BEGIN TRANSACTION
- reference
The BEGIN TRANSACTION statement enables you to begin a transaction.
Purpose
The BEGIN TRANSACTION statement enables you to begin a sequence of statements as an ACID transaction.
Refer to SQL++ Support for Couchbase Transactions for further information.
-
Only DML statements are permitted within a transaction: INSERT, UPSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, MERGE, SELECT, EXECUTE FUNCTION, PREPARE, or EXECUTE.
-
The
EXECUTE FUNCTIONstatement is only permitted in a transaction if the user-defined function does not contain any subqueries other thanSELECTsubqueries. -
The
PREPAREandEXECUTEstatements are only permitted in a transaction for the DML statements listed above.
All statements within a transaction are sent to the same Query node.
| You can also specify a single DML statement as an ACID transaction by setting the tximplicit query parameter. |
Syntax
begin-transaction ::= ( 'BEGIN' | 'START' ) ( 'WORK' | 'TRAN' | 'TRANSACTION' )
( 'ISOLATION' 'LEVEL' 'READ' 'COMMITTED' )?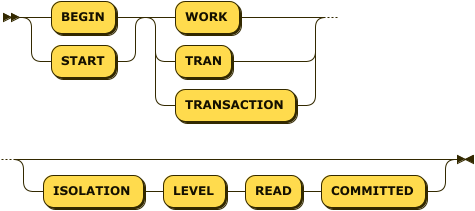
The BEGIN and START keywords are synonyms.
The statement must begin with one of these keywords.
The WORK, TRAN, and TRANSACTION keywords are synonyms.
The statement must contain one of these keywords.
Return Value
The statement returns an object containing the following property.
- txid
-
The transaction ID.
If you are using the Query REST API, you must set the txid query parameter to specify the transaction ID for any subsequent statements that form part of the same transaction.
If you are using the Query Workbench, you don’t need to specify the transaction ID for any statements that form a part of the same transaction within a multi-statement request. If you start a transaction within a multi-statement request, all statements within the request are assumed to be part of the same transaction until you rollback or commit the transaction.
Similarly, if you are using the cbq shell, you don’t need to specify the transaction ID for any statements that form a part of the same transaction. Once you have started a transaction, all statements within the cbq shell session are assumed to be part of the same transaction until you rollback or commit the transaction. [1]
Example
If you want to try this example, first refer to Preparation to set up your environment.
-- Start the transaction
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
-- Specify transaction settings
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ COMMITTED;
-- Create a booking document
UPSERT INTO bookings
VALUES("bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03", {
"date": "07/24/2021",
"flight": "WN533",
"flighttime": 7713,
"price": 964.13,
"route": "63986"
});
-- Set a savepoint
SAVEPOINT s1;
-- Update the booking document to include a user
UPDATE bookings AS b
USE KEYS "bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03"
SET b.`user` = "0";
-- Check the content of the booking and user
SELECT b.*, u.name
FROM bookings b
USE KEYS "bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03"
JOIN users u
ON KEYS b.`user`;
-- Set a second savepoint
SAVEPOINT s2;
-- Update the booking documents to change the user
UPDATE bookings AS b
USE KEYS "bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03"
SET b.`user` = "1";
-- Check the content of the booking and user
SELECT b.*, u.name
FROM bookings b
USE KEYS "bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03"
JOIN users u
ON KEYS b.`user`;
-- Roll back the transaction to the second savepoint
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION TO SAVEPOINT s2;
-- Check the content of the booking and user again
SELECT b.*, u.name
FROM bookings b
USE KEYS "bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03"
JOIN users u
ON KEYS b.`user`;
-- Commit the transaction
COMMIT TRANSACTION;[
{
"_sequence_num": 1,
"_sequence_query": "-- Start the transaction\nBEGIN TRANSACTION;",
"_sequence_query_status": "success",
"_sequence_result": [
{
"txid": "d81d9b4a-b758-4f98-b007-87ba262d3a51" (1)
}
]
},
{
"_sequence_num": 2,
"_sequence_query": "\n\n-- Specify transaction settings\nSET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ COMMITTED;",
"_sequence_query_status": "success",
"_sequence_result": {
"results": []
}
},
{
"_sequence_num": 3,
"_sequence_query": "\n\n-- Create a booking document\nUPSERT INTO bookings\nVALUES(\"bf7ad6fa-bdb9-4099-a840-196e47179f03\", {\n \"date\": \"07/24/2021\",\n \"flight\": \"WN533\",\n \"flighttime\": 7713,\n \"price\": 964.13,\n \"route\": \"63986\"\n});",
"_sequence_query_status": "success",
"_sequence_result": {
"results": []
}
},
// ...| 1 | Beginning a transaction returns a transaction ID. |
Related Links
-
For an overview of Couchbase transactions, refer to Transactions.
-
To specify transaction settings, refer to SET TRANSACTION.
-
To set a savepoint, refer to SAVEPOINT.
-
To rollback a transaction, refer to ROLLBACK TRANSACTION.
-
To commit a transaction, refer to COMMIT TRANSACTION.
-
Blog post: Couchbase Transactions: Elastic, Scalable, and Distributed.