Conditional Operators
- reference
Case expressions evaluate conditional logic in an expression.
case-expr ::= simple-case-expr | searched-case-expr
Simple Case Expressions
simple-case-expr ::= 'CASE' expr ('WHEN' expr 'THEN' expr)+ ('ELSE' expr)? 'END'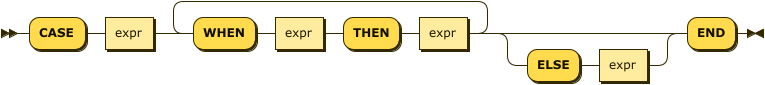
Simple case expressions allow for conditional matching within an expression. The evaluation process is as follows:
-
The first WHEN expression is evaluated. If it is equal to the search expression, the result of this expression is the THEN expression.
-
If it is not equal, subsequent WHEN clauses are evaluated in the same manner.
-
If none of the WHEN expressions are equal to the search expression, then the result of the CASE expression is the ELSE expression.
-
If no ELSE expression was provided, the result is NULL.
Example
The following example uses a CASE expression to categorize flights based on their departed-on date.
WITH flight AS (
[
{ "flight-id": "F101", "departed-on": "2025-12-01" },
{ "flight-id": "F201" },
{ "flight-id": "F301", "departed-on": "2025-12-02" }
]
)
SELECT
`flight-id`,
CASE `departed-on`
WHEN "2025-12-01" THEN "First flight"
WHEN "2025-12-02" THEN "Second flight"
ELSE "Unknown flight"
END AS category
FROM flight[
{
"flight-id": "F101",
"category": "First flight"
},
{
"flight-id": "F201",
"category": "Unknown flight"
},
{
"flight-id": "F301",
"category": "Second flight"
}
]Searched Case Expressions
searched-case-expr ::= 'CASE' ('WHEN' cond 'THEN' expr)+ ('ELSE' expr)? 'END'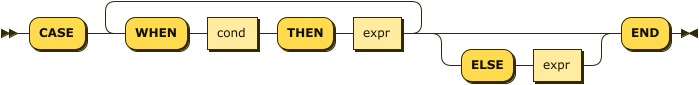
Searched case expressions allow for conditional logic within an expression. The evaluation process is as follows:
-
The first WHEN condition is evaluated.
-
If TRUE, the result of this expression is the THEN expression.
-
If not TRUE, subsequent WHEN clauses are evaluated in the same manner.
-
If none of the WHEN clauses evaluate to TRUE, then the result of the expression is the ELSE expression.
-
If no ELSE expression was provided, the result is NULL.
Example
The following example uses a CASE clause to determine whether a flight has departed.
It scans all flights.
If the flight has a departed-on date, it is provided in the result set.
If not, the result shows the default text "not-departed-yet".
WITH flight AS (
[
{ "flight-id": "F101", "departed-on": "2025-12-01" },
{ "flight-id": "F201" },
{ "flight-id": "F301", "departed-on": "2025-12-10" }
]
)
SELECT
`flight-id`,
CASE
WHEN `departed-on` IS NOT NULL THEN `departed-on`
ELSE "not-departed-yet"
END AS departed
FROM flight[
{
"flight-id": "F101",
"departed": "2025-12-01"
},
{
"flight-id": "F201",
"departed": "not-departed-yet"
},
{
"flight-id": "F301",
"departed": "2025-12-10"
}
]