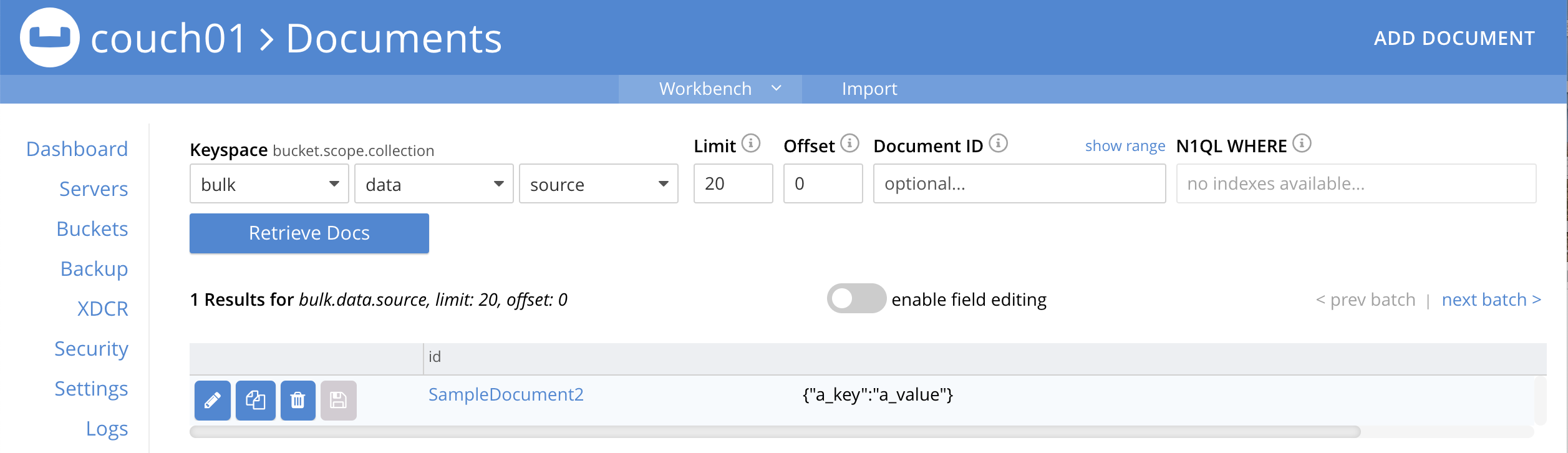
-
[Optional Step] Click on the document’s id, SampleDocument2 to view the documents Data and also the documents Metadata information. Note that the "expiration" field in the Metadata is non-zero (set to a Unix timestamp in seconds since epoch).
-
From the Couchbase Web Console > Eventing page, click ADD FUNCTION, to add a new Function. The ADD FUNCTION dialog appears.
-
In the ADD FUNCTION dialog, for individual Function elements provide the below information:
-
For the Function Scope drop-down, select 'bulk.data' as the RBAC grouping.
-
For the Listen To Location drop-down, select bulk, data, source as the keyspace.
-
For the Eventing Storage drop-down, select rr100, eventing, metadata as the keyspace.
-
Enter add_timer_before_expiry as the name of the Function you are creating in the Function Name text-box.
-
Leave the "Deployment Feed Boundary" as Everything.
-
[Optional Step] Enter text Function that adds timer to fire before document expiry, in the Description text-box.
-
For the Settings option, use the default values.
-
For the Bindings option, add two bindings.
-
For the first binding, select "bucket alias", specify src as the "alias name" of the collection, select bulk, data, source as the associated keyspace, and select "read only" for the access mode.
-
For the second binding, select "bucket alias", specify tgt as the "alias name" of the collection, select bulk, data, and target as the associated keyspace, and select "read and write" for the access mode.
