Query Service
The Query Service supports the querying of data by means of SQL++. The Query Service depends on both the Index Service and the Data Service.
Query Service Architecture
The architecture of the Query Service is shown by the following illustration:
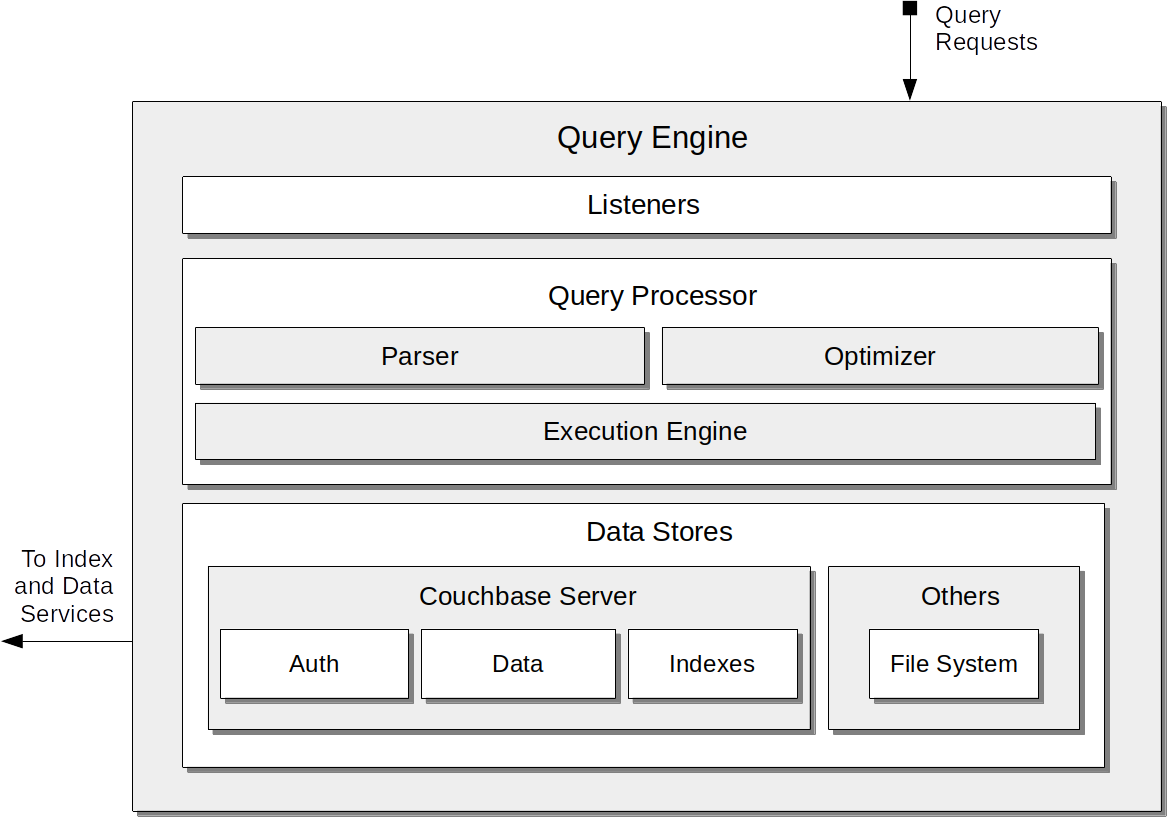
The principal components are:
-
Listeners: Concurrent query requests are received on ports 8093 and 18093 (for more information on port-allocation, see Network and Firewall Requirements).
-
Query Processor: Responsible for applying the Parser to incoming queries, in order to determine whether each is a valid statement. Also employs the Optimizer, which evaluates available execution paths, so determining the path of lowest latency; generates a query-execution plan that uses the lowest-latency path; and assembles the plan into a series of operators. The Execution Engine receives the operators, and executes them — in parallel where possible.
-
Data Stores: Provides access to various data-sources. The Couchbase Server store is used to access the data and indexes on Couchbase Server, and to handle authentication. Other data stores are also included, such as the store for the local filesystem.
Query Execution
The following diagram shows the sequence of operations during query execution.
When the Query Service receives the client’s SQL++ query, it immediately passes it to the Query Processor. The Query Processor first parses the query to validate the statement and then creates an execution plan for the request.
The Execution Engine then begins executing the plan. It performs Scan operations on the relevant index, using either the Index Service or the Search Service. Next, it performs Fetch operations to get the actual data from the Data Service, and then uses this data for Join operations.
The Query Service processes the data further by applying Filter, Aggregate, Project, and Sort operations. These operations can run in parallel. In the diagram, the number of boxes within an operation block represents the degree of parallelism for that operation.
Finally, the service executes Offset and Limit operations to set the result size and starting point, and then streams the results back to the client. For more information about each of these operations, see Query Phases.
Using SQL++
The Query Service supports queries made in SQL++. As well as providing a rich variety of query-options, SQL++ allows statements to be prepared, so that the parsing and compiling of plans is completed prior to execution; and permits consistency-levels to be configured. For detailed information, see SQL++ Language Reference.
See Also
-
For more information about adding or removing the Query Service on an existing node of a cluster, see Modify Services and Rebalance.