-
-
After configuring your settings the ADD FUNCTION dialog should look like this:
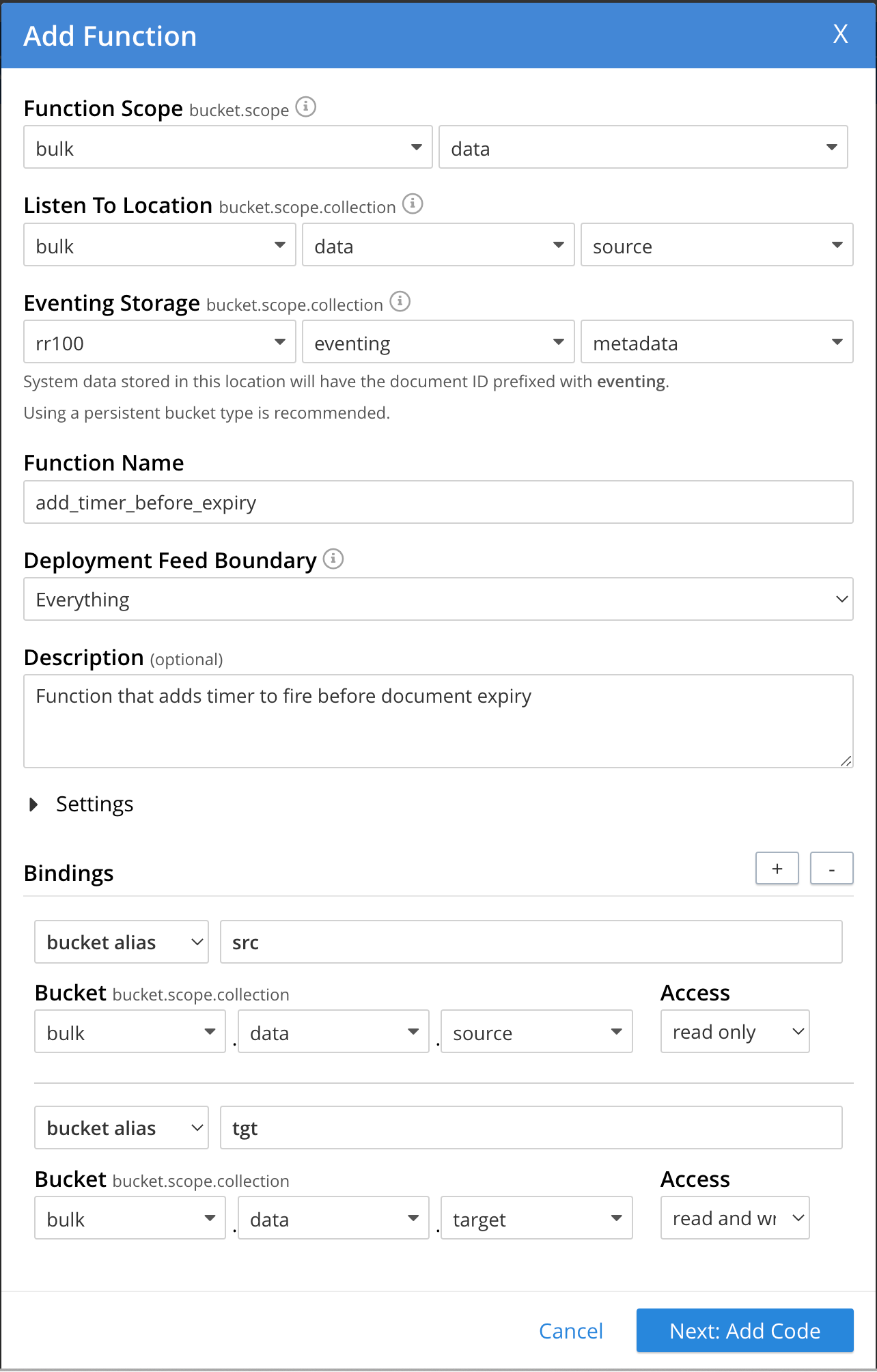
-
-
After providing all the required information in the ADD FUNCTION dialog, click Next: Add Code. The add_timer_before_expiry dialog appears.
-
The add_timer_before_expiry dialog initially contains a placeholder code block. You will substitute your actual add_timer_before_expiry code in this block.

-
Copy the following Function, and paste it in the placeholder code block of add_timer_before_expiry dialog.
function OnUpdate(doc, meta) { // Only process for those documents that have a non-zero TTL if (meta.expiration == 0 ) return; // Get the TTL and compute 2 minutes prior to the TTL, note JavaScript Date() takes msec. var twoMinsPrior = new Date((meta.expiration - 2*60) * 1000); // Create a context and then create a timer with our context var context = { docID : meta.id, expiration : meta.expiration }; createTimer(DocTimerCallback, twoMinsPrior , meta.id, context); log('OnUpdate add Timer 2 min. prior to TTL to DocId:', meta.id); } function DocTimerCallback(context) { log('DocTimerCallback 1 on DocId:', String(context.docID)); // create a new document with the same ID but in the target collection tgt[context.docID] = "To Be Expired in 2 min., Key's Value is:" + JSON.stringify(src[context.docID]); log('DocTimerCallback 2 src expiry:', new Date(context.expiration * 1000)); log('DocTimerCallback 3 tgt archive via Key:', String(context.docID)); }After pasting, the screen appears as displayed below:

-
Click Save and Return.
-
-
From the Eventing screen, click the add_timer_before_expiry function to select it, then click Deploy.
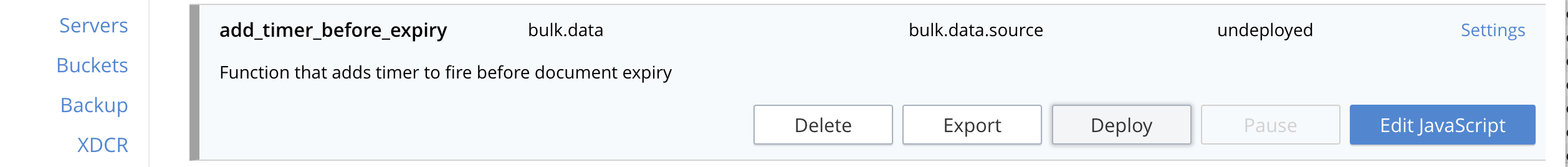
-
Click Deploy Function.
-
-
The Eventing function is deployed and starts running within a few seconds. From this point, the defined Function is executed on all existing documents and on subsequent mutations.
-
Look at the Log for add_timer_before_expiry once it deploys (the "Log" link will appear once the function is deployed)
2022-04-17T15:34:21.034-07:00 [INFO] "OnUpdate add Timer 2 min. prior to TTL to DocId:" "SampleDocument2"
-
Now look at the Buckets in the UI the
rr100.eventing.metadatakeyspace will have 1280 documents related to the Eventing function and three (3) additional documents related to the timer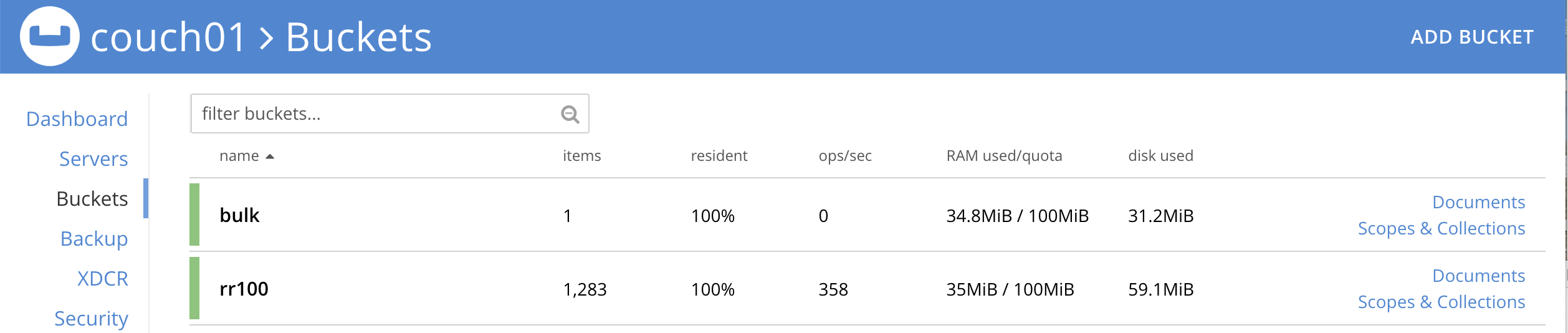
-
If you select Scopes & Collections (on the right) from the bucket bulk, then click on data (on the left) you should see one (1) document in the
bulk.data.sourcecollection (that you poked in via SQL++, cbc, Python or Java).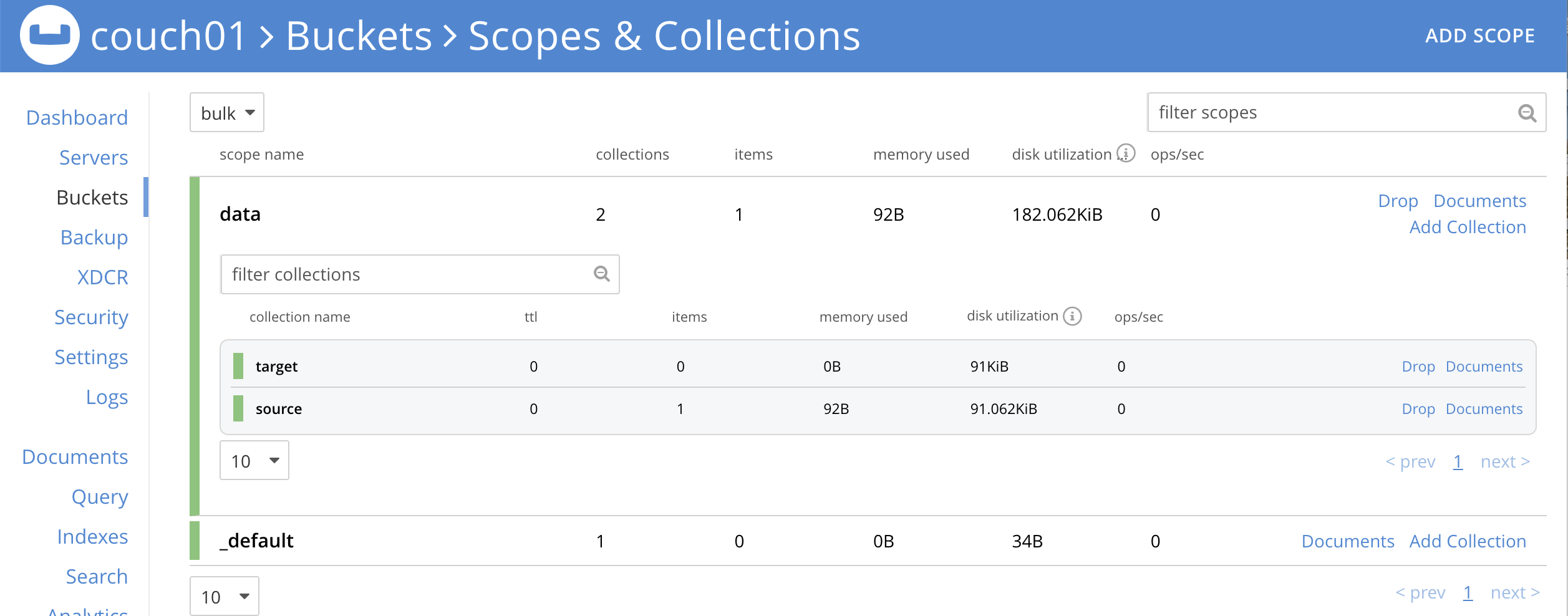
-
Wait a several minutes, return to Eventing in the UI and Look at the Log data again for add_timer_before_expiry at two minutes before the TTL was scheduled the timer will have fired and executed DocTimerCallback (note the logs display by the "Log" link are in reverse time order). Note the document this is based on had a 10 minute expiration and the timer will fire 2 minutes prior to that expiration (thus you might wait almost 8 minutes).
You should see four log lines:
2022-04-17T15:42:03.481-07:00 [INFO] "DocTimerCallback 3 tgt archive via Key:" "SampleDocument2" 2022-04-17T15:42:03.481-07:00 [INFO] "DocTimerCallback 2 src expiry:" "2022-04-17T22:44:00.000Z" 2022-04-17T15:42:03.478-07:00 [INFO] "DocTimerCallback 1 on DocId:" "SampleDocument2" 2022-04-17T15:34:21.034-07:00 [INFO] "OnUpdate add Timer 2 min. prior to TTL to DocId:" "SampleDocument2"
The final result, is a new document containing a copy of the data from the original, named SourceDocument2 being written to the collection 'target' with the same Key in the keyspace
bulk.data.target. -
Now look at the Documents in the UI again you will see one (1) document in the
bulk.data.sourcekeyspace (this will disappear on the document’s expiry of 10 minutes).
-
Now look at the Documents in the UI again you will see one (1) document in the
bulk.data.targetkeyspace (this will persist)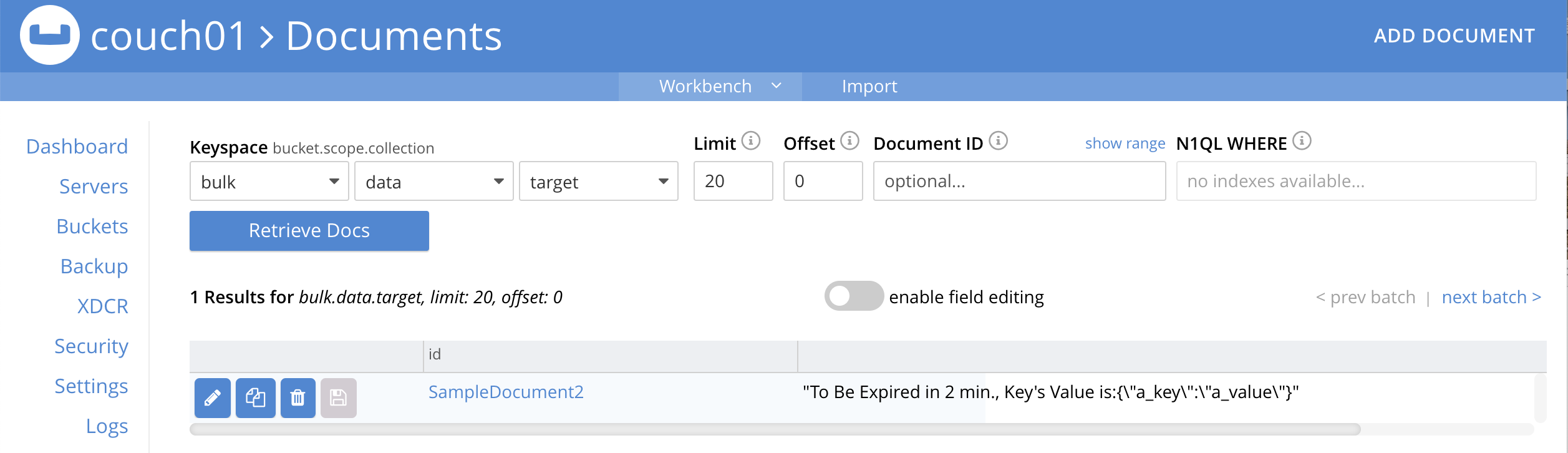
-
Wait a few more minutes (actual just bit more than two minutes) past the 120 second window, then check the document in the
bulk.data.sourcekeyspace', you will find that it is missing and will not be accessible as it has expired due to the defined TTL on the document.If you don’t actually try to access the document by clicking on the *Documents" link the UI and specifying the keyspace bulk.data.sourcethe UI may indicate it still exists until the expiry pager removes the tombstone for the deleted or expired documents (or an actual attempt to access it is made).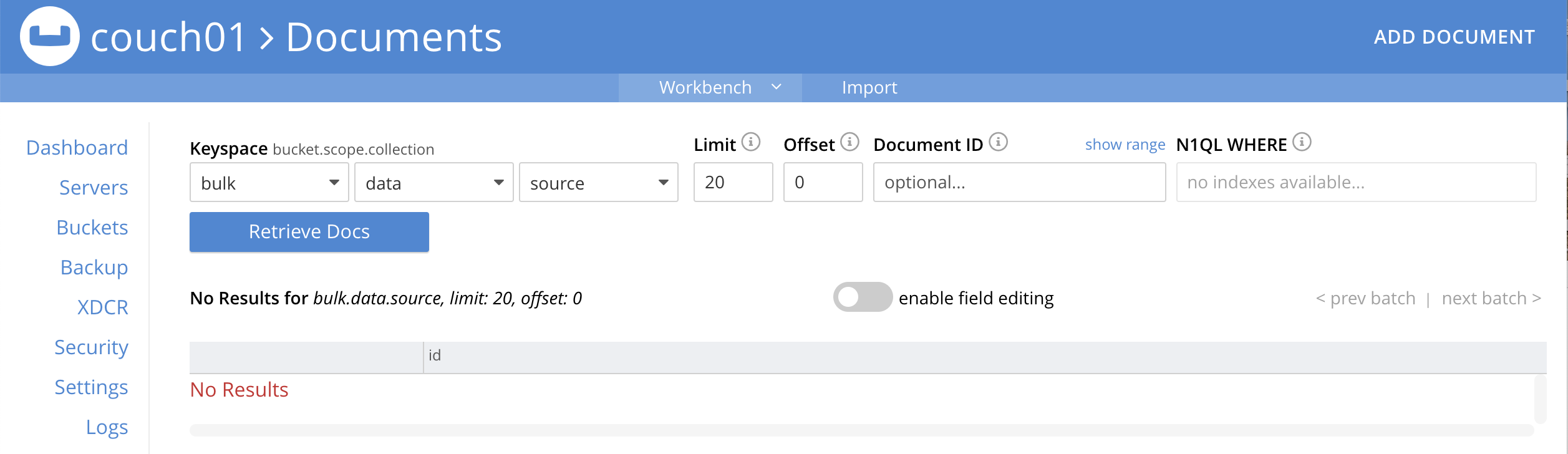
Cleanup:
Go to the Eventing portion of the UI and undeploy the Function add_timer_before_expiry, this will remove the 1280 documents for each function from the 'rr100.eventing.metadata' collection (in the Bucket view of the UI). Remember you may only delete the 'rr100.eventing.metadata' keyspace if there are no deployed Eventing Functions.
Now flush the 'bulk' bucket if you plan to run other examples (you may need to Edit the bucket 'bulk' and enable the flush capability).